Inside the human body are the organs of digestion, blood circulation, hearing, etc. All of them are involved in ensuring the normal functioning of the body. However, it is believed that the key tasks are performed by the circulatory system. Let's consider it in more detail.
General information
Blood circulation is a continuous movement of blood in a closed system. It provides oxygen to tissues and cells. However, this is not all the functions of the circulatory system. Due to their activity, nutrients, vitamins, salts, water, hormones come to cells and tissues. They also participate in the removal of end products of metabolic processes, maintain a constant body temperature.
Biology, Grade 8: circulatory organs
The first acquaintance with the internal structure of the body occurs at school. Students do not just learn that there are circulatory organs. Grade 8 involves the study of their features, interactions with other elements of the human body. For a better understanding of the subject, children are offered simple schemes. They clearly depict what circulatory organs a person has. Schemes model the internal structure of the body.
What applies to the circulatory system?
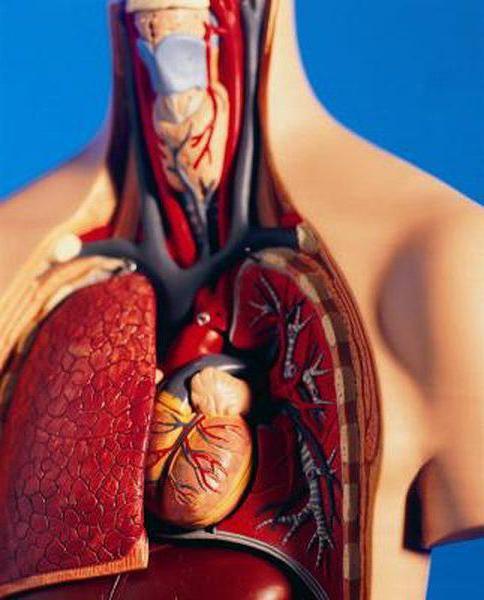
First of all, this is the heart. It is considered the main organ of the system. However, its activity would be useless in the absence of vessels present in all tissues of the body. It is through them that nutrients and other necessary substances are transferred with blood. The vessels have different sizes and diameters. There are large - veins and arteries, and there are small - capillaries.
Heart
It is represented by a hollow muscle organ. There are four chambers in the heart: two atria (left and right) and the same number of ventricles. All these spaces are separated from each other by partitions. The right atrium and ventricle communicate with each other through the tricuspid valve, and the left through the bicuspid valve. The weight of the heart of an adult is on average about 250 g (for women) and 330 g (for men). The length of the organ is about 10-15 cm, and its transverse size is 8-11 cm, the distance from the front to the back wall is about 6-8.5 cm. The average heart volume of a man is 700-900 cm 3 , women - 500-600 cm 3 .
The specifics of the activity of the heart
The outer walls of the organ are formed by muscle. Its structure is similar to the structure of striated muscles. The heart muscle, however, is able to rhythmically contract regardless of external influences. This occurs due to impulses arising in the organ itself.
Cycle
The task of the heart is to pump arterial blood flowing through the veins. The organ contracts about 70-75 times / min. at rest. This is approximately every 0.8 sec. The continuous operation of the body consists of cycles. Each of them involves contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole). There are three phases of heart activity:
- Systole of the atria. It lasts 0.1 seconds.
- Ventricular contraction. It lasts 0.3 seconds.
- General relaxation is diastole. It lasts 0.4 seconds.
Throughout the cycle, thus, the work of the atria lasts 0.1 seconds, and their relaxation - 0.7 seconds. The ventricles contract for 0.3 seconds and rest for 0.5 seconds. This determines the ability of the muscle to work throughout life.
Vessels
High performance of the heart is associated with increased blood supply. It occurs due to vessels departing from it. About 10% of the blood entering the aorta from the left ventricle enters the arteries that feed the heart. Almost all of them carry oxygen to tissues and other elements of the body. Venous blood carries only the pulmonary artery. The wall of the vessel consists of three layers:
- Outer connective tissue sheath.
- Medium, which is formed by smooth muscles and elastic fibers.
- Internal, formed by connective tissue and endothelium.
