An ECG for myocardial infarction helps to establish the cause of the disease, symptoms and prescribe treatment. The clinical picture of PPTS is associated with rheumatic mitral stenosis, preceding heart disease, commissurotomy. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out through x-ray procedures, echocardiography. The treatment methodology is selective - NSAIDs are prescribed in the clinical picture, GC is acceptable for the rapid course of the disease. The latter helps to slow the wound process.
Postpericardial syndrome: signs of large focal myocardial infarction. ECG and diagnostics
This is a combination of two diseases: pericarditis and pleurisy (less often pneumonia, eosinophilia), developing within a month from the onset of acute heart muscle disease. In cardiology, it is called post-infarction pathogenesis, which develops after an organ transplant surgery. Depending on the acquired complications, it can be interpreted as Dressler’s disease.
It is a separate disease resulting from destructively altered myocardial proteins. It was first discovered by William Dressler, a physician, in 1956. His doctrine was developed by Harley, a cardiologist. According to statistics, this ailment occurs among 2-3% of patients, in 38% of patients who have had a heart attack. Among children with congenital malformations, they are diagnosed at 12-14 years of age, therefore, statistics show the percentage of acquired pathogenetic unity. It amounted to 32%.
Causes of postpericardiotomy syndrome: ECG for myocardial infarction as an early diagnosis and prevention
Dressler's endemic is considered a rare complication, although pathology is reported among 7% of the world's population. It is associated with coronary heart disease, the use of NSAIDs, non-invasive CVD treatment methods.
The main etiopathogenetic factors (bases) are:
- Myocardial infarction. It is considered an etiological factor. Due to cardiomyocyte necrosis, the blood is saturated with antibodies that are not accepted by your own body. Sensitivity to the altered protein is formed, cells become autoantigens, destroying organs. An aseptic inflammation of the pleura develops, which leads to a pericardial form. It disrupts the functioning of the main organ.
- Chest surgery. Less commonly, cider occurs after operations, injuries, strokes, and shell shocks.
In rare cases, viral infections that cannot be seen through the ECG can be the cause. With myocardial infarction, neighboring tissues are also affected. At risk are people suffering from vasculitis, sarcoidosis, spondylarthrosis, polymyositis. Children belong to only one risk group - congenital pathology, however, no one will give an accurate prognosis until the child reaches 12 years of age. If the operation was performed for medical reasons in the first three years of life, the probability of developing the disease is 4-5% in the absence of other pathologies, congenital pathologies of the respiratory system.
Pathogenesis: the clinical picture
In severe forms of the course of endemia, postpericardiotomy syndrome does not lead to death. Pathologists indicate fibrotic, serous or serous-hemorrhagic pericarditis, not associated with the development factors of Dressler symptoms. Unlike epistenocardic pericarditis, inflammation of pericarditis in diabetes has a diffuse character that can not be diagnosed.
Research is necessary only to prevent myocardial infarction. ECG diagnosis does not always accurately indicate the causes and symptoms, therefore, additional measures are taken to identify acute pathologies.
Classification of the disease: how to distinguish the type of heart attack
Due to the complex and lengthy diagnosis, the disease is divided according to the forms of manifestation, the rate of onset of symptoms, the possibility / impossibility of diagnosis. On the basis of the data obtained, causes related to risk factors for the manifestation of these diseases are identified.
Stand out:
- Postpericardial syndrome of a typical form. There is pericardium, inflammation of the pleura, lungs, joints. Against this background, pathology develops, a heart attack is possible.
- Atypical postpericardial syndrome - dry integument, pneumonia / bronchitis, asthma, low-grade fever, arthralgia, changes in blood composition. Affect the heart muscle and central nervous system.
According to the speed of manifestation, early or late myocardial infarction is distinguished. ECG signs are not detected, but individual granular membranes can be seen.
Symptoms of a heart attack: early manifestations
Symptoms will determine the factor of the ailment, indicate different ailments. By identifying several of them, you can group a series that indicates a particular risk factor. Thus, further diagnosis, treatment is determined. At different stages of the disease, relative conclusions are drawn, confirmed or refuted by research procedures. Symptoms will be treated based on diseases leading to PPTS.
