Spirometry is designed to assess the condition of the human lungs. The procedure pursues a number of clinical goals, including evaluation, training and diagnostic. This study is intended to identify lung pathologies of various origins, monitor the patient's condition and evaluate the therapeutic effectiveness of the treatment. In addition, spirometry is performed to teach a person the correct breathing technique. The scope of this type of research is quite wide. In this article we will consider the procedure for spirometry, indications, contraindications and features of its use.
What is the FEV1 norm, we will consider in this article.
Indications
The human respiratory system consists of three main elements:
- Airways that allow air to pass into the lungs.
- Pulmonary tissue that promotes gas exchange.
- The chest, which is essentially a compressor.
A malfunction in at least one of these elements inhibits the functioning of the lungs. Spirometry allows you to evaluate respiratory performance, diagnose existing pathologies of the respiratory tract, characterize the severity of the disease and understand whether the prescribed therapy is effective.
The norm of lung volume is of interest to many.
Indications for the appointment of spirometry are:
- Respiratory diseases of a regular nature.
- Chronic cough, shortness of breath.
- In addition to other airway examinations for the diagnosis of pulmonary pathologies.
- Search for the causes of failure in gas exchange processes in the body.
- Risk assessment of prescribed therapy in the treatment of lungs and bronchi.
- Identification of signs of airway obstruction (in the case of smoking patients) in the absence of severe symptoms of this pathology.
- General characteristics of a person’s physical condition. What is the volume of maximum ventilation, consider below.
- In preparation for surgery and lung examinations.
- Diagnosis of the early stages of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, development monitoring and evaluation of further prognosis.
- Determining the degree of damage to the respiratory function in tuberculosis, bronchial asthma, bronchiectatic disease, etc.
- Diagnosis of restriction.
- Allergic reactions (especially those that are asthmatic).

All of the above cases are the reason for the appointment of spirometry. This type of research is not ubiquitous, many simply have no idea about it. However, it is very popular in such medical fields as allergology, pulmonology and cardiology. Together with spirometry, the patient can be referred to dynamometry, which determines the strength of the pulmonary muscles. Peak expiratory flow rate is also detected here.
The main value of spirometry, otherwise called the study of the function of external respiration or VFD, plays in the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. Experts advise to take a lung ventilation test regularly if the patient has one of the above pathologies. This will help prevent the occurrence of concomitant complications.
The table of normal spirometry indicators is presented below.
general information
The study of HPF is carried out using a spirometer. This is a special device that is capable of reading lung parameters during a functional examination. With its help, it is also possible to stimulate respiratory function. This is especially true for patients who have undergone surgery on the lungs and have certain problems with the work of the respiratory system.
Types of spirometry
Spirometers come in many forms, including:
- Computer. Equipped with ultrasonic sensors. It is called the most hygienic spirometer. It has high accuracy indicators, since it has a minimum of internal parts.
- Plethysmograph. This is a special camera where the patient under examination is located, and special sensors transmit indicators. This type of spirometer is considered the most accurate at the moment.
- Water. It does not apply to ultra-precise spirometers, however, the measurement range is quite wide.
- Dry mechanical. The device is quite small, while it can read information at any position of the patient. The range of action is quite small.
- Stimulating or incentive.

The methods of the procedure are also different. Respiration can be examined at rest, or forced expiration is assessed, as well as ventilation of the lungs to the maximum possible. The norm of lung volume is indicated as average. There is also such a thing as dynamic spirometry, which shows the functioning of the lungs at rest and immediately after physical exertion. Sometimes spirometry is used with a test for a drug reaction:
- Test with medicines - bronchodilators, such as Ventolin, Salbutamol, Berodual, etc. Such medications have an expanding effect on the bronchi and help to detect spasm in a latent form. Thus, the accuracy of the diagnosis is increased and the effectiveness of the therapy is evaluated. It is important to understand that obstructive pulmonary disease leads to a change in the flow-volume loop.
- Expert provocative test. It is carried out to clarify the asthmatic diagnosis. Such a check is able to detect hyperreactivity and an emerging spasm in the bronchi. The test is performed using methacholine, which is inhaled by the patient during spirometry. In the spirometry table, normal values are indicated in great detail.
Additional study of diffusion function of the lungs
Modern spirometric devices allow an additional study of the diffusion function of the lungs. This applies to clinical diagnostic methods. The study involves evaluating the qualitative characteristics of the oxygen entering the blood and the carbon dioxide emitted during inhalation and exhalation. If diffusion is reduced, this is a sign of serious pathologies in the function of the respiratory organs.
In the field of spirometry, there is another important study called bronchospirometry. This examination is carried out using a bronchoscope and allows you to evaluate the lungs and external respiration separately. With bronchospirometry, anesthesia should be administered. The examination helps to calculate vital capacity, minute lung capacity, respiratory rate, etc.
Preparation and conduct
To obtain the most accurate results of the study, it is important to properly prepare for spirometry, especially when performing the procedure on an outpatient basis. The study of forced expiratory volume is carried out on an empty stomach in the morning, or at another time, but with the condition of skipping meals. If this is not possible, then it is recommended to eat something non-greasy in a few hours before the procedure.
Recommendations
There are other recommendations for preparing for spirometry, namely:
- Stop smoking before the procedure.
- Do not drink tonic drinks on the eve of the examination.
