As you know, the main function of the joints is to provide movement. In addition, cartilaginous formations are needed to hold bone structures together. Therefore, joint pathologies not only lead to obstruction of active movements, but also increase the risk of osteochondrosis and ankylosis. One of these diseases is synovitis. This inflammatory lesion of the inner surface of the joint most often develops as a result of injuries. In most cases, one joint is involved in the pathological process. Impairment of movements and pain occur when large joints are affected. An example is the synovitis of the shoulder joint, in which discomfort is observed during abduction, raising the arm. It becomes difficult for a person to carry out the usual movements: eat, write, carry a bag, etc.
What is this disease?
Synovitis of the shoulder joint is a common pathology that is often ignored. Especially if the pain occurs on the side of the "inoperative" hand. In such cases, inflammation becomes chronic in the course. The shoulder joint is constantly swollen and painful on palpation. However, people rarely turn to these complaints for medical attention. This is due to the fact that diseases such as synovitis, bursitis of the shoulder joint are rarely accompanied by severe pain. Often people get used to discomfort and do not attach due importance to it. Nevertheless, one should know that even moderate synovitis of the shoulder joint can gradually lead to irreversible consequences. The main one is the development of osteoarthrosis. Synovitis is an inflammation of the connective tissue layer located on the inner surface of the joint. With this disease, tissue edema is observed, resulting in a swelling in the joint area. In addition, there is a change in the composition of the intraarticular (synovial) fluid. White blood cells, neutrophils or lymphocytes predominate in it.
Causes of occurrence
Synovitis of the shoulder joint can occur due to several reasons. In most cases, it develops as a result of exogenous factors. These include various types of injuries of the shoulder joint. For example, synovitis can occur with a fracture or cracking of the bones of the upper limb, improper adhesion under the cast. Sometimes inflammation of the inner articular surface occurs with dislocations and even bruises. Most often, a similar pathology occurs in people engaged in active labor. These include athletes, sculptors, plasterers, etc.
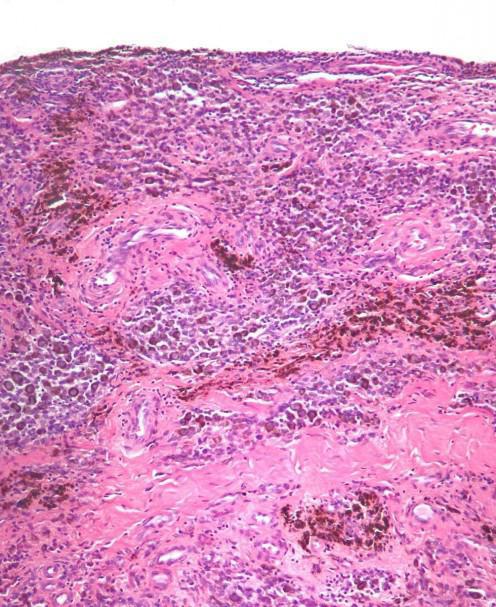
In addition, synovitis of the shoulder joint can occur with systemic inflammatory reactions. Such diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, bone tuberculosis, gout, osteoarthrosis, ankylosing spondylitis. Synovitis can also develop against the background of septic lesion, infectious endocarditis. With such pathologies, inflammation of the inner surface of the joint occurs due to the ingress of microorganisms from distant foci with blood flow. Symptoms of the disease develop due to changes in the plasma impregnation through the vascular wall. As a result, local edema occurs. The pain syndrome is caused by compression of the joint by synovial fluid, which is released in large quantities. Inflammation often goes to adjacent tissues of the joint. As a result, bursitis and arthritis develops.
Classification
Infectious and aseptic inflammation of the synovial membrane is distinguished depending on the etiology. In the first case, the disease develops due to the penetration of bacterial or viral particles into the joint cavity. Pathogens enter the synovial fluid and multiply there. As a result, an inflammatory reaction develops. Most often, in such cases, other joint formations are affected. Aseptic synovitis is associated with bone injuries, sprain, dislocations. Non-infectious inflammation can occur due to allergic reactions, endocrine and neurogenic disorders.
In addition, synovitis is classified by the nature of the course of the pathology. Thus, acute and chronic inflammation of the inner surface of the joint is distinguished. Long-term current pathology often leads to the development of complications.
