Monitoring blood sugar is a mandatory procedure for people with diabetes, as well as for people who are predisposed to this ailment. With age, the effectiveness of insulin receptors decreases. Therefore, individuals after forty years of age are recommended by doctors to monitor the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream. Children with a predisposition to the disease also need to monitor this indicator. Taking biomaterial for analysis is carried out on an empty stomach. There are two ways to determine the concentration of sugar in the blood: in plasma and whole blood. The first is a liquid substance that remains after all blood elements have been removed from it. Allowable values of glucose in whole blood and fasting plasma glucose norm are different. In the latter case, it is slightly higher.
general information
Glucose is actively involved in carbohydrate metabolism, providing cellular tissue with the necessary energy. Its main sources are:
- cereals;
- sweets;
- fruits;
- bread;
- pasta;
- vegetables;
- sugar.
Carbohydrates, when ingested with food, are broken down to glucose, and their excess is deposited in the form of glycogen or polysaccharide. In the intestine, glucose is absorbed into the blood, and then, in order for it to enter every cell, a hormone called insulin is needed. Each glucose entering the bloodstream is accompanied by the release of insulin into it. Therefore, the individual rises for a short time after eating sugar, and then it normalizes. However, it should not fall below an acceptable level, otherwise the body will not have enough energy. For all types of medical examinations, as well as for medical examination, they pass a blood test for this indicator on an empty stomach. The glucose rate depends on age and on where the biomaterial was taken from: from a vein or from a finger.
Indications for analysis
It is necessary to detect blood sugar levels in order to track how the body metabolizes and uses glucose. Some pathological conditions are accompanied by a change in the concentration of sugar in the bloodstream:
- pituitary disease;
- sepsis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- pregnancy;
- shock conditions;
- liver disease
- obesity;
- hypothyroidism;
- other.
The study is also indicated for the purpose of diagnosing and monitoring the condition of patients with diabetes mellitus receiving sugar-lowering therapy. Individuals at risk should be monitored every six months. These include persons:
- overweight;
- taking glucocorticoids;
- having close relatives with diabetes;
- having undergone thyrotoxicosis.
As well as women during pregnancy who have been diagnosed with gestational diabetes or have had miscarriages for unknown reasons.
If the individual has the following symptoms, then the doctor will definitely recommend this analysis:
- increased appetite, but loss of body weight is recorded;
- decreased immunity;
- fast fatiguability;
- constant thirst and dryness in the oral cavity;
- headache;
- in people older than 50 years of vision loss;
- polyuria, especially at night;
- causeless itching in the groin area;
- the formation of boils;
- sores, wounds, or scratches that do not heal for a long period.
Types of fasting blood tests for sugar
Laboratory methods for determining the concentration of this indicator are the most accurate and reliable. The biomaterial is taken from a finger or from a vein on an empty stomach. In the first case, the concentration of glucose in capillary blood is determined. The fasting glucose rate from the finger in both male and female is in the same range. In children, acceptable values depend on age. The analysis is taken in the morning, usually up to eight hours, since during this period the body has not yet begun its work in full force. Later, all processes in the individual's body are actively launched, including the synthesis of hormones that increase the concentration of sugar in the bloodstream. They hand over biomaterial on an empty stomach, since even a small amount of drunk water contributes to the activation of the digestive system. The pancreas, liver, and stomach begin to work, which is reflected in the level of sugar, i.e., it rises. Thus, fasting blood for fasting sugar means the exclusion of food and water at least eight hours before the test. In the second case, the amount of sugar in the plasma of venous blood is also determined on an empty stomach. The glucose rate from a vein is slightly higher than from a finger. This analysis is recognized as basic and most accurate, since pure plasma without impurity of blood cells is examined. The results are ready in a few hours or the next day, depending on the workload of the laboratory.
