One of the important tasks solved by modern medicine is the prevention of pulmonary thromboembolism. This problem is relevant because of the danger of disruption of the circulatory system, and in the period after surgery or during pregnancy, the risk of such a pathology increases sharply. In addition, the prevention of pulmonary thromboembolism is relevant for a fairly wide range of people at risk. From year to year, several more or less interesting works on this pathology are published, and yet the question to this day does not have a universal answer. So, what are the most effective measures to prevent thromboembolism, drugs to prevent this condition are known? Let's try to figure it out.
What is it about?
Thromboembolism is a pathology in which the pulmonary artery is blocked by a blood clot. A blood clot can form in any blood vessel in the human body, but when separated from the place where it formed, the bloodstream carries a clot inside the body. At an unpredictable moment, such a blood clot can block any vessel. One of the most dangerous moments is the blockage of the pulmonary artery. As a rule, a clot that has formed in the right half of the heart or in the veins provokes this situation.
When blocking an artery, the lung tissue does not receive blood, and with it the flow of oxygen is blocked. This leads to either a heart attack or pneumonia, when tissue necrosis provokes inflammatory processes.
How to suspect?
At the national level, the need for the prevention of thromboembolism has been documented. An order dedicated to this issue, as well as affecting several other aspects of health care in our country, was recently issued by the Ministry of Health. However, it is no secret that prevention should begin with an educational program: the general population should be aware of the dangers of such a pathology, the causes that provoke it, as well as the symptoms suggesting that the danger is near.
It is possible to suspect a high probability of pulmonary thromboembolism if a person notices shortness of breath, weakness, fainting. In this state, the head is often dizzy, it hurts in the chest, and the syndrome becomes stronger when coughing, trying to breathe in deeper. The test shows a reduced pressure, accompanied by an increase in heart rate (indicator exceeds 90 beats / min). Swell on the neck, veins begin to pulsate. With thromboembolism, the patient coughs first dryly, then with a slight discharge of sputum, coughs up blood, at the same time the skin turns pale. The face, body in the upper half may acquire a bluish tint. General hyperthermia is possible. The severity of symptoms is determined by which particular artery was struck by a thrombus - if it is a relatively small vessel, some symptoms may manifest very weakly, while others are completely absent.
Where did the blood clot come from?
Many residents ask district doctors about whether it is possible to drink aspirin for the prevention of thromboembolism, but they often do not even try to understand why blood clots form. Of course, aspirin in some cases can show a good result, as it dilutes the blood, but it does not eliminate all the causes of thromboembolism. If you imagine where the blood clots come from, compare this with your lifestyle and diagnoses, you can understand what kind of cause is most likely to provoke a pathology. Based on this, preventive measures can already be taken. Thromboembolism after surgery is believed to have a rather high risk of development, therefore, this situation should be treated with utmost care, even if there are no other reasons for the development of the disease.
According to statistics, mainly blood clots form in the pelvic region, legs. Somewhat less often, the formation of a clot in the cardiac system, veins of the liver, kidneys or in the superior vena cava becomes the primary cause of blockage of the vessel . Having broken away from the vessel wall, gradually such a clot migrates and can reach the pulmonary artery. In some cases, there is a blockage at the same time two arteries - left and right.
Risk group
It is believed that the prevention of venous thromboembolism is most relevant if blood is characterized by a higher than normal rate of coagulation. This is often observed about oncology, and it does not matter in which organ the malignant neoplasm is localized. In addition, the likelihood of blood clots increases with a sedentary lifestyle. This can be if a person is in bed for a long time after a stroke, surgery, injury. Prevention and treatment of thromboembolism is important for the elderly, since age itself is a factor in ranking a person at risk. Also, those who are overweight are more likely to have problems.
Prevention and treatment of thromboembolism is relevant information for those who have already started thrombosis, and there is also reason to believe that there is a genetic predisposition to this pathology. If it is known that increased blood coagulability could be transmitted by inheritance to a person, if close relatives were diagnosed with varicose veins, then proper nutrition, prevention of thromboembolism are important aspects, the knowledge and following of which allows you to maintain health and quality of life longer.
What else to look for?
The prevention of thrombosis and thromboembolism is relevant for those with sepsis. This is a very serious disease, which is characterized by an infectious lesion of the blood, leading to malfunctioning of many internal organs and systems. No less dangerous is the condition of those who inherited blood diseases, including those associated with increased coagulation.
Be sure to know about the rules for the prevention of thrombosis and thromboembolism by those who have antiphospholipid syndrome. This is a pathological condition in which antibodies are produced against the cells of the body, including platelets, due to which the blood has the ability to clot. All this leads to an increased likelihood of blood clots, and the consequences of this process are unpredictable.