- Clinical pericarditis is considered the main indicator of deterioration of the pathogenesis of the heart muscle. It manifests itself as sudden pain in the shoulder, back, neck, gives into the abdominal cavity. The nature of the pain is intense, paroxysmal (inflammation of the pleura), pressing, compressing (ischemic). Intense pain with pericarditis is associated with diabetes. Compressive indicates another disease. To alleviate the condition, you need to breathe not deeply, preferably standing. If it intensifies, there is a suspicion of inflammation of the exudate. The main symptom is the pericardial friction noise detected by the doctor during auscultation. It is present in 90% of patients with pneumonia, the diagnosis of a specific symptom is carried out with holding the breath, torso. Important! If the pain does not disappear when taking drugs from the nitrate group, there is a likelihood of developing clinical form pericarditis.
- Pleurisy. Symptoms of the disease are manifested by pain in the lateral parts of the chest, worse when inhaling, exhaling. It is important to determine interlobar, unilateral or bilateral pleurisy. Postpericardiotomy syndrome is not associated with the first factor, since pleural noise becomes dull with active physical activity. In the remaining two cases, pleurisy will be the only cause.
- Pneumonitis It is determined by the presence of hard breathing. In the acute form, the focus of small bubbling rales develops, leading to pleurisy (the cause of PPTS). Possible cough, sputum, blood impurities.
- Diseases of the joint, tendons. Postpericardial syndrome affects the joints, soft tissues. Symptoms pointing to this ailment are pains of the shoulder-shoulder joints on the left, pains of large joints of the hands and feet.

Rare symptoms of pathogenesis are insufficiency of diastolic dysfunction, hemorrhagic vasculitis, acute glomerulonephritis. They are not related to the origin of the disease. May appear on their own.
Complications of a lack of pathogenesis data
Untimely diagnosis of symptoms (lack of surgery) can lead to repeated myocardial infarction. ECG signs of a possible disease can not always be predicted.
Perhaps the appearance of signs of pericardial effusion, diastolic collapse of the right atrium. Both complications develop tamponade of the heart muscle - a difficult to diagnose complication found among 1-2% of patients. There is a decline / enlargement of the ventricle, the appearance of the sign of "swinging heart", expansion of the inferior genital vein.
Diagnosis of the disease: primary and in-depth studies
Various research methods help establish the nature of endemicity. Conduct laboratory sampling of blood and urine, ECG for myocardial infarction. Photos with decoding prove the doctor's assumptions: if there is reason for the operation, it is performed without the consent of the patient.
Also, analysis fences show the dynamics of the course of the disease. An increase in ESR, white blood cells is noted. If the results showed eosinophilia, an increase in the level of reactive C-protein is characteristic. The method of palpation is excluded, auscultation by a therapist is acceptable, as a physical examination. A full range of symptoms is taken into account, instrumental, differential diagnostics are carried out, allowing to compare the nature of the symptoms. It also helps to establish the stage of myocardial infarction on the ECG. The examination requires passing:
- ECG. The result will show a diffuse ST segment, a depression of the PR segment. If, on the contrary, the QRS amplitude complex can be excluded. Conducted by a doctor of functional diagnosis of ECG with myocardial infarction. Photos with decryption are received on the spot immediately after the procedure.
- Echocardiography is done by the same doctor. The picture allows you to find out if there is an accumulation of fluid. Leaf separation leading to tamponade is possible. For postpericardial syndrome, the separation does not reach 10 mm in diastole, which eliminates the risk of complications and does not confirm this pathogenesis.
- X-ray of the lungs. It is necessary to exclude / confirm pleurisy, pericarditis. The picture should not have any pronounced border of the heart shadow. The opposite indicates the presence of foci inside the lungs - postpericardiotomy syndrome will be a precursor to the development of a dangerous complication. A study is being conducted by a radiologist, laboratory assistant.
- CT (radiologist), MRI (therapist / pediatrician to read a picture of relatively soft tissues) of the lungs are also performed to detect pleural fluid. The technique helps to avoid the development of pulmonary infiltration.
