The chest is a bone-cartilage formation that forms a cavity. It consists of twelve vertebrae, 12 costal pairs. In this section, there is also a sternum and connections of all elements. The internal organs are located in the cavity: the esophagus, trachea, lungs, heart, and others. The shape of the chest is comparable to a truncated cone. The base is turned down. The transverse size is larger than the anteroposterior. Side walls form the ribs of a person. The front wall is short.
It is formed by cartilage and sternum. The back wall is formed by ribs (to the corners) with the corresponding spine. The longest are the side walls.
Human anatomy. Ribs
These symmetrical formations are paired with the thoracic vertebrae. Human ribs include a longer bony part and anterior, shorter, cartilage. There are twelve pairs of plates in total. The upper ones, from I to VII, are attached to the sternum using cartilaginous elements. These human ribs are called true. Cartilage VIII-X pairs are connected to an overlying plate. These elements are called false. XI and XII human ribs have cartilaginous short parts, which end in the muscles of the abdominal wall. These plates are called oscillating.
The structure of the human ribs
Each plate has a narrow, curved surface or edge shape. The posterior end of each human rib has a head. In the IX pair, it connects to the bodies of two thoracic adjacent vertebrae. In this regard, from the second to tenth plates have a comb dividing the head into 2 parts. I, XI, XII pairs articulate on the vertebral bodies with full fossa. The posterior end of the human rib tapers behind the head. As a result, a neck is formed. She goes into the longest section of the plate - the body. Between him and the neck is a tubercle. On the tenth ribs, it is divided into two elevations. One of them lies lower and medially, forming the articular surface, the other, respectively, above and laterally. Ligaments join the latter. The tubercles of the XI and XII ribs do not have articular surfaces. In some cases, the elevations themselves may be absent. The bodies of II-XII plates include the outer and inner surface and edge. The shape of the ribs is somewhat twisted along the longitudinal axis and is bent anteriorly at the tubercle. This section is called the corner. At the lower edge, a furrow extends along the inside of the body. In it lie the nerves and blood vessels.
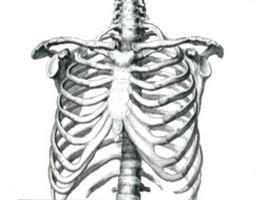
At the front end there is a pit with a rough surface. It connects to the costal cartilage. Unlike others, the first pair has a lateral and medial edge, lower and upper surface. At the last indicated site is the tubercle of the scalene anterior muscle. A groove for the
subclavian artery lies behind the tubercle
, and for the vein in front.
Functions
Forming the chest, the plates provide protection to internal organs from various external influences: injuries, mechanical damage. Another important function is the creation of the frame. The chest ensures the retention of internal organs in the necessary, optimal position, preventing the displacement of the heart towards the lungs.