Tick-borne encephalitis can be transmitted by a person in a particularly severe form, which even leads to death. In the early stages, it is similar to other dangerous diseases, such as acute poliomyelitis, typhus, tick-borne borreliosis, etc. This is why it is important to make a diagnosis that will show the real cause of the symptoms that have appeared. In this article, we will understand how and when to take a blood test for borreliosis.
Borreliosis and viral encephalitis occur in the same regions, occur after tick suction in spring and summer, so they need to be differentiated. If an insect is found on the body, it is necessary to immediately analyze the biomaterial, and if the result is positive, take urgent measures in the next four days after contacting the therapist or infectious disease specialist.
Features of borreliosis and encephalitis
Encephalitis and borreliosis (Lyme disease) are transmitted by ticks in Russia. These infectious diseases are often confused, although they differ dramatically. Tick-borne encephalitis is viral in nature, while borreliosis is bacterial. Both diseases affect the central nervous system, but Lyme disease also affects the joints, heart muscle and skin. Encephalitis is characterized by an acute form, while borreliosis is a chronic course. Developing, each disease receives pronounced differential symptoms. A blood test for encephalitis and borreliosis will help determine the infection.
What is more common?
In Russia, from six to eight thousand new cases of borreliosis are registered each year, and encephalitis is less common - five to six thousand diagnoses.
Tick-borne encephalitis is caused by a virus of the flavivirus family (arbovirus group) and is transmitted by the bites of European forest and taiga ixodid ticks, although there have also been cases of infection through the gastrointestinal tract due to the consumption of raw milk from infected animals (sheep, cows, goats). As the virus develops, slow but often irreversible changes occur in the vessels and membranes of the brain.
At first, the disease is not symptomatically expressed, but by the third week there is an increase in temperature, muscle and headaches, loss of appetite, and nausea. A quarter of patients feel these symptoms even later, after a month. Over time, the pain becomes stronger, limb paralysis, cramps, loss of consciousness, disorientation, coma appear. If help is not available, death can occur . A blood test will help identify the disease in a timely manner.
There are several forms of tick-borne encephalitis, depending on various symptoms. The heaviest are recorded in the Far East, the lungs prevail in the Central European part of Russia.
Is encephalitis treated?
It is possible to cure encephalitis, but it requires a large number of drugs and methods. In this case, there is no specific type of treatment leading to recovery. Therapy is carried out exclusively in a hospital with the appointment of pathogenetic, etiotropic and symptomatic drugs. Compounds with anti-inflammatory, immunological, antiviral, hormonal, anticonvulsant, neuroprotective, psychotropic and other actions are also prescribed in a complex manner. After this, rehabilitation treatment is prescribed: physical therapy, psycho-and occupational therapy, speech therapy, etc. For several years, there may be convulsions, symptoms of muscle atrophy, cognitive degradation and other disorders of the central nervous system. Sometimes the consequences can remain for the rest of your life.
It is worth noting that the most effective protection against encephalitis is the person’s own antibodies, which the body produces after the vaccine is administered in the autumn, six months before the start of the dangerous season. Vaccines are widely prescribed that promote rapid prevention: three doses over twenty-one days, giving up to 97% guarantee of protection.
What about borreliosis?
A blood test for borreliosis is important because there is no vaccine for the disease. In addition, a person does not have a stable immunity to bacteria, he can get sick again.
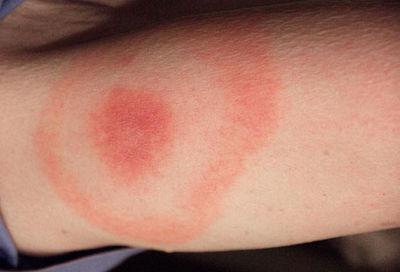
Lyme disease appears in humans after ingestion of Borrelia bacteria. It is immediately attacked by the immune system and moves to where the immune system cannot cope - in the heart, nerve tissue, and tendon. For this reason, unlike encephalitis, the acute stage is not observed, and the disease becomes protracted. The main distinguishing symptom is a migrating annular erythema, which has the appearance of a bright red spot at the site of a bite, gradually growing in size and forming a ring. The skin peels off and necrosis appears. Erythema, which is allergic in nature, may also appear on other parts of the body. In some forms of the disease, they may be completely absent, but intoxication and fever appear, which makes borreliosis almost indistinguishable from encephalitis. A blood test for tick-borne borreliosis and encephalitis will help to differentiate the disease.

After a month, symptoms of central nervous system damage appear: partial limb paralysis, speech disorders, mood swings. Meningitis may develop. If no action is taken, arthritis, hearing loss, neuralgia, disorientation, severe speech defects begin to progress in a year.
The carriers of the class of bacteria to which Borrelia belongs are the same mites that are carriers of encephalitis. The causative agent of Lyme disease lives in the digestive system of the tick, and not in its saliva, so it does not immediately spread in the human body. With timely removal of the insect, there is a chance not to get infected.