Hazardous factors
A general idea of the prevention of thromboembolism is necessary for those who have spent a long time without movement, suffered varicose veins or celebrated their sixtieth anniversary - age also leaves its mark on blood quality. The likelihood of developing the disease is among overweight people and those who lead an unhealthy lifestyle - they smoke, abuse alcohol, eat fatty foods and fast food.
Prevention of thromboembolism is necessary with the long-term use of diuretics, undergoing chemical therapy against cancerous tumors, during recovery from surgery, trauma, and also, if necessary, to be constantly under a venous catheter.
Where to begin?
Prevention of thromboembolism is primary and secondary. Primary - these are measures that need to be carried out among the risk group in the event that the diagnosis of thromboembolism has not been made. Secondary - these are measures aimed at preventing the recurrence of a crisis.
As part of the primary prevention of thromboembolism, comprehensive measures are taken to prevent the occurrence of blood clots in the veins. First of all, doctors' attention is focused on the vena cava inferior. Most relevant for people with a sedentary lifestyle. You should regularly use compression garments or bandage the patient's feet with elastic bandages. Even if a very long recovery period is expected, the prevention of postoperative thromboembolism suggests maximum activity as much as possible in the patient's condition. Bed rest is reduced, if possible, and regularly give the body physical activity, gradually increasing them. Similar measures are needed if the patient has suffered a heart attack, stroke.
What else is needed?
A modern approach to the prevention of thromboembolism in the postoperative period, as well as when a person is at risk, involves regular practice of therapeutic exercises. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe anticoagulants, under the influence of which blood coagulation decreases slightly. As a rule, they are prescribed if there is a high probability of complications.
Prevention of thromboembolism in the postoperative period may include additional surgical intervention. This is necessary if a section of a vein is revealed, abundantly filled with blood clots. With the consent of the patient, this element is removed from the body.
Alternatives
Good results are obtained using the cava filter. This measure of prevention of thromboembolism before or after surgery is relevant for those patients who have blood clots in their legs. The filter is a specialized trap that can pass blood, but retains clots. There are several varieties of such filters, they are somewhat different from each other in design features. Set a trap usually below the mouth of the veins of the kidneys in the vena cava. A patient with a filter regularly undergoes examinations to determine when the trap needs to be changed to a new one.
Pneumocompression of the legs can help. These are special cylinders that are put on legs, then inflated and lowered sequentially. Application of the method allows to reduce swelling, often accompanying varicose veins. Leg tissues receive more oxygen, nutrition improves, the body more efficiently dissolves blood clots that accumulate in the circulatory system.
It is important!
Preventive measures to reduce the risk of thromboembolism always involve a change in the patient’s lifestyle. If a person smokes, you need to completely abandon this bad habit. The use of alcoholic beverages is minimized. You will also have to start eating healthy, balanced foods.
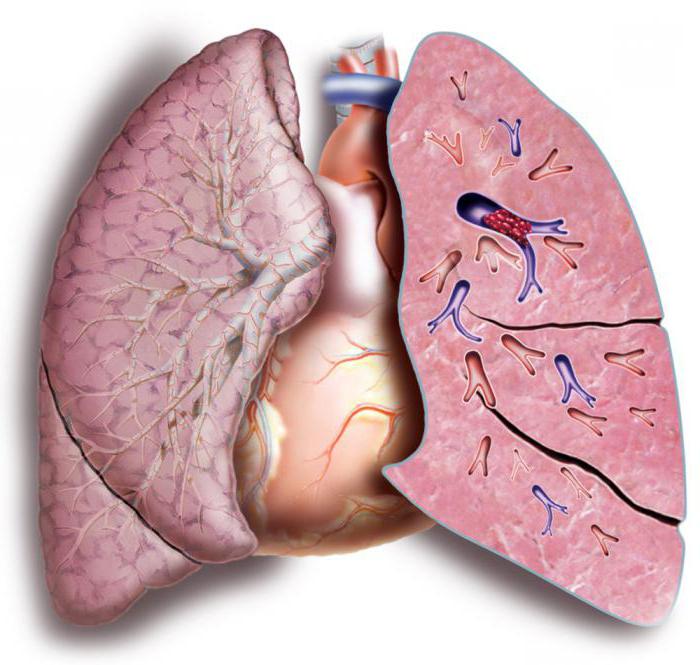
If thromboembolism has already taken place, then it is important to prevent relapse. These measures will accompany a person all his life, since each new blood clot is a very serious risk. In medicine, there are many cases of death of secondary thromboembolism. If the history contains a mention of such a situation, the patient is prescribed anticoagulants and set a filter trap. We’ll have to regularly go to the doctor’s examinations to check if it’s time to change the trap for a new one. The pills that the doctor will prescribe will also have to be drunk constantly, fully following the doctor's instructions. To cancel them or change as you wish is categorically unacceptable. Of course, you can’t smoke with a history of thromboembolism, drink alcohol, fried, fatty, smoked.
