Wind is a stream of air moving in a certain direction. On other planets, it represents a mass of gases characteristic of their surface. On Earth, the wind moves mostly horizontally. Classification, as a rule, is carried out in accordance with the speed, scale, types of forces that cause them, places of distribution. Under the influence of flows are various natural phenomena and weather. The wind promotes the transfer of dust, plant seeds, helps the movement of flying animals. But how does directional air flow appear? Where does the wind blow from? What determines its duration and strength? And anyway, why are the winds blowing? About this and much more - later in the article.
Classification
First of all, winds are characterized by strength, direction and duration. Gusts are considered to be strong and short-term movements (up to several seconds) of air flows. If a strong wind of medium duration blows (about a minute), then it is called a flurry. Longer air currents are named according to their strength. So, for example, a light wind blowing on the coast is a breeze. There is also a typhoon, a hurricane, a storm, a storm. The duration of the winds can also be different. Some last a few minutes, for example. A breeze, depending on the temperature difference on the surface of the relief during the day, can last up to several hours. Local and general atmospheric circulation consists of trade winds and monsoons. Both of these types belong to the category of “global” winds. Monsoons are caused by seasonal changes in temperature and last up to several months. The trade winds are air masses that are constantly moving. They are due to temperature differences at different latitudes.

How to explain to the child why the wind blows?
For young children, this phenomenon is of particular interest. The child does not understand where the flow of air is formed, which is why it is in one place and not in another. It is enough to simply explain to the baby that in winter, for example, a cold wind blows because of the low temperature. How is this process going? It is known that air flow is a mass of atmospheric gas molecules moving together in the same direction. A small volume of air flow, blowing around a high-rise building, can whistle, tear off hats from passers-by. But if the mass of gas molecules has a large volume and a width of several kilometers, then it can cover a fairly large distance. Indoors, the air practically does not move. And you can even forget about its existence. But if, for example, you put your hand out of the window of a moving car, you can feel the air flow, its strength and pressure with your skin. Where does the wind blow from? The movement of the flow is due to pressure differences in different parts of the atmosphere. Consider this process in more detail.

Atmospheric pressure difference
So why is the wind blowing? For children it is better to give a dam as an example. On the one hand, the height of a column of water, for example, is three, and on the other, six meters. When the locks open, water will flow to the area where it is less. Roughly the same thing happens with air currents. In different parts of the atmosphere, the pressure is different. This is due to the difference in temperature. In warm air, the movement of molecules is faster. Particles tend to scatter from each other in different directions. In this regard, warm air is more discharged and weighs less. As a result, the pressure that is created in it is reduced. If the temperature is lowered, then the molecules form closer clusters. Air, accordingly, weighs more. The pressure rises. Like water, air has the ability to flow from one zone to another. So, the flow passes from the area with high pressure in the area with low. That is why the winds blow.
The movement of flows near water bodies
Why is the wind blowing from the sea? Consider an example. On a sunny day, the rays warm up both the shore and the pond. But the water heats up much more slowly. This is due to the fact that surface warm layers immediately begin to mix with deeper, and therefore cold layers. But the shore heats up much faster. And the air above it is more discharged, and the pressure, respectively, is lower. Atmospheric currents rush from the reservoir to the shore - in a freer area. There, they warm up, rise up, again freeing up space. Instead, a cool stream appears again. This is how the air circulates. On the beach, vacationers can periodically feel a light cool breeze.
The meaning of the winds
Finding out why the winds blow, it should be said about what impact they have on life on Earth. Wind is of great importance to human civilization. Vortex flows inspired people to create mythological works, expanded the commercial and cultural range, influenced historical phenomena. Winds also acted as energy suppliers for various mechanisms and assemblies. Due to the movement of air currents, sailing ships were able to travel considerable distances across the oceans and seas, and balloons across the sky. For modern aircraft, winds are of great practical importance - they allow you to save fuel and increase lift. But it should be said that air currents can also cause harm to humans. Thus, for example, control over the control of an airplane may be lost due to gradient wind fluctuations. In small bodies of water, fast air currents and the waves they cause can destroy buildings. In many cases, winds contribute to the scale of the fire. In general, the phenomena associated with the formation of air currents, in various ways, affect wildlife.
Global effects
In many areas of the planet, air masses dominate with a certain direction of movement. In the region of the poles, as a rule, easterly prevail, and in temperate latitudes - westerly winds. At the same time, in the tropics, air flows again take an eastern direction. At the borders between these zones - the subtropical ridge and the polar front - there are so-called calm areas. The prevailing winds in these zones are practically absent. Here, the movement of air is carried out mainly vertically. This explains the appearance of zones of high humidity (near the polar front) and deserts (near the subtropical ridge).
Tropics
The trade winds are blowing westward in this part of the planet, approaching the equator. Due to the constant movement of these air currents, atmospheric masses are mixed on Earth. This can occur on a large scale. So, for example, trade winds moving over the Atlantic Ocean, carry dust from the African desert territories to the West Indies and some parts of North America.
Local effects of air mass formation
Finding out why the winds blow, it should be said about the influence of the presence of certain geographical objects. One of the local effects of the formation of air masses is the temperature difference between not too distant areas. It can be triggered by different coefficients of light absorption or different heat capacity of the surface. The last effect is most pronounced between the water surface and land. The result is a breeze. Another local factor of importance is the presence of mountain systems.
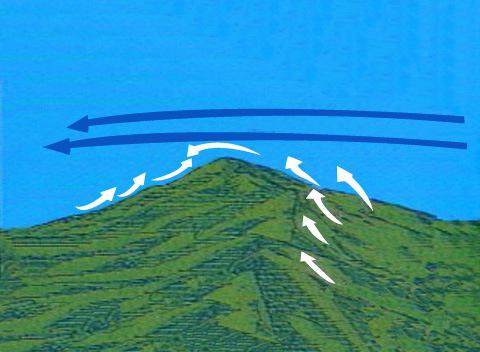
The influence of the mountains
These systems may represent a barrier to the movement of air currents. In addition, in many cases, mountains themselves cause wind formation. The air over the highlands warms up more than the atmospheric masses over the lowlands at the same height. This contributes to the formation of low pressure zones over the mountain ranges and wind formation. This effect often provokes the appearance of mountain-valley atmospheric moving masses. Such winds prevail in cross-country areas.

The increase in friction at the valley surface leads to a deviation of the parallel directed air flow to the height of the mountains nearby. This contributes to the formation of jet high-altitude flow. The speed of this flow can exceed the strength of the surrounding wind up to 45%. As mentioned above, mountains can act as obstacles. When bypassing the circuit, the flow changes its direction and strength. Swings in mountain ranges have a significant effect on wind movement. For example, if there is a pass in the mountain range that the atmospheric mass overcomes, then the flow passes it with a noticeable increase in speed. In this case, the Bernoulli effect works. It should be noted that even slight differences in altitude cause fluctuations in wind speed. Due to the significant gradient of air velocity, the flow becomes turbulent and continues to remain so even beyond the mountain in the plain at a certain distance. Such effects are in some cases of particular importance. For example, they are important for aircraft taking off and landing at mountain airfields.