Borreliosis is treated, the main thing is to avoid the transition to the chronic stage. The patient is prescribed medications, the correct intake of which guarantees recovery.
Lyme disease is not transmitted from person to person, but there is a chance of transmission from a pregnant woman to the fetus. That is why this disease is sometimes diagnosed in newborns.
A blood test for borreliosis, and for encephalitis can be taken in infectious diseases hospitals, commercial and virological laboratories. The main thing is that the clinic conducted parallel studies of both diseases.
Encephalitis Tests
A study is carried out of venous blood (taken from the ulnar vein) and a tick removed from the body.
The following analysis methods are available:
- immunoassay - determines the presence of antibodies to the virus in human blood (two classes: IgG and IgM), due to its high sensitivity it makes it possible to see the disease in the early stages.
- PCR testing of a tick whose task is to determine the presence of encephalitis virus DNA in an insect. Fragments are also suitable for this type of analysis if it was not possible to extract the whole tick. In case of infection of the insect, the patient is immediately given a special immunoglobulin that suppresses the development of the virus. This method saves about 60%. Better protection is provided by routine vaccination. But this does not mean at all that the patient should give up, because the most important thing is timely diagnosis and monitoring of his well-being.
Antibodies to the virus are produced only after 10-14 days, so there is no point in taking tests before this time. By the end of the month and for six months, a peak in concentration is maintained. The insect needs to be brought immediately after removal, and if there is an infection in it, the patient should be observed by a doctor, and be tested after two weeks (it is worth noting that it does not require special preparation, it is only necessary not to eat food four hours before visiting the laboratory) .
Decryption
The results of the analysis for IgG antibodies are quantified with the appearance in the decoding of the concept of “titer” - an indicator of the concentration of antibodies (for example, 1: 100, 1: 400, etc.). If more than 1: 100, then the immune system responds. If less, then this shows the absence of a reaction, and when a virus enters, a person will definitely get sick. The indicator of a healthy body is from 200 to 400.
The results of a blood test for IgM antibodies are of a qualitative nature: detected or not. If the blood contains IgG and no IgM, such results are likely to indicate vaccination. And the presence of both indicators indicates infection. Repeated examination should be repeated after a week to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Blood test for borreliosis
Borrelia is difficult to see, so indirect methods are used. The most acceptable way is serological tests. Venous blood is taken and examined for the presence of antibodies to spirochete. In addition, synovial and cerebrospinal fluid are also being investigated. The tick must be brought to the laboratory immediately after removal from the body by placing it in a biomaterial container or in a test tube.
There are several blood tests for borreliosis. The decoding is presented below.
- Chemiluminescent immunoassay allows you to examine the serum of venous blood for the presence of IgG and IgM in it to the pathogen. This is the main diagnostic method, but it needs to be done 2-4 weeks after the bite, when antibodies appear in the blood.
- Immunoblot (Western blot) - provides an accurate diagnosis in patients with symptoms of Lyme disease, but negative immunoassay results. For example, in those who have already had borreliosis and have kept antibodies in their blood.
- Real-time PCR is used when serological tests are not informative.
- PCR analysis of the insect allows you to find DNA fragments of pathogens in the tick.
Since borreliosis does not immediately develop, it is necessary to take tests at certain times. In a hurry, a false negative result can be obtained. Peak antibody concentrations are observed after three months. Before taking a blood test for encephalitis and borreliosis, for four hours you should stop smoking and do not eat.
The test results can be both qualitative (“detected” or “not detected”), and quantitative, that is, indicating the number of antibodies.
Decoding IgG antibody assay
The interpretation of the values is as follows:
- Less than 10 U / ml - “negative” (no infection or analysis was done early).
- From 10 to 15 - "doubtful."
- Above 15 is “positive.” Such a result may also indicate a past illness and the patient's presence of bacterial endocarditis, syphilis, mononucleosis or other diseases. A blood test for borreliosis is best repeated in one to two weeks.
IgM antibody test scores
The decoding is as follows:
- Less than 18 U / ml - "negative".
- 18–22 - “doubtful.”
- More than 22 - "positive." The recommendations are the same as in the previous analysis.
A Western blot test appears with bands on the membrane, indicating the presence or absence of antibodies to specific antigens. The method is effective as an extra.
The conclusion may be as follows:
- "Positive" - IgM antibodies are present;
- “Negative” - no antibodies;
- "Indefinite" - weak bands that do not allow to judge the presence or absence of antibodies.
It is impossible to diagnose borreliosis on the basis of one analysis, since the process of its development is too complicated. It is also necessary to simultaneously pass tests for encephalitis, since ticks can be carriers of both diseases.
In the article, we examined how blood tests for tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis are given and transcribed.