Hartmann's surgery is performed as a treatment for colon cancer. In most cases, it is the surgical method of treating the disease that is not only the most effective, but the only one, since chemotherapy for cancer that progresses in this area does not give the desired results.
Indications for the operation
Hartmann type surgery is indicated for debilitated and elderly patients with a diagnosis of cancer of the sigmoid colon or rectosigmoid region. There are other reasons why a doctor may schedule a Hartmann operation:
- complicated obstruction of the named areas (in most cases, food does not move along the intestines at all);
- perforation (through violation of the intestine);
- inversion of the sigmoid colon in case of complication of the condition of gangrene or peritonitis (lengthening of the intestine, deformation of its mesentery).
It is performed, as a rule, according to emergency indications, for example, with the manifestation of tumor decay or bowel obstruction.
Hartmann's Operation: Stages
Most patients undergo only its first stage. The next stage, with a favorable recovery period, is carried out only after six months.
Hartmann's operation, the description of which was provided by B. Petrov, is divided into two stages. It is used to treat the descending and transverse colon parts of the intestine.
So, the whole operation consists of the following steps:
- This stage was described by B. Petrov, who gave him the name “obstructive resection”. Very often, patients diagnosed with cancer are only given this procedure. It consists in the removal of a certain section of the intestine, on which the tumor is located. After this, crosslinking of the lumen of the distal segment occurs. This is done tightly, and the lumen itself is left in the abdominal cavity. The proximal end of the operated intestine is displayed by the surgeon on the abdominal wall from its front. This conclusion is called a colostrum, which will be described in more detail below.
- The second stage, with a favorable course of the rehabilitation period, is carried out not earlier than two months later, in some cases even after six months. It consists in restoring the continuity of the colon with end-to-end anastomosis . The colostomy is removed. Side-by-side anastomosis is possible, but in most cases, surgeons reject it.
Preparing the patient for surgery
First of all, the procedure for preparing the patient for its implementation is carried out. Since they usually make her sick and debilitated, it is necessary to conduct a series of examinations, as well as general strengthening treatment, so that a person can undergo surgery without fatal outcome. Used for this means, the action of which is aimed at enhancing cardiac activity, regulating the gastrointestinal tract, possibly blood transfusion, as well as the appointment of a large number of vitamins and a special diet.
Hartmann's operation: technique
For surgery, the patient is laid on his back. The abdominal cavity is revealed by the lower middle section from the pubis and 5 cm (sometimes slightly less) above the navel. After this, the patient is transferred to the position of Trendlenburg (the patient's head and shoulder girdle are located below the pelvic region). Next, the so-called mobilization of the sigmoid colon is carried out, for this purpose a towel is usually used. A certain amount of novocaine (about 250 ml) is usually injected into the root of the mesentery, as well as under the peritoneum of the Douglas pocket. Now an audit is being carried out and the localization of the tumor and its other characteristics are being specified. The sigmoid colon, on which the operation is performed, needs to be taken out into the wound and taken to the right side closer to the midline. The mesentery is stretched. Next, scissors are used to cut the outer sheet of the peritoneum. This is carried out in the place where the root of the mesentery is located. Dissection is carried out along the entire length of the loop, which will subsequently be removed. After this, the intestine is diverted outward, and the dissection of the inner sheet of the peritoneum occurs. The second and third arteries intersect at the site that was previously located between the clamps. This place is characterized by a departure from the inferior mesentery artery. Then it is tied with silk thread. The surgeon carefully monitors that the left artery is preserved, if possible, the doctor also preserves the upper and rectal arteries.
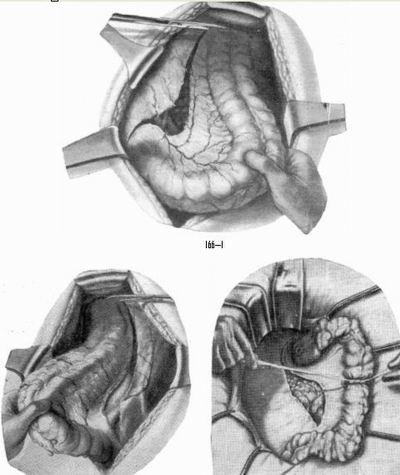
The mesentery is also clamped on both sides and intersects between the instruments, after which the vessels passing inside it are additionally bandaged.
In the event that the removal of the upper ampullar section occurs, the artery of the rectum, which is located at the very top, is bound without fail.
Clips are applied in the following places:
- over the affected area of the intestine;
- upper ampullar segment of the rectum.
Between these clamps, the affected intestine is removed with a sharp scalpel. This happens within healthy areas. The end of the intestine is sutured tightly. Catgut and silk threads are used for this.
Postoperative period
During this period, the following actions are performed:
- Through special tubes three times a day, the intestine is washed. A weak solution of antiseptics is used for this , the appointment of which the doctor makes a decision on the basis of analyzes.
- Within five days, antibiotics are administered.
- A special diet is prescribed, during which you can take exclusively liquid food.
- The doctor prescribes taking medications that help stool retention.
Intestinal lavage tubes are removed after 7–9 days immediately after surgery.
After 3-6 months of the postoperative period, provided its favorable course, intestinal continuity can be restored, as well as the elimination of the unnatural anus.
Possible complications after surgery
The main complication, which can be very dangerous for the patient’s health, is bleeding. It can occur both during the operation and after it.
After surgery, shock may occur, which also threatens the patient's life. Statistics confirm that most often the operated patients die within one to two days after the operation.
The most common complication is infection entering the wounds. To avoid this, especially careful preparation of the intestine for surgery is required in order to save the patient from the need to defecate in the first days of the postoperative period. If, due to the narrowing of the intestine, it is not possible to remove its contents, then the operation occurs in two stages, which were described in the first half of the article.
Postoperative procedures
During rehabilitation, urinary retention can be observed , and complaints from patients, as a rule, are not received. Urine is excreted artificially, and this happens only 10 hours after the operation is completed. The procedure is carried out at least three times a day. Ignoring this can lead to the fact that the bladder simply stretches, tilts backwards and, of course, will lose the ability to contract.
Instead of a conclusion
The effectiveness of the operation is affected by many factors, in particular, the condition of the patient before the operation, the timing of the surgical intervention, the choice of the correct method of conducting the operation. But despite this, in many cases, Hartmann’s colon surgery may be the only treatment.