Currently, the meaning of the word “drift” can be applied in several areas of science at once. This term applies to geography, optics, anatomy, and many other areas of activity.
Mainland drift
In 1912, the German scientist Alfred Wegener proposed a heuristic theory of the infinite movement of continental masses. The geologist made such conclusions based on his own observations and discoveries. What is the continental drift? Wegener suggested that the continents are in constant motion, but the speed is so low that it is impossible to feel. At the beginning of the 20th century, such a report caused a lot of criticism and ridicule from the scientific world.
It is worth noting that continental drift was discovered long before the German geologist. In the 1620s, the notorious enthusiast Francis Bacon noted in his manuscript works some coincidences in the outline of the coast of America and Africa. Based on his notes, decades later, the Frenchman Franco Placke, and then the German Theodor Lilienthal, put forward the idea of moving the continents. In 1858, the American theologian Antonio Snyder proposed a more radical theory that, after cooling the Earth, the surface could not withstand the pressure and split into parts.
For a long time, continental drift has not been proven. In most of Europe and the USA, this theory is still rejected. Nevertheless, in the early 1960s, Soviet scientists came to the conclusion that Wegener's judgments are reliable. In turn, the concept of fixism continued to uphold the famous Russian geologists M. Usov and S. Obruchev.
Continental drift theory
At the beginning of the 20th century, Alfred Wegener traveled around the world in order to learn the essence and origins of all life on the planet. Based on numerous data from the expeditions, the German geologist determined that all continents have a similar structural structure. Moreover, the scientist proved the commonality of the fossil fauna and flora of the continents in the past. Parallels could also be drawn in climatic zones.
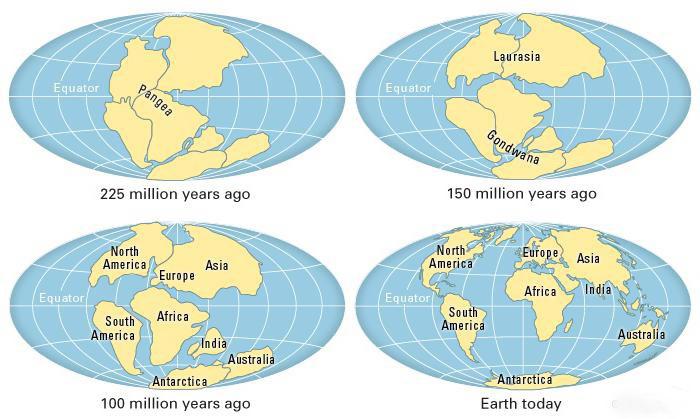
According to Wegener, a granite layer first appeared on the surface of the planet. Over time, the growths of the breed concentrated in a large prakontinent called Pangea. This formation dates back to 500 million years BC. It was then that a single praocean formed. As a result of tectonic movements, Pangea began to split into small parts. So there was a continental drift.
The motion of the continents is achieved by the centrifugal forces of rotation of the Earth. An important factor is the attraction of the sun and moon. Thanks to this, North America, and then Africa, was estranged from Eurasia. A giant crevice filled the Atlantic Ocean. The consequence of the split of Pangea was the mountain ranges of the Andes and the Cordillera.
As a result of drift, the continents of Africa and Europe collided with each other, forming the Alps, the Himalayas, the Carpathians and other mountain ranges. According to Wegener's hypothesis, the main points of rotation of the continents were the poles of the Earth.
Ice drift
It is no secret that frozen masses of water move through the seas and oceans due to the internal flow. But what is ice drift? This is by no means free movement along the water surface. In this case, it is the movement of icebergs in the ocean or sea under the influence of winds and various currents.
Most ice drifts in the Arctic, where research does not stop even for a day. Such movements are represented mainly by anticyclonic movement, in other words, clockwise. As a result of such a cycle, ice flows from the Arctic Ocean to the shores of Greenland in three streams. On such a path, a small iceberg will need from 1 to 5 years, depending on the starting point of the breakaway. The trajectory of movement depends on the Greenland current.
The scientist F. Nansen began to observe the first unique phenomenon back in 1893. Then the ship "Fram" drifted from the Novosibirsk coast to the Greenland Sea. Nansen tracked the relationship between ice characteristics throughout the entire 3-year expedition journey. As a result, the scientist identified two important rules: the iceberg drift speed is approximately 2% of the speed of the accompanying wind, and the direction of motion lies 30 degrees to the right of the current. Nansen's data was subsequently confirmed by Soviet professor Vladimir Wiese.
Baric ice drift
This unique natural phenomenon from 1913 to 1940 in the waters of Greenland studied dozens of expeditions, and each time scientists agreed that Nansen was right in his writings and conjectures. In the late 1930s, the Soviet Union launched a network of weather stations into the Arctic. The project was led by the scientist N. Zubov.