- Pleural, pericardial puncture of the lungs (pulmonologist). If liquid is detected, the sampling is examined. The character is established - serous / serous-hemorrhagic. The substance is sent to the laboratory to determine the level of leukocytes, C-protein, eosinophilia. Reading the results, prescribing the treatment requires a consultation of doctors of cardiologists, traumatologists, phthisiologists, and oncologists.
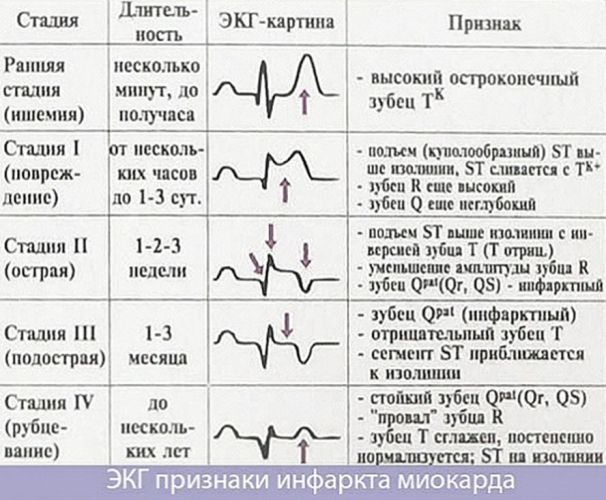
If all indicators indicate a minimum of two diseases, differential diagnosis methods are additionally carried out, taking into account relapses of a heart attack, bacterial pneumonia, pulmonary embolism. Diagnostics also involves laboratory studies of additional markers for the presence of fibrin degradation products - D-dimer.
Treatment of heart attack and postpericardial syndrome
PPTS occurs due to acute myocardial infarction. An ECG can be performed in cases of detection of pathogenesis. Some croupous membranes are not detected. The formation of pleurisy, pericarditis, pneumonitis is observed. To treat all the causes of one symptom, it is required to determine the severity of the disease. Assign outpatient or inpatient treatment. It involves medical or conservative treatment by prescribing drugs of the following groups:
- NSAIDs - to eliminate signs of an autoimmune indicator. Sometimes they are canceled if they harm the patient.
- Glucocorticoids are needed for those who suffer from a refractory factor to NSAIDs.
With prolonged use of hormonal drugs, improvement occurs on 3-4 days without relapse. To achieve a clinical picture (reduce inflammation), this group of substances is slowly canceled in order to avoid a relapse with a fatal outcome. Rarely, two groups of drugs are prescribed simultaneously because of the risk of a relapse of the autoimmune indicator. In the treatment of NSAIDs, gastroprotection is prescribed to protect against ulcers.
Additional supportive treatment
Anticoagulants are necessary for long-term therapy with the threat of hemopericarditis, tamponade. Pericardiocentesis is canceled, pericardectomy is prescribed (with confirmation of the threat of constrictive pericarditis).
After discharge, the patient is prescribed symptomatic therapy with beta-blockers, cardiotropic drugs, ACE inhibitors, lipid-lowering drugs and anticoagulants. It is also recommended to eliminate bad habits, establish the right diet. The treatment is supplemented by conservative methods in the form of physical education and therapeutic respiratory gymnastics. Surgical intervention is indicated only with exacerbation of the symptoms of the triad - acute effusion pericarditis, pleurisy and pericardial sac. Too much fluid is removed by puncture of the pleura or pericardium.
Forecast and Prevention
When conducting an ECG diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction, a risk group can be determined in advance. A progressive and developing disease requires the abolition of NSAIDs due to ineffective action. To exclude anemia, occlusion of the coronary shunt, glucocorticoids are prescribed.
According to doctors' forecasts, the survival rate for the next 5 years after a heart attack has been steadily declining, and the risk of death due to pathogenesis is increasing. However, statistics report the opposite - myocardial infarction always leads to an ailment, since it is of a relapsing nature. Medicine can prevent, cure pathogenesis, eliminating sharp outbreaks of repeated heart attack, the occurrence of PPTS and its complications.