Mammals (Grade 7 studies this topic in the zoology section) unite all animals that feed their young with milk. Since this is the largest class of vertebrate animals, there are several classifications within this systematic unit. One of them is based on where the mammalian embryo develops. We will consider this question in detail in our article.
Species of mammals
All mammals are dioecious highly organized animals. Both females and males have paired gonads: ovaries and testes, respectively. Outward, they open with specialized ducts. All these animals are characterized only by internal fertilization. However, its further formation and level of development depends on where the embryo of the mammal develops.
Who are the Beasts
Surprisingly, it is a fact: there are mammals that lay eggs. They are called the "First Beasts" and form only one squad - One-Pass. And he was named so because these animals have a cesspool. This is a primitive trait characteristic of previous chordates. Cesspool is one hole in which the products of the exchange of the urinary, digestive and reproductive systems are released.
First beasts are very small, include only 6 species. Their habitat is Australia with adjacent islands. Their representatives are echidna, prokhidny and platypus. They do not have nipples, and milk is released through the ducts of the glands to the surface of the skin. Cubs have to lick it to get enough.
The appearance of these animals is also very unusual . Echidna is very similar to a large hedgehog. Its long and sharp needles are nothing but a modification of the hairline that is characteristic of all mammals. Under them is a layer of dense wool. And given the fact that the front of the muzzle is extended into the proboscis, and on the extremities there are sharp claws designed for digging, the echidna will completely resemble a fantastic non-existent animal. Their females bear a single egg. They carefully store it in a fold of skin located on the ventral side of the body.
The platypus looks completely different. By its name, it is not difficult to guess that it has a wide and flat nose. Fingers are located on the fingers, and the tail has a flattened shape, acting like flippers. Platypuses hatch their eggs in nests that they arrange on their own.
Subclass Real Animals
These animals are united by the fact that they immediately give birth to live cubs, and do not hatch them, like birds. They no longer have cesspool, and the ducts of the digestive, reproductive, and urinary systems open with separate specialized openings. Depending on where the embryo of the mammal develops, marsupial and placental mammals are distinguished.
Squad Marsupials
These are also typical inhabitants of the Australian continent. They are characterized in that the place where the mammalian embryo (egg) develops, they leave very quickly. This is because they completely lack the placenta. As a result, the cubs are born underdeveloped, small in size and incapable of independent life. After birth, they are for a certain time in a skin bag, also located on the abdominal side of the body. The ducts of the mammary glands open into it.
A newborn baby is so weak and helpless that at first it cannot even suck on its own. The gland muscles contract spontaneously and automatically spray milk directly into the mouth of a small marsupial animal. Representatives of these animals are primarily kangaroos. They are able to move at a speed of about 60 km / h.
Quite common in Australia are the marsupial koala bear and possums.
Placental: where the mammalian embryo develops
The greatest development, and hence spread around the planet, has been achieved by mammals with a uterus, in which a placenta is formed during pregnancy. It binds the body of the mother and child throughout the entire period of pregnancy. Through the blood vessels of this formation, respiration and nutrient metabolism are carried out. As a result, the future organism is provided with all vital conditions, and the walls of the uterus are protected from adverse environmental conditions. He is gaining strength enough to be completely viable right after birth and, after a short period of time, switch to independent existence. How progressive this feature is, says the number and dominant position of animals having this organ. Insectivores, Bats, Rodents, Hares, Artiodactyls and Equidae, Carnivores, Pinnipeds - this is not a complete list of orders that are placental. Yes, and primates, which include the modern view of Homo sapiens, have reached their development thanks to the presence of this attribute as well.
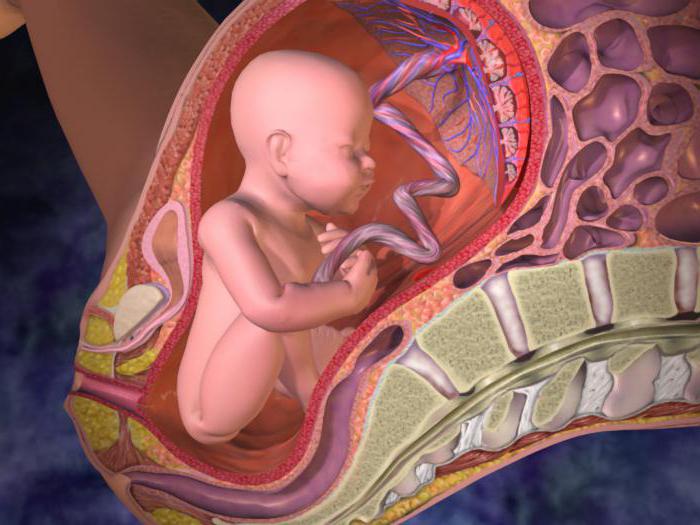
Features of mammals: advantages and disadvantages
Of course, the development of the embryo in the uterus using the placenta is the most advanced way. With its formation, the uterine walls and the germinal membrane are tightly fused. Through the placenta, all the necessary substances that are in the mother's body are transported into the body of the unborn child. In the uterus, he is not afraid of temperature extremes or predators. Naturally, egg-laying are in a less favorable position. This is an obvious fact. Of course, eggs contain a large amount of nutrients necessary for the development of the embryo. But they can become the coveted prey of predatory animals. And considering that the number of eggs is 3-4 maximum, you can generally remain without offspring. Marsupial cubs are born too underdeveloped. For example, the length of the pregnancy process in the possum barely reaches two weeks. Naturally, in such a short period of time, such a complex organism will not have time to achieve the proper degree of development.
Thus, the development of mammals has its own characteristics, which allow them to be combined into three groups, each of which has its own adaptation features: single-pass, marsupial and placental.