The vascular system of the body is very important. Indeed, thanks to arteries and veins, blood and oxygen are delivered. Without this feature, people would not be able to live. The vasomotor center is responsible for this function of the body. Like all regulatory mechanisms, it is located in the brain. Its damage is very dangerous and often incompatible with life. Indeed, thanks to the vasomotor center, blood is distributed to the organs. It also partially regulates cardiac activity. Despite the autonomy of the myocardium, control of the nervous system is still necessary.
The concept of the vasomotor center
The concept of “vasomotor center” is explained in this way: it is an anatomical formation located in the brain. Nevertheless, this term should be considered more extensively. First of all, this is not one organ, but a set of formations consisting of nervous tissue. Each part is responsible for certain functions. However, they all work together in order to ensure the activity of the cardiovascular system. These departments of the vasomotor center are interconnected not only functionally, but also anatomically. That is, through nerve fibers. For the first time, the regulation of the vascular system became known at the end of the 19th century. When conducting experiments on animals, the scientist Ovsyannikov found that when transecting the nervous tissue located below the hillocks of the quadruple, changes in blood pressure occur. The physiologist made the following conclusion: a violation of this structure of the brain causes the expansion of some vessels, and the narrowing of others. After that, the regulatory function began to be actively studied.
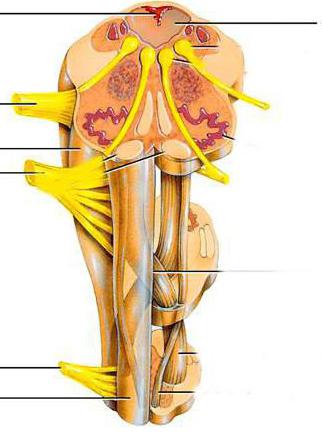
Location of the vasomotor center
The vasomotor center is believed to be located in the medulla oblongata. But if we take into account all the structures that affect the regulatory function of blood supply, then this judgment is not entirely true. Since the nerve fibers of the vasomotor center originate from the spinal cord, and the cortical layer is its last link. The first are axons - processes of cells. The neurons themselves are located in the three upper lumbar and all thoracic segments of the spinal cord. Their exact localization is the side horns. Because of their location, they are called spinal vasoconstrictor centers. However, this name is incorrect, since the fibers are not able to exert influence apart from other links. The vasomotor center of the medulla oblongata is located in the 4th ventricle. It is a collection of nerve cells. A more accurate localization of the vasomotor center is the lower and middle part of the rhomboid fossa. Some neurons are located in the reticular formation.

The following departments related to the regulatory links of the center are the hypothalamus and midbrain. There are nerve fibers responsible for changes in vascular activity. The final link is the cerebral cortex. The pre-, motor, and orbital departments are more involved.
Vasomotor Center: Organ Physiology
If you imagine all the links of the vasomotor system from the bottom up, you should start with the neurons located in the spinal cord. Sympathetic preganglionic axons (fibers) depart from them. These links are not able to independently regulate the tone, but they transmit impulses from other nerve cells to the vessels. For the first time, the scientist Ovsyannikov learned about their significance, thereby making a great discovery in physiology. He found that when the brain and spinal cord are separated, a drop in blood pressure occurs. However, after some time, blood pressure rises again (below the initial level) and is independently supported by preganglionic fibers. In the medulla oblongata there is a nerve center - the vasomotor. It is he who is responsible for the regulation of the spinal section. His physiology is as follows: the neurons located in this center are divided into 2 types. The former are responsible for pressor function (vasoconstriction). The second group leads to relaxation of the endothelium. It is believed that the neurons responsible for vasoconstriction prevail in quantity. Cells in the midbrain can cause an increase in blood pressure. Neurons of the hypothalamic region, on the contrary, act as depressors, that is, lead to relaxation of blood vessels. Most of the nerve fibers pass through the center located in the medulla oblongata. In addition, part of the axons directly connect the spinal section and the hypothalamus. The anterior region of the cerebral cortex affects both the enhancement and inhibition of the activity of neurons located in the underlying links.