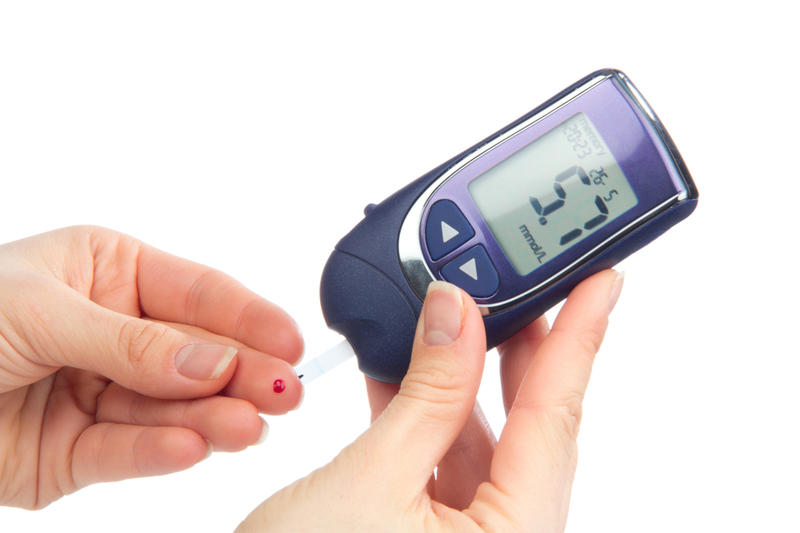
At home, an empty stomach test is performed from a finger using a glucometer. A finger is pierced with a special device that is part of the kit, a drop of blood is applied to the test strip, which is inserted into the included device. After a short period of time, the result appears.
Preparatory Activities
No special preparation is required. The main thing is to lead a habitual lifestyle and not to starve, because during this period the body actively extracts glucose reserves from the liver. Starvation will negatively affect the results of a fasting blood glucose test, the norm will be exceeded. Compliance with the following recommendations before the delivery of biomaterial will make the analysis more accurate:
- For several days, do not starve, eat as usual.
- For three days, abandon the use of alcohol-containing drinks.
- For three days, stop taking certain medications: oral contraceptives, salicylates, corticosteroids, thiazides, ascorbic acid (as agreed with your doctor).
- For eight hours, stop eating and drinking water.
- The day before, exclude physical activity, medical and diagnostic manipulations, visits to the solarium, saunas or baths, and smoking.
- Try to exclude stressful situations, since an adrenaline rush provokes an increase in excess of normal glucose in the blood on an empty stomach.
- On the day of blood donation, do not brush your teeth, as the substances contained in them can increase the level of sugar.
- Before entering the laboratory cabinet, sit calmly and calm down.
Preparations for donating blood for sugar during pregnancy do not differ from those described above. The only point is that with severe early toxicosis accompanied by vomiting, one must refrain from taking biomaterial. Otherwise, the concentration of fasting glucose will differ from the norm in pregnant women. If you feel better, you can take an analysis.
Algorithm for blood sampling from a vein
When performing this manipulation, the nurse must observe the following procedure:
- Prepare a container for collecting biomaterial.
- The individual takes a horizontal position if he is dizzy, or sits on a chair.
- The patient holds out his hand, palm up. Under the elbow, the paramedic places a roller.
- A rubber tourniquet is applied to the forearm and a pulse is felt on the vein.
- The place where the needle will be inserted is treated with an alcohol solution. During this period, the individual is asked to work with his hand to fill the vein with blood.
- At a sharp angle, a needle is punctured. Its cut should be directed downward.
- The nurse slowly pulls the syringe plunger up until blood appears inside it. On average, take no more than five milliliters.
- A sample of biomaterial is poured into a prepared test tube. The needle is removed and placed in a special container, and the syringe is placed in a container with disinfectants.
- A cotton pad moistened with an alcohol solution is applied to the puncture site. In order to avoid the formation of hematomas, the patient is recommended to bend his arm at the elbow for at least five minutes.
- The tube is labeled and sent to the laboratory.
