Duodenal sounding is the procedure for introducing a probe, for the purpose of diagnosis and treatment, into the duodenum. For research, it is necessary to extract the contents of the duodenum, bile and pancreatic juice produced by the pancreas. Sometimes the procedure is used for therapeutic purposes to remove secretions from the body during sluggish inflammation of the gallbladder or to rinse and administer drugs in the treatment of pancreatitis and peptic ulcer disease.
What is the study?
The research method of duodenal contents has a nearly hundred-year history and is often used in gastroenterology for diagnosis. The composition of the fluid of the duodenum obtained using the probe consists of the secretion of the intestine and pancreas, bile and gastric juice. This method is used to determine the condition of the gallbladder and biliary tract. It is used for suspected parasite levels in the liver and duodenum, for cirrhosis and viral hepatitis, gallstone disease. For the study, several servings of samples are taken that reflect the state of the biliary system. For the manipulation is required:
- A probe with an elastic rubber tube with a diameter of three to five millimeters and a length of one and a half meters, the end of which is equipped with metal or plastic olive with holes. There are three marks on the probe: the first at a distance of 0.45 m from the olive, the second at 0.7 m and the third at 0.8 m.
- A syringe with a volume of 10 or 20 ml.
- Tubes for collecting individual servings of bile.
It takes from one and a half to two hours to collect three servings of the contents of the duodenum. After this, a study of the duodenal contents in the laboratory.
Indications for diagnosis
The procedure for collecting material for research has its own characteristics and causes a certain discomfort to the individual, therefore, it is carried out only with unusual symptoms and suspicions of certain diseases. These include:
- constant feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- pain and discomfort in the right hypochondrium;
- stable nausea and vomiting;
- discoloration of feces and alteration of the color of urine to brown or tan;
- bile stasis detected by ultrasound;
- confirmation of the existing diagnosis;
- diseases of the bile duct and liver;
- suspected inflammation in the gallbladder;
- cholelithiasis.
Taking material to study the duodenal contents in the presence of stones in the gallbladder has a risk of complications, therefore, when prescribing the procedure, the doctor must evaluate the benefits and harms for the patient.
Contraindications for duodenal sounding
The manipulation is accompanied by increased secretion of bile and increases the number of contractions of the biliary tract, so the study is undesirable for:
- Exacerbation of chronic or acute cholecystitis.
- Esophageal varicose veins - possible damage to the walls of blood vessels by the probe and the occurrence of bleeding.
- Presence in the gall bladder of stones - the movement of stone may begin, which clogs the bile duct.
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding - the use of drugs during the study procedure of the duodenal contents leads to a decrease in blood pressure, which contributes to the deterioration of the blood supply to the fetus, in addition, medications penetrate into breast milk.
- Cancer of the digestive tract.
Before the appointment of the procedure, the doctor assesses the feasibility of its implementation.
Types of manipulations for duodenal sounding
Methods of collecting duodenal fluid can be of several types. The following types of sensing are distinguished:
- Blind - performed without the use of a probe. The patient is injected with choleretic drugs to clean the gallbladder. This method is used for stagnation of bile and the risk of stones.
- Fractional - a classic method of obtaining duodenal contents, consisting of taking three portions of bile using a probe at set intervals.
- Chromatic - a special staining of cystic bile is used to accurately determine its amount. For this, the individual 12 hours before the procedure takes a contrast agent.
In addition, duodenal sounding is also used for therapeutic purposes.
How to prepare for the study? Doctor's recommendations
Duodenal sounding is performed on an empty stomach. For 8-10 hours before it, the patient should not eat food, and for 3-4 hours - liquid. When preparing for the procedure of probe examination of the duodenal contents five days before its start, it is necessary to exclude the following products from the menu:
- all bakery and confectionery products;
- vegetables and fruits with a lot of fiber, in any form;
- milk and products made from it;
- fatty varieties of fish and meat;
- legumes.
Diet helps to reduce gas formation in the intestines. In addition, the patient must stop taking the following drugs:
- antispasmodics - "Papaverine", "Beshpan", "Spazmalgon", "No-shpa";
- choleretic - “Holosas”, “Flamin”, “Allohol”, “Barberin”;
- vasodilator;
- laxatives;
- containing enzymes - "Festal", "Pancreatin", "Creon".
Before the study, it is recommended to take eight drops of a 0.1% Atropine solution and drink a glass of warm water, dissolving 30 grams of xylitol in it. The objectivity of the results depends on compliance with the preparatory measures.
