Dysenteric amoeba is the simplest unicellular organism. However, despite the harmless dimensions, it poses a serious threat to humans. You will learn about the features of the structure and activity of the amoeba of this species from our article.
General characteristics of the kingdom
Representatives of this systematic unit are distinguished by a primitive structure. Dysenteric amoeba is no exception. The body of the simplest animals consists of one cell. Its surface apparatus, unlike similar algae and fungi, is devoid of a dense shell.
A single cell is able to carry out all the processes of life. So, the movement is carried out using specialized organelles: flagella, cilia or pseudopods (pseudopodia). The breakdown of organics occurs due to the digestive vacuoles, and the excretion of metabolic products - contractile. Gas exchange occurs through the surface of the cell. Reproduction can be both sexual and asexual.
Type Amoebae
The representative of the protozoan group, which is discussed in our article, moves with the help of pseudopods. So called inconstant outgrowths of the cytoplasm.
Dysenteric amoeba - a parasite related to the type of amoebozoi. It lives in the large intestine of animals and humans. Although among the representatives of this type, free-living species and saprophytes are found. Dysenteric amoeba is a heterotrophic organism that feeds on red blood cells and intestinal epithelial cells.
Life Cycle of Dysenteric Amoeba
Throughout life, this organism goes through several stages. Each of them has its own morphological and physiological features. But at each stage, the dysenteric amoeba is a unicellular structure of an irregular shape. During the movement, it forms specialized organelles. They are called pseudopods, or pseudopodia. These are outgrowths of the cytoplasm that form, and then disappear. But the number of nuclei and the structure of the cytoplasm can vary significantly depending on the stage of development.
At the dormant stage, the dysenteric amoeba is a cyst - a cell covered with a dense membrane. Being in the environment, it does not show signs of life. But when it enters the body, the active phase begins. Amoeba sequentially goes through the following forms: intermediate, luminal, tissue, vegetative.
The process of dissolution of the dense shell of the cyst is facilitated by enzymes that are in the lower part of the small intestine. As a result, an intermediate form with four cores is formed. It begins to divide by mitosis until 8 new cells form. Each of them contains one core. This is a translucent form of dysenteric amoeba. It descends into the large intestine, where it continues to divide. This is the next period of development of protozoa, which is called the vegetative form.
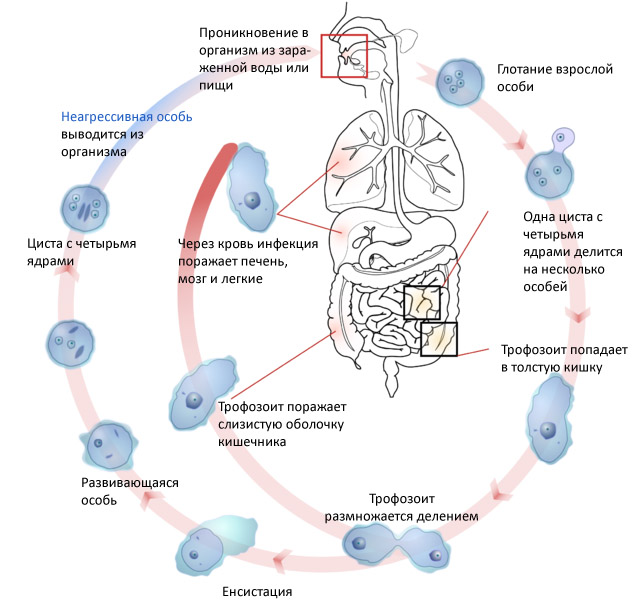
Amoeba gradually penetrate the intestinal mucosa, which causes ulcers and colic in the host. This stage of the life cycle is called tissue. Some of these individuals again enter the intestinal cavity. Here, protozoa absorb red blood cells - red blood cells. At the same time, the size of amoebas increases significantly. This determines the name of this stage - a large vegetative. For the host, it is the most dangerous. The development of dysenteric amoeba of this form is the most dangerous, since it causes damage to blood vessels. This is the path of their penetration into other organs and causes a further abscess. This is especially true for the liver.
Amoeba enters the environment along with feces. If this happens at the vegetative stage, then amoeba die very quickly. In the case of cyst formation, the viability of amoebas increases significantly. They are also excreted from the host with feces and remain there until they enter it again.
