Lipid peroxidation (lipid peroxidation) is a vital link in metabolic metabolism. Its main function is to update the lipids of cell membranes.
In a healthy person, the processes of lipid peroxidation are controlled by the so-called antioxidant system, which regulates the rate and activity of phosphorylation by binding provoking factors or neutralizing a sufficient amount of peroxides to prevent an excess of the final metabolic products. Strengthening the oxidation process can be the starting point in the pathophysiological processes of a significant number of diseases. This process includes the stages of enzymatic and non-enzymatic autooxidation.
Kinds
Enzymatic oxidation takes place to modify the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes. In addition, he is involved in the formation of biologically active substances, detoxification, metabolic reactions. Non-enzymatic oxidation also manifests itself as a destructive factor in cell life. Due to the formation of a large number of free radicals and the accumulation of peroxides, the activity of the antioxidant system decreases and, as a result, the death of body cells is observed.
FLOOR cycle
To start lipid peroxidation, it is necessary to have free oxygen radicals having one unpaired electron at the extreme energy level. After the molecule is restored, oxygen superoxide is formed, which reacts with hydrogen atoms, turning into hydrogen peroxide. To regulate the amount of superoxides inside the cell, superoxide dismutase, which forms hydrogen peroxide, exists, and catalase, peroxidase neutralize it to water. If a living organism is exposed to ionizing radiation, the amount of free hydroxyl radicals will increase dramatically. In addition to oxygen hydroxide and its other active forms, they can initiate the start of the lipid peroxidation process.
The products of lipid peroxidation are either utilized by the body or used to synthesize prostaglandins (substances involved in inflammation reactions), thromboxanes (included in the cascade of thrombogenic reactions), and adrenal hormones.
Control system
Depending on the basic structure of the cell membrane, the speed, activity and amount of the resulting oxidation products may vary. For example, the activity of lipid peroxidation is higher where unsaturated fatty acids predominate in the cell wall , and slower if cholesterol is the basis of CS. In addition, metabolic enzymes are a factor regulating the amount and rate of formation of free oxygen radicals, as well as the utilization of peroxides. Even in the reaction of lipid peroxidation, substances are involved that affect the lipid composition of the cell membrane and its arbitrary change in accordance with the needs of the body. These include vitamin E and K, thyroxine (thyroid hormone), hydrocortisone, cortisone and aldosterone (by feedback). Metal ions, vitamins C and D are destabilizing the cell wall.
Process violation
The metabolic products of lipid peroxidation can accumulate in the tissues and body fluids if the antioxidant system does not have time to utilize them at the required speed. As a result, the transport of ions through the cell membrane is impaired, which can indirectly affect the ionic composition of the liquid part of the blood, the rate of polarization and depolarization of the membranes of muscle cells (disrupt the conductivity of nerve impulses, their contractility, increase the refractory period), and facilitate the exit of fluid into the extracellular space (edema, blood thickening, electrolyte imbalance). In addition, the main products of lipid peroxidation, after a series of biochemical reactions, turn into aldehydes, ketone bodies, acids, etc. These substances have a toxic effect on the body, which is manifested in a decrease in the rate of DNA synthesis, an increase in the permeability of capillaries, an increase in oncotic pressure, and, as consequence, sludge syndrome.
Clinical manifestations
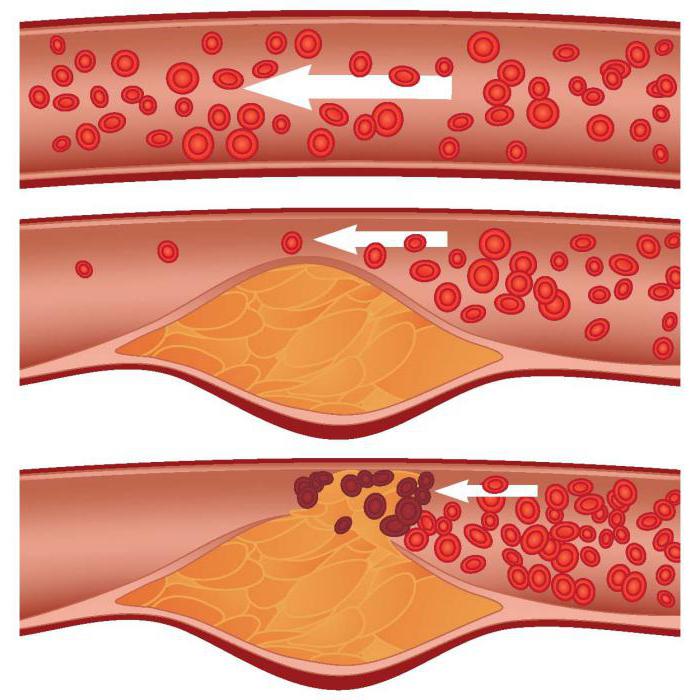
Since an increase in the number of oxygen free radicals has a damaging effect on the cell wall, and metabolic products disrupt the metabolism and synthesis of nucleic acids, as well as poison the body, they are a pathophysiological factor in the development of a number of clinical conditions. The role of lipid peroxidation is important for diseases of the liver, joints, parasitic infectious diseases, hemodynamic disorders, cancer, injuries and burns. FLOOR is one of the factors in the development of atherosclerosis. Free radicals, oxidizing cholesterol and its low molecular fractions, form products that damage the vascular wall. This starts a cascade of typical pathological reactions aimed at repairing damage. This provokes thrombosis, the accumulation of blood clots in the lumen of small vessels or attachment to their walls. As a result, the movement of blood in this area slows down, as the lumen of the vessel has become narrower. This contributes to the further accumulation of blood clots. The most susceptible to such changes are the coronary arteries, the aorta, which are manifested in the clinic as symptoms of
coronary heart disease.
Preventive measures
Practitioners need to remember that diagnostic and therapeutic procedures can activate the mechanism of lipid peroxidation. The patient should be warned about this. The provoking factors include radiation therapy (for oncology), ultraviolet radiation (for rickets, inflammatory diseases of the sinuses, antibacterial treatment of rooms), magnetic fields (MRI, CT, physiotherapy), sessions in a pressure chamber (for polio,
mountain sickness).Prevention and Therapy
X-ray staff, nurses and nurses, physiotherapists, climbers, overweight people should eat foods that contain natural antioxidants: fish, sunflower or olive oil, greens, eggs, green tea.
In addition to changing the diet, you can use drugs that bind some groups of free radicals or combine with metals of variable valency. Thus, they replace free molecules of active oxygen, preventing them from binding to lipid peroxidation enhancers.
Diagnostics
At the current stage in the development of laboratory research, we are able to detect peroxides in the composition of biological fluids of the human body. To do this, conduct
fluorescence microscopy. Simply put, detect lipid peroxidation. The significance of this diagnostic test needs no explanation. Indeed, a significant number of diseases are based on the excessive activity of lipid peroxidation. The identification of this condition determines the tactics of treatment.
From the point of view of normal physiology, lipid peroxidation is necessary for the formation of steroid hormones, inflammatory mediators, cytokines and thromboxanes. But when the amount of metabolic products of these chemical reactions exceeds the permissible value and peroxides damage the organelles of the cell, disrupt the synthesis of DNA and proteins, an antioxidant system comes into play, which reduces the number of free radicals of oxygen, metal ions with variable valency. In addition, it enhances the synthesis of catalase and peroxidase in order to utilize excess peroxides and products of their further metabolism.