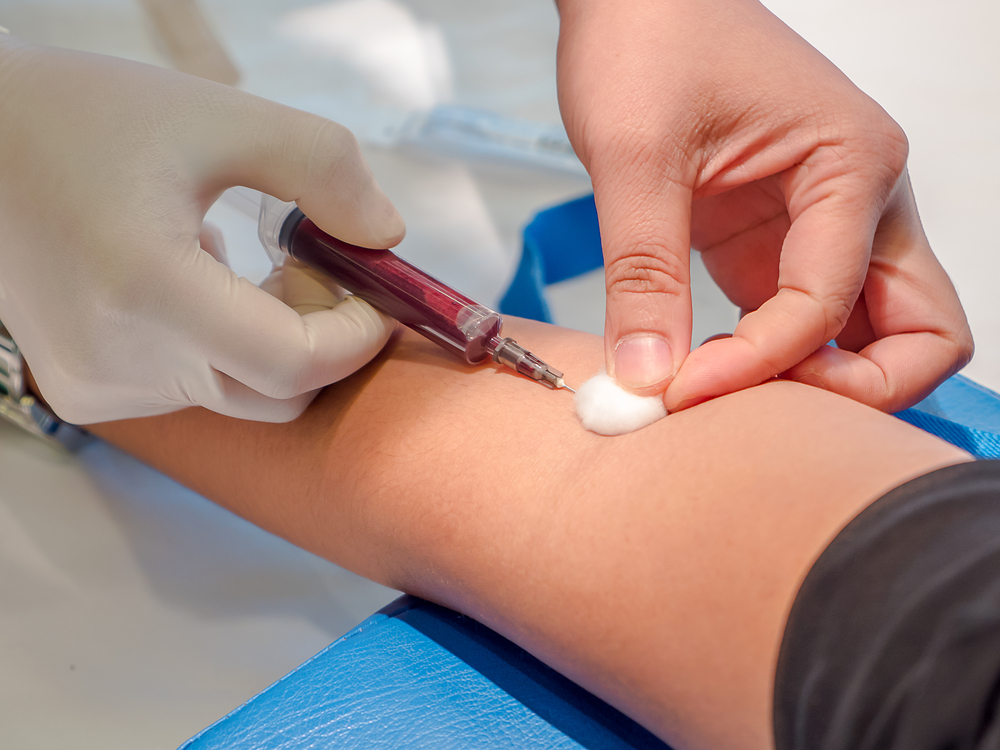
The algorithm for collecting biomaterial in children is practically no different from that described above. However, in this case, factors such as:
- During the manipulation, parents should distract the baby due to his fear of injections.
- Blood sampling can be taken from the forearm, the back of the palm, head, vein of the elbow.
- Twenty minutes before the test, the child should be in a calm state.
Vacuum blood sampling has several advantages over the conventional method:
- contact of a medical worker with biomaterial is excluded;
- test tubes are made of unbreakable material;
- the number of actions of the nurse decreases.
The process of collecting biomaterial using vacuum tubes basically coincides with the usual method. The difference is observed only during the puncture of the vein.
Fasting and after glucose (mmol / l)
For self-control it is necessary to know the permissible values, with age they are higher. Below is the minimum and maximum level for monitoring sugar with an empty stomach glucose meter by age:
- from three to six - 3.3–5.4;
- from six to eleven - 3.3–5.5;
- up to fourteen - the lower limit of 3.3; top - 5.6;
- from fourteen to sixty - the lower limit of 4.1; top - 5.9;
- from sixty to ninety - the lower border is 4.6; top - 6.4;
- older than ninety - the lower bound is 4.2; upper - 6.7.
The baby was not measured with a glucometer due to the instability of blood sugar.
Any, even a small deviation from the norm requires an appeal to the doctor. For persons older than 40 years and in pregnant women, slight fluctuations in the indicators are possible due to a malfunction of the hormonal background.
Permissible range for fasting finger extraction in a laboratory:
- adults - from 3.3 to 5.5;
- pregnant women - from 3.3 to 4.4;
- children - from 3.0 to 5.0.
At a vein fence for:
- adults - the minimum level is 3.6; the maximum is 6.1;
- pregnant women - not less than 3.3 and not more than 5.1;
- children from fourteen years old - from 3.5 to 5.5;
- fasting glucose in primary school children - from 3.3 to 5.5;
- newborns - from 2.7 to 4.5.
Normal glucose levels after meals are different in healthy individuals and those with diabetes. Below is information on acceptable values after eating:
- in a practically healthy individual, after sixty minutes - 8.9; in two hours - 6.7;
- in a diabetic - in an hour - 12.1 and higher; in two - 11.1 or more;
- in pregnant women - in an hour - from 5.33 to 6.77; after two - 4.95–6.09;
- in children - in an hour - 6.1; in two - 5.1;
- in patients with diabetes - in an hour - 11.1; in two - 10.1.
It is quite difficult to establish an acceptable blood level in children. This phenomenon is associated with the fact that sugar fluctuations during the day occur quite sharply. In the first months of his life, he is not at all stable. The norm in each case will be told by the attending doctor.
The indicators according to the results of the analysis may not coincide with the norms, but be both higher and lower.