Low molecular weight heparins against thromboembolism
A good result in the prevention of thromboembolism can show calcium nadroparin. Drugs with this active component can not be used during the period of gestation, feeding. As far as it was possible to identify during clinical trials, calcium nadroparin can penetrate the placenta, it was also found in breast milk, which caused a rather severe restriction. The use of this medication activates the processes of leaching of calcium from the body. In addition, there is a double risk of bleeding than with other heparins.
An alternative is fragmentin. Medicines made on this active component do not affect the concentration of calcium in the patient's body. The drug is most widely used in Belarus and the CIS countries. Clinical trials have shown that Fragmin can be used even during gestation, when the choice of drugs is very limited. The use of the medication is associated with a minimal likelihood of hemorrhage. If the patient has artificial heart valves, if a shock condition is detected, it is recommended to resort to drugs based on Fragmin.
Prevention after surgery
Features of preventive measures directly depend on the reason for the operation and what organs it affected. There are three risk groups - low, medium, high. Thromboembolism is least likely if a short-term operation lasting no more than half an hour, accompanied by one risk factor, was performed. If the operation was completely without risk factors, then the low likelihood of thromboembolism is also characteristic of those patients who underwent a longer surgical intervention. The probability of death caused by blood clots in such conditions is less than a hundredth of a percent. To prevent even this small risk, it is necessary to start active movements as soon as possible, apply elastic compresses to the legs, wear special compression underwear, do pneumatic compression and electrical stimulation of the muscle tissue of the legs.
An average level of risk is characteristic of those patients who have revealed heart diseases, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as undergoing emergency gynecological operations. Patients who take oral contraceptives are at moderate risk. In this group, the probability of death in thromboembolism reaches one percent. Preventive measures include the use of frammin, clexane. These drugs begin to be taken even before surgery (a couple of hours), then the course is continued during the rehabilitation period from seven to ten days.
Hazard level: maximum
Those who are considered to be at high risk should be most attentive to prevention. These are people who underwent emergency, planned major surgical interventions. There is a high probability of developing thromboembolism with caesarean section. Cancer patients suffering from extragenital pathologies, thrombosis, and thrombophilia are included in this group. If there is a history of pulmonary thromboembolism, the patient here is automatically assigned to the high-risk group.
For people from these categories, the probability of death caused by thromboembolism of the arteries of the lungs reaches ten percent. To prevent a negative outcome, it is necessary to take measures to accelerate the flow of blood in the body. For this, anticoagulants are usually prescribed in a dose doubled in comparison with the medium-risk group. It is important that the doctor selects the drugs based on the data obtained from the patient’s analysis. It is unacceptable to neglect the doctor's recommendations related to preventive measures, and in the first place it is important to regularly use the prescribed medications.
Prevention: Surgical Method
Pulmonary thromboembolism can be prevented in a rather radical way - by operation. There are several methods that can effectively prevent the development of the disease. In some cases, the trunk veins are ligated below the femoral level. Many patients, especially recently, are equipped with trap filters that can quite effectively block possible complications if there is already a history of thromboembolism. Endovascular and some other high-tech surgical techniques allow thromboembolectomy, which also shows a high level of effectiveness with an increased likelihood of pathology. Finally, they resort to the method of plication, treating the vena cava in the lower extremities.
Cava filter: when is it necessary?
The filter trap seems to many to be perhaps the best option to prevent pulmonary thromboembolism. And yet it is impossible to resort to it in all cases without exception. There are a number of indications in which you can implant such a filter. Indications consider:
- inability to use anticoagulants;
- pulmonary embolism;
- a rather large, prolonged, floating, blood clot of the ileocaval type;
- increased likelihood of relapse provoked by deep vein thrombosis;
- the period of bearing a child;
- relapse of pulmonary embolism;
- proximal spread of phlebothrombosis, which is not prevented by the anticoagulants taken.
Prevention: research and their effectiveness
, . – . , , . , . , , , . . , , .
As can be seen from medical statistics, conducting regular studies using the most advanced ultrasound devices, as well as installing filter traps when detecting increased risk factors for thromboembolism, gives a significantly better result than regular ultrasound, accompanied by conservative therapy. In addition to implantation, studies have also shown improved results and a decrease in the annual mortality rate for ligation of a vein above the level of a dangerous thrombus, with crossectomy.
Specialists pay special attention: the most important element is modern diagnostics, including regular ultrasound testing, if there is a chance of developing thromboembolism of the arteries of the lungs.