Ganglia (aka ganglia) are a collection of special cells. It consists of bodies, dendrites and axons. They, in turn, belong to nerve cells. Also, nerve nodes include auxiliary glial cells. Their task is to create support for neurons. As a rule, the nerve ganglia are covered with connective tissue. These clusters are found not only in vertebrates, but also in some invertebrate animals. Connecting with each other, the nerve nodes create complex structural systems. An example would be chain or plexus structures. Further in the article it will be described in more detail what are the nerve nodes, how the interaction between them occurs. In addition, a classification and description of the main species will be given.
Vertebrate animals
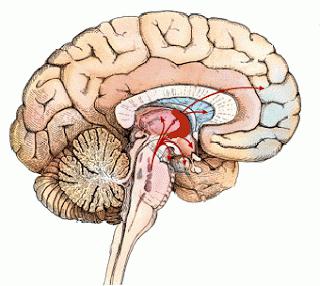
The ganglia that exist in these individuals have some features. So, they do not enter the central nervous system. Some call them basal ganglia. However, the term "core" is considered the most correct. Nerve nodes and the system that they form are the connecting elements between the components of the nervous system. They pass impulses and control the work of certain internal organs.
Classification
All ganglia are divided into several types. Consider the main ones. The concept of "spinal ganglion" combines sensory (afferent) elements. The second type is autonomous elements. They are located in the corresponding (autonomous) nervous system. The main view is basal. Their components are neural nodes that are in white matter. It is found in the brain. The work of neurons is to regulate certain body functions, as well as to assist in the implementation of nervous processes. There is also a vegetative type. It is a single nerve node. This element belongs to the autonomic nervous system. These nodes run along the spine. Vegetative ganglia are very small. Their size can be less than a millimeter, and the largest are commensurate with peas. The objective of the autonomic ganglia is to regulate the functioning of internal organs and the distribution of impulses.
Comparison with the term "plexus"
In books, the concept of "plexus" is often found. It can be taken as a synonym for the word "ganglia". However, the plexus is called specific nerve nodes. They are present in a certain amount in a closed area. And the ganglion is the area of connection of synaptic contacts.
Nervous system
From the point of view of anatomy, two types are distinguished. The first is called the central nervous system. These include the brain and spinal cord. The second type is a combination of nodes, nerve endings and the nerves themselves. This complex is called the peripheral nervous system.
The nervous system is formed by the neural tube and ganglion plate. The brain with sensory organs is referred to the cranial part of the first, the spinal cord to the trunk. The ganglion plate forms the spinal, autonomic nodes and chromaffin tissue. Nervous tissue exists as a component of the system that regulates the corresponding processes of the body.
General information
Nerve nodes are a union of nerve cells that extends beyond the borders of the central nervous system. There are vegetative and sensitive species. The latter are located next to the roots of the spinal cord and cranial nerves. The shape of the spinal node resembles a spindle. It is surrounded by a connective tissue sheath. It also penetrates the node itself, while retaining blood vessels in itself. Nerve cells located in the spinal node are light, large, their nuclei are easily distinguishable. Neurons form groups. The components of the center of the spinal node are the processes of nerve cells and the layer of endoneuria. The dendritic processes begin in the sensitive area of the spinal nerves, and end in the peripheral part where their receptors are located. A common case is the transformation of bipolar neurons into pseudo-unipolar ones. This occurs during their maturation. From the pseudo-unipolar neuron comes out the appendix, entwining a cell. It is differentiated into afferent, another name is "dendritic", and efferent, otherwise - axonal, part.
Dendrites and axons
These structures cover the myelin sheaths of which the neurolemmocytes constitute. Nerve cells of the spinal node surround oligodendroglia cells, which have such names as mantle gliocytes, sodium gliocytes, as well as satellite cells. These elements have very small round cores. In addition, a capsule of connective tissues surrounds the membrane of these cells. Its components differ from other oval-shaped cores. The biologically active substances contained in the nerve cells of the spinal node are acetylcholine, glutamic acid, substance P.
Vegetative, or autonomous, structures
Autonomic nerve nodes are located in several places. Firstly, near the spine (there are paravertebral structures). Secondly, in front of the spine (prevertebral). In addition, autonomous nodes are sometimes located in the walls of organs. For example, in the heart, bronchi, and bladder. Such ganglia are called intramural. Another species is located near the surface of the organs. Preganglionic nerve fibers connect with autonomous structures. They possess processes of neurons from the central nervous system. Autonomic clusters are divided into two types: sympathetic and parasympathetic. For almost all organs, postganglionic fibers are obtained from cells that can be in both types of vegetative structures. But the effect that neurons have is different depending on the type of clusters. So, a sympathetic action can enhance the work of the heart, while a parasympathetic one slows it down.
Structure
Regardless of the type of autonomous unit, their structure is almost identical. Each structure is covered by a connective tissue membrane. In the vegetative nodes, there are special neurons called "multipolar". They are distinguished by an unusual shape, as well as the location of the core. There are neurons with several nuclei and cells with an increased number of chromosomes. Neural elements and their processes are enclosed in a capsule, the components of which are satellite glial cells. They are called mantle gliocytes. On the upper layer of this membrane is a membrane surrounded by connective tissue.
Intramural structures
These neurons, together with the pathways, can constitute a metasympathetic region of the autonomic nervous system. According to the histologist Dogel, three types of cells stand out among the intramural types of structures. The first include long axon efferent elements of type I. These cells have large neurons in which the dendrites are long and the axon is short. Equidibular afferent nerve components are characterized by long dendrites and an axon. And associative neurons connect the cells of the first two types.
Peripheral system
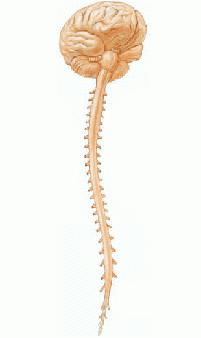
The task of nerves is to provide communication to the nerve centers of the spinal cord, brain and nerve structures. Elements of the system interact through connective tissue. Nerve centers are areas responsible for processing information. Almost all considered structures consist of both afferent and efferent fibers. A set of fibers, which is, in fact, a nerve, can contain not only structures protected by an electrically insulating myelin sheath. They also contain those that do not have such a “coating”. In addition, nerve fibers are separated by a layer of connective tissue. It is distinguished by friability and fiber. This layer is called endoneurium. It contains a small number of cells, its main part is collagen reticular fibers. In this tissue are small blood vessels. Some bundles with nerve fibers are surrounded by a layer of another connective tissue - perineurium. Its components are sequentially located cells and collagen fibers. A capsule enveloping the entire nerve trunk (called epineurium) is formed from connective tissue. It, in turn, is enriched with fibroblast cells, macrophages and fat components. It contains blood vessels with nerve endings.