The diameter of the human arteries is in the range of 0.4-2.5 cm. On average, the total blood volume in them is 950 ml. Arteries branch into smaller ones - arterioles. They, in turn, pass into the capillaries. These circulatory organs are considered the smallest. The diameter of the capillaries is not more than 0.005 mm. They permeate all tissues and organs. Capillaries connect arterioles to venules. The walls of the smallest vessels are composed of endothelial cells. Through them, the exchange of gases and other substances. Veins carry blood enriched in carbon dioxide, containing metabolic products, hormones and other elements from organs to the heart. The walls of these vessels are distinguished by subtlety and elasticity. Medium and small veins have valves. They prevent backflow of blood.
Circles
Blood and circulatory organs were described as early as 1628. At that time, the English doctor V. Harvey studied the cardiovascular system of mammals and humans. He found out that the circulatory organs form two circles - small and large. They differ from each other in their tasks. In addition, there is a third circle, the so-called heart. He serves the heart directly. The circle begins with coronary arteries extending from the aorta. The third circle ends with cardiac veins. They converge into a coronary sinus, which flows into the right atrium. Other veins enter its cavity directly.
Small circle
With its help, the respiratory and circulatory organs interact. The small circle is also called pulmonary. It provides blood enrichment in the lungs with oxygen. The circle begins from the right ventricle. Venous blood moves to the pulmonary trunk. It is divided into two branches. Each of them carries blood, respectively, to the right and left lung. Inside them, the arteries diverge into the capillaries. In the vascular networks that surround the pulmonary vesicles, the blood gives off carbon dioxide and receives oxygen. She becomes scarlet and goes through the capillaries into the veins. Then they connect into four pulmonary vessels and flow into the left atrium. Here, in fact, the small circle ends. Atrial blood flows through the atrioventricular opening into the left ventricle. From here begins a big circle. Thus, the pulmonary arteries carry venous, and the veins carry arterial blood.
Big circle
All blood circulatory organs are involved in it, except for pulmonary vessels. The big circle is also called corporal. It collects blood from the veins of the upper and lower torso and distributes the arterial. The circle begins from the left ventricle. From it, blood flows into the aorta. It is considered the largest vessel. In arterial blood there are all the substances necessary for the life of the body, as well as oxygen. The aorta diverges into the arteries. They go to all the tissues of the body, pass into the arterioles and then into the capillaries. The latter, in turn, are connected into venules and then into veins. Through capillary walls there is an exchange of gases and substances. Arterial blood gives off oxygen and takes away metabolic products and carbon dioxide. Venous fluid has a deep red color. The vessels are connected into the vena cava - large trunks. They flow into the right atrium. Here the big circle ends.
Vessel movement
The flow of any liquid occurs due to the pressure difference. The larger it is, the higher the speed. Similarly, blood moves through the vessels of the small and large circles. Pressure in this case is created by contractions of the heart. In the aorta and the left ventricle, it is higher than in the right atrium and vena cava. Due to this, the fluid moves through the vessels of a large circle. In the pulmonary artery and right ventricle, the pressure is high, and in the left atrium and pulmonary veins - low. Due to the difference, movement occurs in a small circle. The largest pressure in the large arteries and aorta. This indicator is variable. In the course of the blood flow, part of the energy from the pressure is spent on reducing the friction of blood on the vascular walls. In this regard, it begins to gradually decline. This process is especially evident in the capillaries and small arteries. This is due to the fact that these vessels have the greatest resistance. In veins, pressure continues to decrease and in hollow vessels it becomes atmospheric or even lower.
Movement speed
Features of the circulatory system are in their internal structure and size. For example, if we talk about vessels, then the speed of the fluid will depend on the width of their channel. The largest, as mentioned above, is the aorta. This is the only vessel with the widest channel. All the blood leaving the left ventricle passes through it. This also determines the maximum speed in this vessel - 500 mm / sec. Arteries branch into smaller ones. Accordingly, the speed in them decreases to 0.5 mm / s. in the capillaries. Due to this, the blood manages to give nutrients and oxygen and take the metabolic products. The movement of fluid through the capillaries is caused by a change in the lumen of the small arteries. With their expansion, the current amplifies, while narrowing, it weakens. The smallest circulatory organs - capillaries - are represented in large numbers. In humans, there are about 40 billion of them. Moreover, their total lumen is 800 times greater than the aortic. Nevertheless, the fluid velocity along them is very low. Veins, approaching the heart, become larger and merge. Their total clearance decreases, but the blood flow velocity in comparison with capillaries increases. The movement in the veins is due to the pressure difference. The blood flow is directed to the heart, which is facilitated by the contraction of skeletal muscles and chest activity. So, when inhaling, the pressure difference at the beginning and end of the venous system rises. With a reduction in skeletal muscles, veins are compressed. It also promotes blood flow to the heart.