According to the data received, he and his team managed to identify the pattern of drift that occurs along isobars. As it turned out, the current in the Greenland waters is extremely weak, but a very strong wind. It was he who drove the ice floes to the shores of large islands. So the baric drift was discovered. He met two rules:
1. The directions of motion of ice and isobars coincide. In this case, the pressure is significantly increased in the right area.
2. The speed of movement is inversely proportional to the distance between the isobars.
As for the angle of 30 degrees, this deviation occurs under the influence of
the Coriolis force and friction.
Gene Drift: Definition
In the human body at the cellular level, millions of automatic processes occur. One of the most interesting and unique of them is considered to be genetic drift. This is almost the only mechanism that is caused by random static phenomena. So what is gene drift? This is a chaotic change in the frequency of gene alleles, that is, population variations.
The mechanism of the phenomenon consists in the reproduction procedure, as a result of which a huge number of germ cells, called gametes, are formed. These cells are not able to form zygotes, but there are rare exceptions. It is from them that unique species are formed in the population. It is worth noting that the shift of the frequency range of alleles is possible only relative to one previous generation.
Thanks to drift, species evolve in local populations. It is important to understand that such a change in frequencies occurs regardless of any factors.
Gene drift: population waves
This process does not in any way affect the number of species, since ups are always followed by declines. Many scientists still wonder what gene drift is about evolution. The Russian scientist S. Chetverikov tried to answer this in his research. He drew attention to regular fluctuations in the number of populations. During the experiments it was revealed that these processes play a decisive role in the evolution of all life on the planet. Fluctuations in numbers are called population waves.
The genetic structure of a person is built in such a way as to produce offspring at the right time - a new individual of a similar type. In animals and plants,
population waves depend on the territorial characteristic. In a certain zone, only species with the original genetic code can appear. Nevertheless, alleles are responsible for the evolution in fauna and flora.
Gene Drift: Molecular Evolution
The end result of the phenomenon will be the complete disappearance from the population of one allele and the fixing of another in it. The higher the level of gene drift, the faster the molecular evolution of the species. Studies show that the probability of fixation of a moving allele is equal to the frequency of the population.
It is noteworthy that each similar gene molecule arose once as a result of a mutation. Evolutionary leaps occur at a frequency of about 10-5 per gene / gamete. It is logical to assume that the lower the population level, the lower the likelihood of a new mutation.
Nevertheless, many scientists are sure that the degree of evolution does not depend on the size of the species and the number of drifting genes. American researchers Polling and Zuckerkandl found that neutral alleles move at a constant speed. This applies to any species.
Electron drift
This process is the movement of charged particles under the influence of a static field. Moving can be messy and natural. It all depends on the conductivity of the electric field.
The drift of particles in gases and metals under the influence of current is determined by thermal motion. In this case, it will not be possible to predict the speed and direction of movement. The fact is that thermal exposure does not form a single macroscopic flow of charged particles. Here, the connection of electrons with the field is characterized by the intensity and density of the medium. In a plasma, particles are exposed to a magnetic field, so the motion will be uniform and regular.
The drift velocity of charges in an electric field is much higher than that of ions. This is due to a stronger momentum of the medium.
DC drift
The PT amplifier has one main problem - spontaneous voltage drop. This phenomenon is called zero drift. As a result of turning off the current at the amplifier output, the value of the indicator drops to the initial one. Zero drift is most often observed in the absence of an input signal.
The reasons for this shutdown may be:
- malfunction of the power source;
- instability of resistors or transistors;
- low-frequency noise;
- high ambient temperature;
- interference or interference.
The most rare and complex consequence of disconnecting the current in the CTF can be a galvanic connection between the cascades. It quickly transmits changes in signals, so the instability at the input is practically not tracked.
To neutralize zero drift, you can use temperature-compensating components, deep OOS, DC / DC converters, and a state detection mechanism. It would be useful to change the balanced scheme of the UPT.
Eye drift
This process is due to a smooth slow displacement of the eyeball. In other words, this is an involuntary fixation of the central part of the retina on an object. The logical question is what is eye drift and what are its causes.
To answer it, you need to understand that the human retina has 3 types of movements that are not even felt: constant tremor, jerk fixation and smooth movement. The first condition is the norm. The frequency of contraction of the eye muscles is up to 80 Hz. The second condition is also within normal limits. The mechanism is controlled by a sudden reaction. The third state is allowed only together with the first two, but not separately. Its cause may be the retinal denial of the feedback mechanism.
Ship drift
Displacement of the vessel off course occurs most often under the influence of strong winds. The main characteristic of such a drift is the angle between the lines of the true and false directions of the route.
Demolition of the vessel may occur under the influence of the current. The drift also indicates the displacement in the “anchored” position, when the load creeps along the bottom.
The most dangerous consequence of such a demolition is the likelihood of a ship entering a cliff or shallow water. To eliminate this situation, it is necessary to direct the ship with its nose against the wind.