Microsoft Excel has powerful tools that can help solve difficult computing problems. One of the most used tools in this set is the IF function.
Function value
When working in Excel, you need to understand the meaning of the IF function in order to construct the correct syntax queries. Thanks to its algorithm, some logical comparison is performed, depending on the results of which one of two actions will be performed.
In simpler words, the function "IF" in the case of the true value of some expression, performs one action, in the case of a false - another. At the same time, the actions can be either an explicit value or a certain function, including “IF”. Due to this, in the "Excel" function, the "IF" allows a branch when performing a certain algorithm of actions in solving various problems.
IF syntax
A simple description of most syntactic constructions is one of the main advantages that Excel is famous for. The function "IF" also refers to their number - after the keyword in brackets, the condition is alternately indicated, the action is true, and then false. In a schematic form, it looks like this:
IF (log_expression; [value_if_true]; [value_if_false]);
Nesting
One of the features that distinguishes the IF function is nesting. That is, inside one design, there may be another one, the value of which depends on the overall result of the query. In addition to the function itself, there may be others inside the IF. But in the first case, this component can be located in any of the three parts of the syntactic construction.
Several conditions
When working with complex tasks, the IF function is used with several conditions, however, at this stage, most users have a problem. This is due to the specific task of the multi-conditional algorithm. In Excel, the function "IF" checks only one comparison operation in a logical expression, that is, it will not work to use conjunction or disjunction. To check several conditions, you must use the nesting property.
To understand how to set several conditions in the "IF", it is convenient to use an example. Let it be necessary to check whether the number in cell "A1" is in the specified interval - from 5 to 10. As you can see, in this case it is necessary to check two conditions, checking for validity of comparison with two values - 5 and 10. To implement this example in "Excel", you must write the function in the following form:
= IF (A1> 5; IF (A1 <10; "falls into the range"; "falls outside the range"); "falls outside the range")
To avoid repeated repetition of the displayed phrase, it is worthwhile to apply the nesting principle again, choosing the check of the return of the function values as arguments, depending on which to output, or at the very beginning use the "AND" function, combining all the conditions in it at once. This approach will complicate the understanding of the written design with a small level of nesting, but with a significant number of conditions, this approach will be more optimal.
Special function options
It is worth noting that the “IF” function allows you to leave one or more of your parameters blank. In this case, the results will depend on which arguments were omitted by the user.
If you leave a void in place of a logical expression, the result of the function will be the execution of the action responsible for the false execution of the algorithm. The reason for this is the fact that the program associates an empty space with zero, which in a logical language means "FALSE". If you leave one of the values responsible for the execution in the case of truth or falsehood, then when it is selected, the result will be "0".
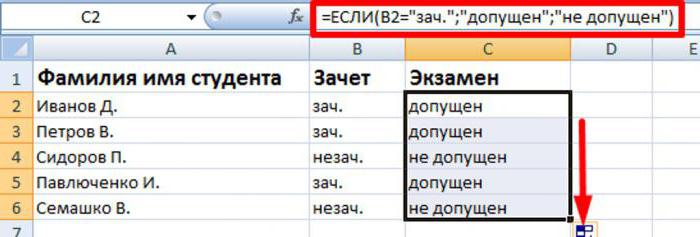
Separately, it is worth noting the case when instead of a logical expression, not a construct was introduced that returns the value "TRUE" or "FALSE", but a certain set of characters or a link to the cell. In the case when an expression is written as a parameter containing something other than a numerical value or logical words, this will cause an error when executing the function. If you specify the address of the cell or register a certain number / logical value, the result will determine this content. When the number 0, the word "FALSE" or the void is written in the cell or condition, the result will be a false execution of the function. In all other cases, a true action scenario will be executed.
When working with the English version of Excel, it is necessary to take into account the fact that all functions are also written in English. In this case, the function "IF" will be written as IF, but otherwise the syntax and operation algorithm will remain the same.
What you should pay attention to
"Excel" allows you to use up to 64 of the embedded functions "IF" - this amount is enough to solve almost all problems, however, even this small number often becomes a problem for the user. There are several reasons for this: when creating a request, it is easy enough to make a mistake in writing the formula - according to statistics, every slightest inaccuracy in 25% of cases leads to an incorrect result, which is a fairly large indicator.
Another disadvantage of IF's large nesting is low readability. Despite the color highlighting by the program of some parts of the request, even several nested functions, which are very difficult to parse. Thus, if after some time you have to return to the design or start working with someone else’s request, it will take a lot of time to understand the record. In addition, each function has its own pair of brackets, and accidentally putting it in its place, you have to look for an error for a long time.
Examples
To consolidate the understanding, it is worthwhile to consider in practice how the IF function works in Excel. The examples below demonstrate all the main ways to use it.
The simplest example for parsing a function is comparing two numbers. For variability, we set the values of two numerical variables in cells A1 and B1, which we will compare with each other. To solve this problem, use the following record:
= IF (A1 = B1; "numbers are equal"; "numbers are unequal").
In this case, if there are identical values in both cells, the result will be a record of "numbers are equal", in all other cases - "numbers are unequal".
To consider the operation of a conditional operator with several conditions, as an example, we can use the number of solutions of the quadratic equation. In this case, the check is performed according to the discriminant - if it is less than zero, then there are no solutions, if it is zero - it is one, in all other cases - there are two roots. To record this condition, it is enough to make a request of the following form:
For those who want to better understand all the possibilities that the IF function has , the examples in Excel are in the help section, which describes in detail the course of solving each of them.