Pathological conditions
Circulatory diseases today occupy one of the first places in statistics. Often, pathological conditions lead to complete disability. The reasons why these or other violations occur are very diverse. Lesions can appear in various parts of the heart and in the vessels. Circulatory diseases are diagnosed in people of different ages and sex. According to statistics, however, some pathological conditions can occur more often in women, and others in men.
Symptoms of lesions
Circulatory diseases are accompanied by various complaints of patients. Often, symptoms are common to all pathological conditions and do not apply to any particular disorder. Cases when in the early stages of the occurrence of violations a person does not present any complaints at all are considered quite common. Some diseases of the circulatory system are diagnosed by chance. However, knowledge of the most common symptoms allows you to timely identify pathology and eliminate it in the early stages. Diseases may be accompanied by:
- Shortness of breath.
- Pain in the heart.
- Puffiness.
- Cyanosis, etc.
Heartbeat
It is known that healthy people do not feel the contractions of their heart at rest. The palpitations are not felt with moderate physical activity. However, with its increase, even a healthy person will feel a beat of the heart. His heartbeat can intensify when running, excitement, at high temperature. The situation is different for people who have problems with the heart or blood vessels. They can feel a strong heartbeat even with a slight load, and in some cases even at rest. The main reason for this condition is considered a violation of the contractile function of the body. The heartbeat in this case is a compensatory mechanism. The fact is that with this violation, for one contraction, the organ ejects a smaller amount of blood into the aorta than is necessary. Therefore, the heart goes into an intensive mode of operation. This is extremely unfavorable for him, since the relaxation phase is significantly shortened. Thus, the heart rests less than it should be. During a short relaxation, the biochemical processes necessary for recovery do not have time to go through. A rapid heartbeat is called tachycardia.
Pain
This symptom accompanies many diseases. Moreover, in some cases, pain in the heart may be the main symptom (for example, with ischemia), and in others it may not have a determining value. In CHD, the pain is caused by insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle. The manifestation of the pathology is quite clear. The pain has a compressive nature, short-term (3-5 minutes), paroxysmal, occurs, as a rule, during physical exertion, at low air temperature. A similar condition may occur in a dream. Usually a person who feels such pain takes a sitting position, and it is like. Such an attack is called angina pectoris. With other diseases, pain does not have such a clear manifestation. Usually they are aching and last a different time. They do not differ in high intensity. In this case, the stopping effect of taking certain medications does not occur. Such pains accompany various pathologies. Among them are heart defects, pericarditis, myocarditis, hypertension and so on. Pain in the area of the heart may not be associated with diseases of the circulatory system. For example, they are diagnosed with left-sided pneumonia, osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic regions, intercostal neuralgia, myositis, and so on.
Heart failure
In this condition, a person feels the irregularity of the organ. It manifests itself in the form of fading, a strong short blow, stop, etc. For some people, such interruptions are single, in others they are longer and sometimes permanent. As a rule, such sensations are accompanied by tachycardia. In some cases, interruptions are noted with a rare rhythm. The causes are extrasystoles (extraordinary contractions), atrial fibrillation (loss of the rhythmic function of the heart). In addition, disorders of the conduction system and organ muscles may be present.
Heart Hygiene
Normal stable activity of the body is possible only with a well-developed healthy circulatory system. The current velocity determines the degree of supply of tissues with necessary compounds and the intensity of removal of metabolic products from them. In the process of physical activity, oxygen demand increases at the same time as heart contractions become more frequent. In order to avoid interruptions and disturbances, it is necessary to train the organ muscle. To do this, experts recommend doing exercises in the morning. This is especially important for those people whose activities are not associated with physical activity. A greater effect of exercise occurs if they are done in the fresh air. In general, doctors recommend walking more. Along with this, it should be remembered that excessive psycho-emotional and physical stress can disrupt the normal activity of the heart. In this regard, stress and anxiety should be avoided whenever possible. Being engaged in physical work, it is necessary to choose loads proportional to the capabilities of the body. Nicotine, alcohol, narcotic substances have an extremely negative effect on the work of the body. They poison the central nervous system and heart, cause serious dysregulation of vascular tone. As a result, severe diseases of the circulatory system can develop, some of which are fatal. People who drink alcohol and smoke more often have vascular cramps. In this regard, it is necessary to abandon bad habits and in every possible way to help your heart.