- Alcohol consumption before spirometry is also prohibited.
- Sometimes you may need to stop taking certain medications.
- Clothing during the procedure should not hamper movement and interfere with breathing.
- Before the procedure, the doctor must measure the height and weight of the patient, as these indicators are important for evaluating the results of the study.
- Before starting the procedure, you must be at rest for about 15 minutes, so you should come in advance. Breathing should be calm.
Spirometry is performed on an outpatient basis. Different methods and types of research suggest different sequences of actions. The algorithm of steps during the examination can also be influenced by the patient's age and general health. If we are talking about spirometry in a child, then a prerequisite is the creation of comfortable conditions so that the child does not feel fear and excitement. Otherwise, indicators may be blurred.
Standard conditions
Standard conditions for spirometry:
If the patient does not have information about his height and weight, then the doctor takes the necessary measurements. A special disposable mouthpiece is put on the device before starting the procedure.
Patient information is entered into the spirometer program.
The doctor gives explanations on how to breathe during the study, how to properly inhale as much as possible. The position of the patient should be with a flat back and a slightly raised head. Sometimes spirometry is performed in a lying or standing position, which is mandatory in the program. The nose is clamped with a special clothespin. The patient's mouth should fit the mouthpiece tightly, otherwise the performance may be underestimated.
The study begins with a phase of calm and even breathing. At the request of the doctor, a deep breath and exhalation is performed with maximum effort. Next, the air velocity is checked with a quiet exhalation. To get the full picture, the breathing cycle is carried out several times.
The duration of the procedure is no more than 15 minutes.
Indicators and norm FEV1
Spirometry provides data on many indicators that have certain standards. Interpretation of the results of the study makes it possible to identify pathologies in the respiratory system and prescribe the correct therapy. The main indicators of spirometry include:
- JELL. This is nothing but the vital capacity of the lungs, which is calculated by the difference between the volume of inhaled and exhaled air. This is an actual indicator. There are other indicators besides FEV1.
- FVC. Actual lung capacity. It is also determined by the difference between the volume of inhaled and exhaled air, however, the exhalation in this case should be forced. The norm is 70-80% VC.
- Rovd. This is the reserve inhalation volume. Determines the amount of air that a patient can inhale after a standard breath. Norm 1.2-1.5 liters
- Rovyd. Reserve expiratory volume. This is the volume of air inhaled after a standard exhalation. The norm is 1.0-1.5 liters.
- OEL or total lung capacity. Normally, it is 5-7 liters.
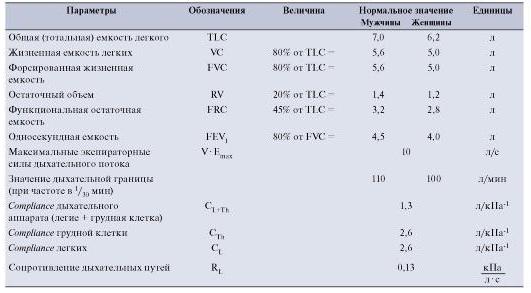
- Norm FEV 1. The volume of exhaled air at maximum boost in the first second. The norm is more than 70% FVC.
- Tiffno Index. Designed to determine the quality of patency of the respiratory system. Norm 75%.
- Pic. Exhaled air volume. Norm - more than 80% of FEV1.
- MOS. Instant space velocity. This is the rate at which airflow is exhaled. The norm is considered more than 75%.
- BH or respiratory rate. The norm is 10-20 breathing maneuvers per minute.
There are certain features of spirometry in children. The first is age; the child should not be younger than five years old. This limitation is due to the fact that at a younger age the child is not able to complete a correct exhalation, which will reduce performance. Starting from the age of nine, a child can undergo research as an adult. Before this age is reached, it is important to create a comfortable atmosphere for the baby with the use of toys and friendly treatment. For this reason, spirometry in young children should be performed in special centers specializing in pediatrics.
Before the procedure, it is important to explain to the child how to inhale and exhale. Sometimes pictures and photos are used for clarification. The specialist should carefully monitor that the child’s lips fit tightly around the mouthpiece.
Deciphering the results
The indicators obtained during spirometry are compared with the norm taking into account gender, weight and age. The survey conclusion is a graph with interpretation of indicators. An explanation of the results can be given by the attending physician.
The following data is decrypted:
- Inhaled air volume in milliliters.
- Exhaled volume after the deepest breath.
- Exhaled gas volume.
- The difference between the inhaled and exhaled air volume.
- Expiratory and inhalation rates.
- The volume of forced exhaled air.
Features of the procedure
Spirometry in adult patients can be performed by a number of specialists, including a pulmonologist, a nurse, or a functional diagnostician. In childhood, the procedure is carried out by a pediatrician. There are also compact spirometers that allow you to do the simplest test at home. This is true for people suffering from asthma who need to control possible attacks.
Spirometry is a safe procedure and makes it possible to use it without restrictions. Among the side effects can be called slight dizziness during the procedure, but this phenomenon disappears after a couple of minutes.
However, forced inhalation and exhalation can affect intracranial and intra-abdominal pressure, therefore it is not recommended to carry out the procedure after undergoing abdominal surgery, myocardial infarction, stroke, pulmonary hemorrhage, pneumothorax, hypertension and poor blood coagulation. Age over 75 years is also a contraindication.
We considered the FEV1 norm and other indicators.