The carotid artery is considered one of the largest circulatory organs in humans. This vessel belongs to a large circle of blood circulation. It consists of paired elastic tubular formations that, with the help of branches, deliver blood to the brain that nourishes it with oxygen and necessary substances. Also, these vessels are connected to the neck and eyes.
The carotid artery has a vulnerable location. At any moment, a mechanical effect can be exerted on it. The body, receiving a signal of an increase in pressure, reacts, lowering it. At the same time, the heart rate decreases, due to which a fainting condition may occur. With sufficiently intense exposure, a fatal outcome is likely.
Interruption of blood circulation in an artery can occur when it becomes clogged or the slightest weakening of blood flow in it. Sometimes a person does not even realize the presence of such a pathology as the tortuosity of the carotid artery. Meanwhile, this condition can cause ischemic attacks and lead to a stroke. We will talk about this problem in detail in the article.
The location of the carotid artery in humans
When a critical situation arises, skills in determining the heartbeat of the carotid artery can save a person’s life. One of a pair of arterial vessels is located on the left side of the neck. It is more extended than the right one, has a length of up to sixteen centimeters and starts from the brachiocephalic trunk. The vessel, located on the opposite side, comes from the aortic arch. Its size varies from six to twelve centimeters.
The artery itself is located in the direction from the thoracic to the line of the trachea and esophagus. At the same time, it branches and then passes opposite the processes of the vertebrae of the neck to the frontal section of the human body. There are external and internal cerebral blood vessels.
External carotid artery
This organ branches into four departments: anterior, posterior, medial and terminal. The functions of the external carotid artery are the provision of blood movement in the thyroid and salivary glands, muscles of the face and tongue, occipital and parotid regions, upper jaw and temporal part. Consider the internal carotid artery.
Internal carotid artery
This is the posterior component of the artery. Where is she located? It is located along the cervical region, from which it goes to the human skull from the side of the temple. The main function of this organ is the nutrition of brain cells.
The tortuosity of the internal carotid artery within the limits of physiology is in every healthy person. The structure of this vessel reproduces the relief of the cervical spine and the inner part of a certain part of the skull. This form of the blood organ does not affect complex symptoms. With pathological tortuosity of the internal carotid artery, changes in the blood supply to the brain occur.
Performance measurement
To determine the degree of blood movement in the carotid artery, it is necessary to be examined using duplex and radioisotope scans, in which the following indicators are determined:
- the size of the space of the blood organs;
- plaque formation;
- the number of blood clots, their absence;
- the presence of tissue damage;
- aneurysms;
- the degree of deformation of the tubular formation.
The norm of the level of blood flow in the cerebral organs is 55 milliliters per 100 grams of the brain tissue structure. The pathological tortuosity of the carotid arteries diagnosed by comprehensive examinations with a significant degree can serve as a reason for surgical intervention.
Causes of pathology
Most often, this physiological feature is transmitted genetically. The formation of tortuosity of the carotid artery is due to the dominance of elastic fibers over collagen. As a result, wear occurs, the walls of the vessels become deformed and become thin. Atherosclerosis can also be the cause of the occurrence. With this disease, plaques form, due to which the lumen in the vessels narrows, which leads to improper functioning of the blood circulation.
Curvature of the carotid artery is often detected by a preventive study. As a rule, initially it is asymptomatic, but subsequently the patient may experience transient disturbances in the circulation of the lymph of the brain, leading to a micro stroke. It is very important to diagnose the cause in time.
Pathology, its types
Usually there is a pathological tortuosity of the internal or common carotid artery. Perhaps the development of the pathology of tortuosity from two sides. The following types of deviations exist:
- S-shaped tortuosity of the carotid arteries. The deformation of the vessel occurs due to an increase in the size of the artery. Usually this does not cause problems, it is diagnosed by chance during an examination for prevention. Over time, the bend can transform into an inflection, which further leads to impaired blood movement.
- Kinking. The carotid artery is bent at an acute angle. Often this deformation occurs at birth. With its presence, a person from an early age suffers from problems with blood circulation of the brain. In other cases, kinking develops from the S-tortuosity of the carotid arteries with a prolonged course of hypertension and atherosclerosis in the vessels. In this situation, instability occurs in the blood circulation of the brain with pronounced signs of nausea, vomiting, pain in the head.
- Coiling. The artery is looped. In this case, the vessel is bent smoothly, forming loops. The blood flow in these parts of the artery is slowed down, sometimes very much, due to which sudden attacks can occur. An unforeseen condition occurs due to such a factor as a pressure indicator.
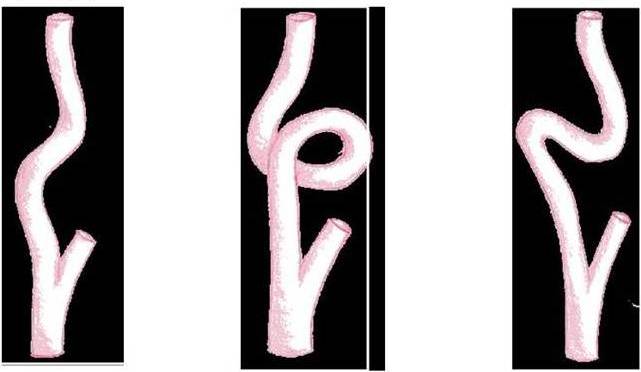
Signs of tortuosity of the carotid artery
The described pathology has the following clinical manifestations:
- different in intensity intense headaches;
- sensation of unpleasant tinnitus, burdens in the head;
- sudden fainting, ripples in the eyes;
- cyclical occurrence of problems with the processes of coordination of movements and balance;
- impaired cognitive function, weakening of the hands.
The identification of pathological tortuosity of the carotid arteries is complicated by the similarity of symptoms with other vascular diseases.
Pathology treatment
Is it possible to fix this problem? Unfortunately, at the moment, the pathology of the artery can be eliminated only with the help of surgical intervention. The operation is prescribed for significant violations in the movement of blood through the vessels.
In this case, angioplasty and stenting are performed. This is a rather complex process in which the vessel is straightened to restore its patency and remove the excess affected area. When the prosthesis is installed - in order to create an obstacle for relapse - the stent remains inside the artery. After surgery, in most cases, negative symptoms disappear without a trace.
Preventative measures
To prevent defects in the tissues of the walls of the blood cerebral vessels, it is necessary:
- observe the level of cholesterol, do not eat foods that provoke its increase;
- get rid of bad habits, especially smoking;
- control weight, perform physical exercises.
If the vessels are tortuous, it is recommended to avoid head bumps and heavy lifting. Manual therapy treatment methods and professional sports activities are contraindicated.