In patients with diabetes, glucose concentration changes rapidly and dramatically. For them, the permissible limits are slightly higher than for healthy individuals. The doctor sets the limit values on an empty stomach and after eating for each patient individually, depending on his condition and the degree of compensation of the disease.
Causes of High Blood Sugar
Pathological conditions in which the fasting blood glucose norm is exceeded from a finger and from a vein:
- thyrotoxicosis;
- diabetes;
- adrenal disease;
- pituitary tumor;
- infectious diseases in the acute stage;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- extreme stress.
In addition, an increase in blood sugar provokes the use of certain medications: diuretics, hormones, antihypertensive drugs, improperly selected doses of sugar-lowering tablets and insulin, as well as the delivery of biomaterial after meals. Among the main reasons for an increase in fasting glucose from the norm is diabetes. Individuals suffering from this disease are required to regularly monitor the concentration of sugar in the blood, eat properly and take appropriate medications. This pathology is fraught with serious complications. Excess glucose levels in the tests indicate a failure of carbohydrate metabolism. The abuse of pastries, sugary, carbonated drinks increases sugar, and in some cases provokes irreversible processes on the part of the pancreas. If this is revealed for the first time, the doctor will prescribe additional studies, for example, a glucose tolerance test and determination of glycated hemoglobin.
Causes of Low Blood Sugar
For health, both an increase and a decrease in blood sugar are unfavorable. Factors contributing to its reduction:
- the use of alcohol-containing drinks;
- excessive physical activity;
- low carbohydrate intake with food;
- starvation;
- overdose of drugs taken to treat diabetes;
- neoplasms in the pancreas.
Any deviation of glucose from normal on an empty stomach is an alarm.
Deciphering the results
If a decrease in sugar level is found below acceptable values, then this condition is called hypoglycemia. Symptoms such as:
- hunger;
- weakness;
- persistent drowsiness;
- tremor;
- arrhythmia;
- pallor of the dermis;
- anxiety;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- aggressiveness;
- other.
The reasons for this condition lie in the following:
- excessive physical activity;
- insufficient carbohydrate intake;
- neurohumoral pathologies;
- excessive synthesis of insulin;
- improperly selected doses of sugar-lowering medications;
- hypothyroidism;
- cirrhosis;
- pancreatic disease;
- poisoning with substances of toxic nature;
- swelling of the stomach.
In some cases, severe symptoms are absent and a decrease in sugar occurs gradually. In severe hypoglycemia, the patient requires a rapid rise in sugar, i.e., the intake of carbohydrates, which begin to be absorbed in the oral cavity, intramuscular injection of drugs.
With an increase in fasting glucose, hyperglycemia develops. In a practically healthy individual, normal blood sugar levels increase after eating. However, if it remains stably high, then the doctor suspects the presence of pathological conditions such as:
- pancreatitis
- diabetes;
- various endocrine disorders;
- stress
- premenstrual syndrome;
- errors in nutrition.
An increase in sugar is accompanied by the following clinical picture:
- visual impairment;
- itching and various rashes on the dermis;
- frequent urination
- uneven breathing;
- fast fatiguability;
- thirst;
- other.
If the analysis showed that the amount of glucose is higher than the permissible values, then this is an occasion to consult a doctor. He will prescribe additional examinations and make the correct diagnosis. It is important to remember that fasting blood glucose from a vein will be twelve percent higher than from a finger. Doctors warn that an independent interpretation of the results and taking medications without consulting a specialist is fraught with serious consequences. For example, a condition such as stress promotes an active release of adrenaline, which increases sugar levels. However, this phenomenon is not a pathology and does not require specific treatment.
Obligatory decoding at the doctor glucose tolerance test, passed on an empty stomach. It makes it possible to assess the dynamics of changes in sugar levels. Thus, regardless of the research results obtained, a doctor’s consultation is required.
Adult Blood Sugar
The fasting blood glucose rate in women varies with age, the unit of measurement is mmol / l:
- from 18 to 30 - the lower limit of 3.8; top - 5.8;
- from 39 to 60 - the lower limit of 4.1; top - 5.9;
- from 60 to 90 - the lower limit of 4.6; top - 6.4;
- 90 and more - the lower limit of 4.2; upper - 6.7.
The main reason for its fluctuation is the instability of the hormonal background in different periods of life. Permissible values of this indicator in the blood on an empty stomach in the age category from 18 to 90 years and above are the same for both sexes. In addition, when interpreting the results, the doctor must take into account the increased physical activity of the stronger sex. Sports loads affect the performance, but subject to the rules of preparation for the analysis, the results of the study will be reliable. Thus, the fasting glucose norm in men also depends solely on age.