Ways of infection and prevention
Dysenteric amoeba is an extremely prolific organism. Just imagine: within a day about 300 million individuals develop from one cell. How can these parasites enter the body? There are several ways. This is the use of insufficiently thermally processed foods, boiled water, unwashed vegetables and fruits. Bathing in a natural or natural body of water, a person is also at risk of infection in the event of accidental ingress of fluid into the body.
The carriers of the parasite are many insects, for example flies or cockroaches. Therefore, food contaminated by them is also a source of infection. But the main danger is an infected person. If he does not follow basic hygiene rules, then the parasite can fall on any surface with which it came into contact. This can be bedding, dishes, clothes, towels, pet hair. You can become infected with a dysenteric amoeba even through a handshake. Moreover, on any surface, parasites can remain viable for about 7 days.
To avoid infection with dysenteric amoeba, basic hygiene rules should be observed. So, in food it is necessary to use only well-washed or thermally processed products, as well as boiled or bottled water.
Translucent form
This stage is the first in the active phase of the development of dysenteric amoeba. It develops from a cyst. The size of its cells in this period is 20 μm, and the place of dislocation is the upper part of the large intestine. The translucent amoeba cell has one spherical nucleus, actively moves with the help of pseudopods, feeds on bacteria.
Fabric form
When an amoeba of the luminal stage enters the mucous membrane of the large intestine, it proceeds to the next stage. At the same time, its dimensions increase to 60 microns. The tissue form of amoeba is characterized by a change in the composition of the cytoplasm. It does not contain inclusions. So called inconstant cell structures. The tissue form of the amoeba is constantly being divided. This causes the development of ulcers, the appearance of mucus, purulent and bloody secretions.
Large vegetative form
Some of the dysenteric amoeba cells from the mucous membrane return to the intestinal lumen. Here they acquire the ability to absorb red blood cells, so the amoeba of this stage is also called erythrophages. It is they that cause the acute phase of the disease, since the vessels can move to other organs. Here they cause extraintestinal amoebiasis, or secondary foci of inflammation.
Cyst stage
The structure of the dysenteric amoeba of this form is characterized by the formation of a dense membrane around the cell of the luminal form. Its size is 12 microns, and the cytoplasm contains a vacuole rich in glycogen carbohydrate. The formation of cysts occurs when undigested food debris accumulates in the colon.
Once in the environment with feces, in the presence of moisture, they can remain alive for a month. If infection occurs, cysts divide and again turn into luminal forms.
Signs of illness
Dysenteric amoeba causes serious disruption of the activity of many organ systems. The disease amoebiasis, which causes this organism, manifests itself in the form of intoxication. A person experiences nausea, vomiting, cramping abdominal pain, diarrhea, dizziness. Body temperature often rises.
Initially, such symptoms are very reminiscent of typical dysentery. But they are only manifestations of the incubation period of the disease. A maximum of a month later, these symptoms appear. These include frequent urge to defecate - from 4 to 20 times a day. In this case, blood clots appear in the stool. This process is accompanied by an increase in body temperature above 38 degrees, sometimes fever. During bowel movement, pain intensifies.
These are manifestations of the acute form of the disease. If you do not take any measures within a month, it develops into a chronic one. And initially there is an improvement in well-being and unpleasant symptoms disappear. This is a stage of remission that lasts several months.
Next, manifestations of the chronic form of amoebiasis begin, which can last for years. Its symptoms are somewhat different from acute. These include a decrease or complete lack of appetite, which leads to weakness, rapid fatigue and further exhaustion. The physiological manifestations of amoebiasis also include the appearance of an unpleasant aftertaste in the oral cavity, an increase in the size of the liver, heart palpitations, pulse rhythm disturbance, and pallor of the skin. The latter is a manifestation of anemia - a decrease in hemoglobin levels. This disease is a consequence of the defeat of red blood cells by parasite cells.
Diagnosis and treatment of amoebiasis
Since the symptoms of this disease are similar to other infections, a number of tests are necessary. First of all, this is a microbiological study of feces. Usually, a large vegetative form or parasite cysts are found in patients.
Amebiasis treatment is medication. Depending on the form of the disease, there are drugs that affect unicellular, which are located in the walls or lumen of the intestine, as well as the liver. In folk medicine, tinctures from the fruits of sea buckthorn or hawthorn, bird cherry, caraway are used. Decoctions of herbs of plantain, cinquefoil, shepherd’s bag, horse sorrel will also be effective.
So, dysenteric amoeba is a unicellular parasite that causes a dangerous disease - amoebiasis. Infection occurs by contact through infected surfaces. When symptoms of amoebiasis appear, you must consult a doctor and undergo a number of necessary studies.