Division of the vasomotor center into departments
Given that the regulation is carried out by several parts of the nervous system, the following sections of the vasomotor center can be distinguished:
- Spinal cord. In the lateral horns of the thoracic and lumbar segments are preganglionic nuclei. Axons - fibers depart from them.
- Directly vasomotor center. Neurons responsible for endothelial relaxation and vasoconstriction are localized in this section.
- Midbrain. The cells available in this department can cause narrowing of the vascular wall.
- Hypothalamic region. Neurons responsible for the relaxation of vascular tissue are connected both with the center itself and separately with the cells of the spinal cord.
- The area of the cortex. Despite the fact that the main part of neurons is located in the anterior region, the influence of other parts of the brain is not excluded.
Despite the presence of 5 departments, physiologists subdivide vasomotor regulation into only 2 links. These include spinal cord fibers and the bulbar region. It contains all other nerve cells that affect vascular tone. Both classifications are considered correct.
Vasomotor center: organ functions
As you know, the main purpose of the vasomotor center is the regulation of tone. Each of its departments performs its own function. Nevertheless, switching off at least one link leads to disruption of the blood vessels of the whole organism. The following functions are distinguished:
- Conducting impulses (signals) from the cortical departments and the medulla oblongata to the periphery. This refers to the effect of neurons on blood vessels and blood supply organs. This function is carried out thanks to the spinal preganglionic fibers.
- Maintaining vascular tone. During normal operation of each department, blood pressure is maintained at the proper level.
- Relaxation and narrowing of blood vessels. The center located in the medulla oblongata has a direct effect.
- Ensuring adequate blood flow and its distribution to each organ.
- Thermoregulation. This function is carried out through changes in the lumen of the vessels. Their expansion is observed in a warm environment, and narrowing occurs at low temperature.
The connection of the center with the heart
In addition to the fact that the vasomotor center is responsible for the narrowing and expansion of endothelial tissue, it also affects the heart muscle. This involves cells located in the lateral part of the fossa 4 of the ventricle.
It is known that the
innervation of the heart is due to sympathetic fibers. On them are impulses from the medulla oblongata. As a result, cardiac activity is activated. This is manifested by tachycardia. Neurons of the vasomotor center also participate in the weakening of the activity of the heart. They are located in the medial part. From there, the signals go to the dorsal nuclei of the
vagus nerve. Despite the fact that one function of the heart muscle is automatism, its work is impossible without the participation of the brain.
Regulation of the vasomotor center
Cortical structures can affect the neurons of the vasomotor center located in the medulla oblongata. After all, they are the main mechanism of regulation of all underlying departments. Cortical neurons can cause both a decrease and an increase in the activity of the vasomotor center. In addition, there is reflex regulation. It is carried out from the sinuses of the carotid arteries and from the aortic arch. This is due to mechanoreceptors. From their surface, impulses rise along the vagus and depressor nerves to the vasomotor center. In this case, the activity of the depressive part of this department is enhanced. The result is relaxation of blood vessels and a decrease in blood pressure. Also, vasodilation is caused by activation of the vagus nerve nuclei.
Changes in the tone of the vasomotor center
Under the influence of various factors, dysregulation occurs. As a result, the tone of the vasomotor center changes. Under normal conditions, this is due to reflex regulation. With pathologies, a violation of tone occurs. Examples are various vascular diseases, atherosclerosis, and obesity. Also, a decrease or increase in tone can be regulated under the influence of drugs (antihypertensive drugs, vasopressors).
The effect of chemicals on the vascular center
A direct effect on the regular mechanisms of the vascular system can have chemicals in the body. An example is carbon dioxide, which accumulates in the blood with a lack of oxygen (asphyxiation). Under the influence of this substance, the vasomotor center is stimulated. In severe cases, a prolonged lack of oxygen can lead to paralysis.