Synovitis of the shoulder joint: symptoms, treatment of the disease
In most cases, synovitis does not completely restrict movement. Therefore, a person can do the usual work. Nevertheless, sudden movements in the shoulder joint are accompanied by pain. Unlike arthritis, joint deformation is not observed. However, a swelling appears in the shoulder area. In infectious inflammation, the symptoms of synovitis are combined with the clinical picture of the underlying disease. The severity of the pain syndrome depends on the nature of the exudate. With a purulent inflammatory process, the patient cannot make active movements in the joint. The treatment of synovitis is medication. Alternative recipes are also used to help cope with inflammation. With the development of severe complications, they resort to surgical intervention. Surgical treatment is necessary when a large amount of fluid accumulates in the joint cavity, and bone tissue is also infected.
Shoulder joint synovitis
Depending on the phase of the inflammatory reaction, 3 stages are distinguished that are characteristic of such a pathology as synovitis of the shoulder joint. Symptoms of the disease are directly related to the nature of the exudate. To a greater extent, this applies to pain. The first stage develops immediately after an injury or penetration of microorganisms into the joint cavity. It is characterized by slight irritation of the synovial membrane and hyperemia. Edema and exudation are slightly expressed. The stage of serous inflammation (second) develops if treatment for synovitis has not been started. It is characterized by severe exudation and swelling of the tissues. In the study of synovial fluid, cell infiltration and proliferation are detected. A large amount of yellow exudate and fibrin clots accumulate in the joint cavity. The transition to the third stage is observed with the development of purulent inflammation. Edema becomes more pronounced, a large number of leukocytes and neutrophils are found in the exudate. Synovitis of the shoulder joint is most dangerous at the stage of purulent inflammation. As a result of the attachment of a bacterial infection, the adjacent tissues are often involved in the pathological process. As a result, complications such as arthritis, osteomyelitis, and sepsis develop.
Diagnostics
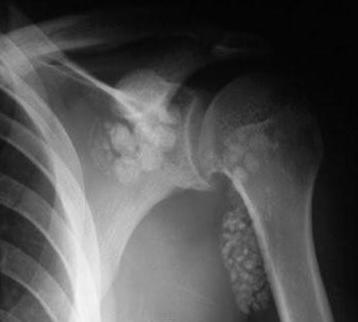
Synovitis of the right shoulder joint can be suspected more often, since most people perform basic movements with this hand. This diagnosis is based on the clinical picture, laboratory data and instrumental diagnostic methods. The main clinical manifestations are pain when moving the arm, swelling of the joint and smoothing of the contours. With significant edema, palpation of the bones of the shoulder is not always possible. If the disease has passed into the third stage, then symptoms such as fever, headache, and deterioration of health are observed. Synovitis of the left shoulder joint has the same manifestations. However, in the early stages, discomfort is less often paid attention to. The exception is people working with the left hand. Changes in the general analysis of blood are observed with severe inflammation. Of great importance for differential diagnosis is x-ray examination. It helps to distinguish synovitis from fracture and crack of the humerus, dislocation of the joint. To establish the final diagnosis and stage of inflammation, a microscopic examination of the exudate is performed.
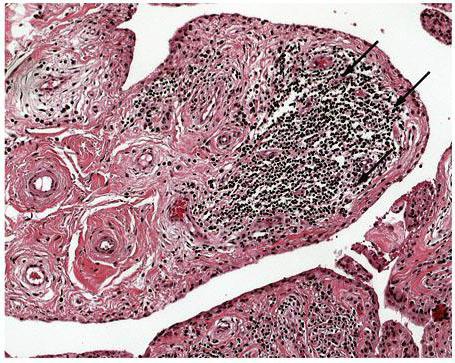
Synovitis of the shoulder joint: treatment of the disease
Treatment should be aimed at stopping the pain syndrome, fighting infection and preventing the development of complications. At the first and second stages of the disease, conservative therapy is enough. To reduce swelling, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. These include drugs "Diclofenac", "Artoxan." With infectious synovitis, the appointment of antibacterial medications is necessary. In some cases, injections are made directly into the joint cavity. In addition to drug therapy, a tight bandage is applied to the affected area. This is necessary to limit movement in the joint.
Surgical treatment of synovitis
In some cases, surgical intervention is required. It is necessary with a large amount of accumulated synovial fluid in the joint cavity. Treatment consists of inserting a needle into the affected area and aspirating the exudate. This procedure is also carried out for diagnostic purposes. With purulent synovitis, surgical intervention is necessary. It consists in opening the joint cavity and providing drainage.
Prevention of synovitis and bursitis
Primary prevention is to limit physical activity. If human activity is associated with monotonous work with hands, it is necessary to alternate motor activity with rest.