Possible complications after the procedure
With the introduction of the probe and the use of medications to obtain material for the study of gastric and duodenal contents, undesirable phenomena may develop:
- Increased salivation.
- Bleeding that occurs as a result of damage to the mucous membrane with rapid swallowing of the probe.
- Nausea and vomiting. It is advisable for patients with hypersensitivity to the occurrence of an emetic reaction to anesthetize the posterior pharyngeal wall using a special spray before the procedure.
- Diarrhea. “Magnesia sulfate” used during the manipulation has a strong laxative effect. Patients with digestive problems should use other drugs.
- Dizziness occurs as a result of a decrease in blood pressure under the influence of "Magnesulphate".
Doctors recommend that after the procedure, lie down quietly for several minutes, and then slowly stand up.
Method of duodenal sounding and study of duodenal contents
For diagnosis, certain portions of bile are obtained from different places of localization and then microscopic and chemical analysis is carried out. The fluid intake procedure takes place in several stages:
- The patient is in a sitting position. The probe is inserted into an ajar mouth, placing the olive near the root of the tongue. The individual makes swallowing movements, and the probe begins to move along the pharynx into the esophagus. With vomiting, it is advisable for the patient to breathe deeply through the nose. In rare cases, anesthesia is performed. The first mark on the probe means that it is in the stomach. Unclear fluid will flow from the outer end of the rubber tube into the syringe.
- To facilitate further passage of the probe when taking the duodenal contents, the nurse performs the following manipulations: turns the patient on his right side, and puts a soft roller under the pelvic area so that the probe, under the weight of the olive, goes to the pylorus - the part of the stomach that passes into the duodenum.
- When passing a mark of 70 cm, the olive reaches the duodenum, and a transparent golden-yellow liquid begins to flow into the syringe. It is a mixture of bile, intestinal juice and pancreatic secretion and is called a portion A, which is placed in the first tube in a volume of 40 ml.
- To stimulate the secretion of bile, “Sorbitol”, “Xylitol” or “Magnesium sulfate” are introduced into the intestine, a clamp is placed on the probe for 10 minutes.
- After the break, they begin to collect a second portion of B, consisting of gallbladder bile. The process lasts half an hour to collect 60 ml.
- After 30 minutes, the secretion of hepatic bile begins, which has a bright yellow color. A portion of C is collected in an amount of 20 ml.
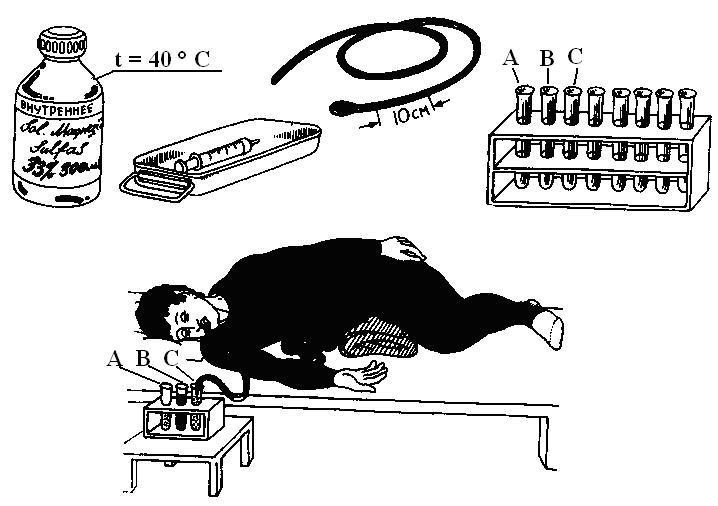
After the end of the fence, the probe is carefully removed. After half an hour, the patient can eat sparing food. Three collected portions of bile are sent to the laboratory for microscopic, chemical, and, if necessary, bacteriological examination.
What happens to the content received?
Each portion of the substance that requires research is collected in a separate sterile tube, in which the edges are fired before and after bile sampling using a gas burner. Tubes are immediately sent to the laboratory for testing. Delay in sending will violate the correctness of the results: leukocytes will be destroyed, giardia detection will be difficult, because when the temperature drops, they stop moving. Decryption of the analysis is carried out by a doctor with the appropriate qualifications. Registration of studies of duodenal contents is made by the doctor in writing and is recorded in special documents. Using duodenal sounding, you can detect the occurrence of viral and bacterial infections, the presence of stones in the bile ducts, pathologies in the functioning of the sphincter and walls of the gallbladder, various pathologies in the stomach and duodenum, traces of parasites. The patient with the obtained transcript of the results returns to the attending doctor for further treatment.