Doctors suggest diabetes with:
- Exceeding the permissible maximum age norm of glucose in the blood donated to an empty stomach. The analysis is repeated twice.
- Exceeding the mark of 11 mmol / l after eating or when taking biomaterial at any time of the day.
To determine the level of glucose, capillary or venous blood is taken.
Blood sugar test during pregnancy
While waiting for the baby, the expectant mother repeatedly passes the glucose test. This is an important source of energy for both the woman and the fetus. For analysis, venous or capillary blood is taken. Excessive fasting glucose during pregnancy indicates the development of diabetes. :
- obesity;
- ;
- , ;
- ;
- 30 ;
- ;
- genetic predisposition;
- ;
- .
In different laboratories, the allowable glucose values for pregnant women on an empty stomach from a vein may differ slightly depending on which units of measurement are used. If a pregnant woman is at risk, after registration, in addition to analysis for sugar, she will have to pass a glucose tolerance test, in case of overestimation of acceptable indicators. In all other cases, pregnant women pass such a test in the middle of the term. If, according to the results of these analyzes, the permissible levels are not exceeded, then there is no reason for excitement. If the pregnant woman exceeds the fasting glucose norm from a vein, the study is repeated, since the reasons for the increase may be factors not associated with abnormal phenomena:
- changes in hormonal levels and metabolic processes;
- physical activity, which includes walking;
- fatigue;
- infectious diseases;
- bad dream.
The above reasons can distort the result of the analysis even in a healthy woman, so re-examination is extremely necessary.
Blood sugar in women over forty
The fasting blood glucose rate in women changes with age. The determination of this indicator helps in the diagnosis of not only diabetes, but also other pathological conditions, for example, connective tissue, liver, stroke, etc. In women in old age, the concentration of sugar increases significantly after eating, or rather, after two hours, and on an empty stomach within acceptable values. All women after forty years are at risk for diabetes and therefore must be tested for glucose. In addition, it is recommended to monitor its level during pregnancy and for persons who are overweight. For example, the maximum glucose in fasting blood is normal for women at sixty or more years of age, 6.2 millimoles per liter, and up to fifty - only 5.5. The reasons that provoke the excess of normative indicators in old age are:
- the use of a large number of high-calorie foods;
- decreased tissue sensitivity to insulin and a decrease in its synthesis by the pancreas;
- unbalanced diet;
- the presence of concomitant diseases, for the treatment of which medications are used that negatively affect the metabolism of carbohydrates.
In women after sixty years, they are most often diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, which is characterized by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the neck and face;
- heartache;
- decreased visual acuity;
- loss of sensation in the limbs;
- the appearance of ulcers on the body;
- the appearance of signs of a diabetic foot.
In addition, exceeding the fasting glucose norm in women is possible due to the disease pancreatitis, which occurs without characteristic signs and disguises itself as other pathological conditions, gradually destroying the pancreas. Reducing the concentration of sugar is quite possible with a diet. Should be excluded from the diet:
- animal fats;
- bananas
- figs;
- sweets;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- fast foods
- juices.
To maintain glucose at an acceptable level and in order to normalize metabolic processes, it is recommended to include in the diet:
- herbal teas;
- mineral water;
- seafood;
- fish
- vegetables;
- beef;
- rabbit meat.
The danger of exceeding fasting glucose in older women lies in the development of various complications. In addition, high sugar gradually weakens the immune system and the body becomes vulnerable to infectious and viral diseases. To prevent such conditions, one must promptly respond to any deviations of glucose in the blood from normal values and regularly visit a doctor.
How to regulate the concentration of glucose in the blood?
No kind of sugar adjustment is allowed on its own. After passing the analysis, and especially if the norm of glucose from a vein on an empty stomach is exceeded, it is recommended to consult a specialist. He will individually select a pharmacotherapy and dietary regimen depending on the individual's state of health. In the pre-diabetes state, a diet is indicated.
In diabetes of the second type, medications are prescribed based on alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, derivatives of benzoic acid, sulfonylurea, and others. A diet with a strict restriction of certain foods is also an essential element of therapy. In the first type of disease, insulin preparations, a strict diet with the obligatory calculation of bread units and physical activity are prescribed.