According to the terminology used in medicine, the foot is the part of the leg located distally (remotely) from the center of the body. The anatomy of the human foot is quite complex and ideally performs the tasks assigned to the feet.
Foot anatomy
The main part of the functions is performed by arches, due to which the depreciation required to protect other joints, including the spine, from excessive loads occurs. An important role here is played by the cuboid bone.
The main elements of the foot are the bones of the skeleton, interconnected by joints, ligaments, tendons and muscles.
The role of the shock absorber is played by the arches of the feet - longitudinal and transverse. They are formed by bones, joints, muscles, tendons, making the leg flexible. Due to this structure, the load is distributed evenly between the first, fifth metatarsal bones and the heel.
Bone skeleton of the foot is formed of 3 departments:
- tarsus (7 bones arranged in two rows);
- metatarsus (5 short tubular bones);
- phalanges are the smallest bones of the fingers.
You can independently find where the cuboid bone is, in simple terms - from the outside of the foot from the heel, it will be the first towards the phalanges of the fingers. This is a fairly dense bone mass, and it is extremely difficult to break it.
Tarsal bones
Tarsus - the widest part of the foot, consisting of the talus, calcaneus, scaphoid, lateral, intermediate, medial sphenoid and cuboid bones.
- The talus, in other words, the heel bone. Connection with the scaphoid occurs through the head. The posterior process consists of two tubercles with a tendon.
- The calcaneus plays the role of a softener, a kind of springboard during movement. Despite the fact that this is the most massive formation, it is vulnerable and is often damaged. According to the anatomy of the heel, it is located under the talus, with which they are connected by a short process. Through the hillock located behind the calcaneus, the lateral and medial processes depart from the surface of the foot.
- The scaphoid bone. The structural element of the tarsus, located in the inner edge of the foot. In the medial section, the concave lower surface is tuberous, palpable through the skin. The joints are reduced with the talus and cuboid bones, forming the arch of the foot.
- The lateral bone is located in the upper outer part of the foot, helps a person to make maneuvering movements during cornering. The joint of the fibula connects to the lateral-ankle surface of the talus.
- The cuboid bone is located outside the lateral sphenoid bone, behind the base of the IV and V metatarsal bones and in front of the calcaneus.
- The sphenoid bones of the foot are in front of the scaphoid.
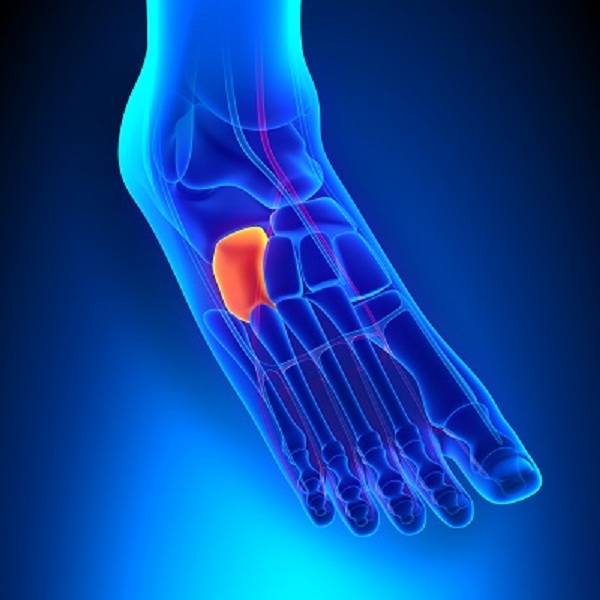
Communication with the metatarsal bones is due to the articular surface. Despite the fact that the cuboid bone is located in the outer part of the foot, its fractures separately from the joint are quite rare. Among the injuries of the skeleton, they make up 0.14%, foot bones - 2.5%.
Joint Features
The foot has a complicated anatomical structure with a large number of joints that form two or more bones. The main joint is the ankle, consisting of the tibia and tibia, with lateral outgrowths and the talus.
This joint is responsible for the main function of the foot - its mobility, the rest provide the necessary firmness and elasticity.
Intertarsal joints
- Ankle joint due to the lateral processes (ankles) together with the talus forms a kind of block. Protection is provided by the joint bag and ligaments, so that the ankle joint can produce posterior and anterior flexion movements.
- The subtalar joint is a less mobile joint between the calcaneus and the talus.
- The ram-calcaneo-navicular joint is formed by the bones of the tarsus. A ligament connecting the calcaneus and talus passes through the cavities of these joints.
- The heel-cuboid joint forms the articular surfaces of the cuboid and calcaneus. The joint is strengthened by a common bifurcated ligament, starting on the calcaneus.
- The wedge-shaped joint is formed by the articular surfaces of the sphenoid and scaphoid bones.
Judging even by the photo offered by the Internet, the cuboid bone is well located in the joint and it is not easy to damage it. However, this is possible if measures are not taken in time for the provision of surgical care, a person may begin to limp on one leg and even remain disabled.
Serious static and dynamic loads of the foot can withstand due to the anatomical features of the structure and the presence of a large number of elastic elements.
Calcaneo-cuboid joint
It is located between the articular surfaces of the cuboid and calcaneus. Movements are carried out only in one direction, despite the fact that the saddle joint. The capsule attaches to the edges of the articular cartilage and is pulled tight. The joint takes part in the movements of the previous joints and increases their amplitude. It is strengthened by the plantar, heel-cuboid and long plantar ligament.
Together with the ram-calcaneo-navicular joint forms one transverse joint of the tarsus.
Bone fracture
X-rays and other photos of the cuboid bone of the foot are required for a fracture, so that there is no doubt about the diagnosis.
With a fracture, pain occurs during turns of the foot inward and outward. Feeling the location of the injury brings great discomfort. Treatment involves a circular plaster cast for 5 weeks. To fully restore working capacity, it is required to wear an arch support for a year after the fracture.
Injury occurs due to the fall of heavy objects on the foot or a direct hit. If at the same time there is a scaphoid fracture with a subluxation, the defect becomes highly noticeable, which depends on the debris and the degree of displacement. The arch of the foot is sealed, the front section deviates inward or outward.
After an injury, you can’t step on your foot and walk for the first week, later you can dose the load. To fully restore motor functions, orthopedic shoes are worn throughout the year.