Physical properties of bile
As already mentioned above, the study is carried out necessarily on an empty stomach and after preliminary preparation in diagnostic centers, specially equipped offices of clinics or hospitals. Most often, when examining the duodenal contents, decryption is done in three portions of bile A, B and C. The physical properties of the investigated contents include:
- Color. Normally, a portion of A, which is taken from the duodenum, is stained with an amber, golden yellow tone, B (from the gallbladder) is of an intense yellow tint, C is a hepatic portion of a light yellowish tint. Color modification is performed with inflammation of the duodenum, as a result of the formation of stones and tumors of various origins, as well as impaired bile flow.
- Transparency. All portions of bile are normally transparent. A slight turbidity at the very beginning of sounding occurs due to an impurity of hydrochloric acid and is not associated with the inflammatory process.
- Density. In portion A, the upper limit is 1016, B - 1032, C - 1011. Its increase indicates the occurrence of gallstone disease, thickening of bile and impaired liver function.
Description of microscopic examination of duodenal contents
Immediately after the extraction of the duodenal fluid, a microscopic examination is done, because the white blood cells are destroyed ten minutes after the material is taken, and the other elements are a little later. In the absence of the possibility of an immediate study, formalin is added to bile, which adversely affects the processing results.
The bile of each portion is distributed in Petri dishes and analyzed in turn on a black and white background. Slime flakes are placed on a glass slide and examined under a microscope. Sometimes another method is used to study the duodenal contents. For this, bile is subjected to centrifugation for 7-10 minutes. The resulting liquid is drained, and the precipitate is subjected to microscopic examination:
- White blood cells. Normally, these elements are contained in a single amount. Their increased amount in bile indicates an inflammatory process in the bile secretion system. It must be borne in mind that white blood cells can enter the test fluid from the oral cavity, stomach and respiratory organs.
- Epithelial cells. The content in portions B and C of a large number of round epithelial cells indicates abnormal changes in the duodenum, and cylindrical - about inflammation of the biliary tract.
- Calcium bilirubinate. Microscopic examination of the duodenal contents is found in the form of shapeless grains of black, brown, brown or yellow-golden color. Their high content indicates cholelithiasis.
- Cholesterol crystals are quadrangular plates that are thin and colorless. Normally found in portions B in a small amount.
- Microlites are dark multifaceted or rounded formations consisting of mucus, lime and cholesterol. Identified with a predisposition to stone formation.
- Parasites - most often in bile they find lamblia and helminth eggs, which affect the liver and duodenum.
Chemical analysis
In a chemical study of duodenal contents, the presence of the following components is determined:
- Bilirubin (μmol / L). Its norm in bile: in servings A - 227, B - 657, C - 339. Increased values in the first two servings confirm stagnation and thickening of bile. Reduced - signal a failure of the concentration function of the gallbladder. When the indicators are modified in portion C, liver dysfunctions associated with the release of bilirubin are judged.
- Cholesterol (mmol / L). It is determined to establish an assessment of the colloidal stability of bile. In the study of duodenal contents, normal, the upper limit of cholesterol is in the portion A - 2.08, B - 10.04, C - 2.08. With cholecystitis and gallstone disease, these indicators increase.
- Bile acids. The functional abilities of the liver, gall bladder and bile ducts are determined by the amount of their content in the duodenal fluid. The secret of the duodenum normally does not contain free bile acids.
- Squirrels. In normal bile are absent. Their appearance indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process.

It should be noted that the indicators of the content of bile components may differ from the above. It depends on how they are defined, of which there are several.
Bacteriological research
A bacteriological examination of the duodenal contents of the duodenum and gall bladder is carried out to detect microorganisms in each portion of bile. It can be difficult to locate seeded microorganisms. It may mean the intestines, oral cavity and bile ducts. When conducting secondary surveys and sowing the same microflora in the same portion of bile, it is regarded in such a way that the microorganisms found were in the bile ducts. The norm is the complete sterility of all servings of bile.
Conclusion
The duodenal fluid of the duodenum includes intestinal juice, bile, pancreatic secretion, gastric juice, which enters the intestine through the pylorus, and a small amount of mucus. Under abnormal conditions, a significant amount of mucus, blood, pus, bile with a changed composition or digestive juice is added to this content.
Therefore, the study of bile and duodenal contents by a physical, microscopic, chemical and bacteriological method provides the necessary data on various lesions and functional activity of the pancreas, liver, biliary tract and duodenum.