The organizational structure of an organization is ... What? A diagram of the squares with the names of units of the organization, built in a certain order?
It is generally accepted by the layman that the organizational structure is a certain theoretical concept that has a very mediocre relationship to a real-life organization. Moreover, within some existing enterprises, when they carry out economic activities, the organizational structure is given too little importance. As a result, there are vague functions and responsibilities among the heads of departments, the randomness of the subordination system, the lack of coordination of work and tasks to achieve the common goal of any business - making a profit.
Analysis of the financial condition of the organization begins with a study of its organizational structure. Who needs this? Representatives of the external environment of the company - lenders, investors, suppliers, buyers and customers, they all need to clearly understand the logic of the partner company. Representatives of the internal environment - directly to employees of the enterprise, who also need to know how they interact with colleagues, to whom they obey, and to whom part of the duties can be delegated. The set of groups of all employees makes up the organizational structure of the organization’s personnel.
What is an organizational structure?
So what is this concept? The organizational structure of an organization is the totality of all its units, between which functions and tasks are distributed, as well as the relationship between them.
Organizational structure of enterprise management
The organizational management structure is the configuration of the management system that defines the authority and responsibility, accountability and the relationship between the heads of departments, as well as establishing a list of staff duties.
Among the main types of organizational structures, linear, functional, linear-functional, divisional, matrix, and combined are distinguished.
Linear structure
The linear type of organizational structure is characterized by the fact that each unit of the organization is managed by one leader, who reports to a higher leader, etc. This type has outlived itself because it is not flexible and does not contribute to adaptability to economic changes and the growth of the company in modern conditions. The leader must be able to navigate in different areas, to be truly a specialist with a wide profile in order to give orders to each service of the organization. Although the basic advantages of the linear type can be distinguished by its simplicity, the clarity of the relationship of the enterprise units and their functions.
The linear structure of the organization on the example of the army
The most striking example for characterizing the linear form of organizational structure is the army, where, as you know, a clear-cut organization scheme for the subordination of the junior in rank to senior is guided.
The organizational structure of the officer corps of the army is presented above.
Functional structure
A functional organizational structure assumes the existence of separate services in an organization (for example, a sales department, a personnel department, an accounting department, a production and technical department, etc.), each of which may interact with each other, and not just with the main manager. This removes most of the burden from the chief manager, removes the task of searching for wide-profile specialists, which are the advantages of this structure. The presence in the departments of specialists in their field contributes to improving the quality of products. Nevertheless, the use of a functional organizational structure complicates intercompany relations and contributes to the development of a tendency to shift the responsibility of employees of some services to employees of others.
The functional form of the organizational structure of management on the example of the organization for the production of dairy products
Consider this type of organizational structure on the example of the food industry.
The functional type diagram of the organizational structure shows the relationship between the departments of the enterprise. So, for example, the transport department interacts in the process of fulfilling its duties with the financial service divisions: with accounting for fuel consumption rates and write-off of spare parts, with a sales department for issuing shipping documents and coordinating the route, with a warehouse of raw materials and the main production for transportation between them materials for workshop needs, etc. That is, units are functionally related to each other, but not subordinate to each other.
Linear Functional Structure
The linear and functional forms of organizational management structures are rarely used in their pure form. To solve the shortcomings of these types of organizational structures is able to linearly-functional management structure. With linear it generalizes the presence of linear managers, from the functional she borrowed the presence of functional services that help the first, but they are not administratively accountable to them.
Among the advantages of this structure, it should be noted a reasonable correlation between unity of command and narrow-profile specialization of heads of functional services; the ability to delegate authority to lower levels of linear links of functional services. But the disadvantages include a low degree of interaction between the personnel of functional units, since the relationship is often debugged only among their leaders. The principle of unity of command, when strengthened, can adversely affect the quality of products manufactured and sold.
Linear-functional structure on the example of a home appliance store and digital electronics
To illustrate clearly what this type is, we will present in the form of a diagram the organizational structure of a household appliance store and digital electronics.
In the diagram, solid lines show linear connections, and dashed lines show functional ones. So, for example, the cash desk is directly (linearly) accountable to the accounting department, but in the process of performing its functions it interacts with the cash collection sales department, with the store sales department, with the submission report funds department, with the purchasing department for organizing payment to suppliers and contractors in cash . The store’s sales departments are directly subordinate to the sales department, but in the process they are functionally interconnected with the procurement department, accounting, and personnel services.
Divisional structure
The divisional structure is distinguished by the fact that the units are grouped according to some criterion: by type of output, by region, by consumer group. The positive aspects of using this model are a high level of response and adaptability to changes in the external environment of the company, the release of a product of higher quality and competitiveness due to the orientation of all participants in the production process in one division. Among the minuses of the structure, it should be noted such negative phenomena as duplication of functions of units and management, the growth of conflicts due to the duality of subordination, the complexity of managing divisions as a whole.
Divisional structure as exemplified by a food manufacturing plant
As an example, the organizational structure of a food factory is presented. The company manufactures several types of products. One of the directions is the production of soft drinks and kvass, and the other is the production of gingerbread and cookies.
As can be seen from the diagram of the divisional organizational structure of the enterprise, it took the types of products as the basis for divisional separation. Each includes a team of workers, a laboratory service, a group of sales managers and the composition of accounting for payroll, costing the product, etc.
Matrix type of organizational structure
A matrix structure is a type of dual accountability structure. This type of organizational structure implements itself in design work. For example, an organization receives an order to perform some type of work. To do this, a project manager is appointed and a number of performers from different functional services are assigned to him. However, they do not leave the subordination of their immediate superiors, but upon completion of work they return back to their unit. Among the advantages of this type of organizational structure: high response rate and susceptibility of the enterprise to changes in the external environment, high level of adaptability, optimal distribution of powers, responsibility, accountability between functional and linear units. The disadvantages include the confusion in prioritizing tasks between working on a temporary project and a permanent unit, which also poses the threat of conflicts between project managers and the management of functional units. The principle of dual accountability greatly complicates the entire management system.
To more clearly imagine this form of organizational structure, let us turn to the scheme of the enterprise, which took it as a basis.
The company has 5 types of activities: emergency dispatch service, which provides emergency response services to several companies; the provision of ongoing sanitary repair of residential buildings; intercom installation services; Wholesale and retail trade in electrical equipment. But also the company takes part in electronic bidding and undertakes the implementation of temporary projects. For each individual project, its leader is appointed, and a number of employees from each functional unit are released to subordinate to it: accountant, personnel officer, procurement officer and work team. After completion of work on the project, the production team dissolves in places of direct duties.
Combined structure
The main characteristic of the combined organizational structure of the organization is the combination of several of the above types. It contains features of linear leadership, functional relationships, division of services according to selected criteria, as well as the principle of duality of subordination. The combined organizational structure makes it possible to increase the flexibility of the enterprise and its susceptibility to changes in the internal and external environment. The advantages and disadvantages of the combined structure are the same as the structures underlying it.
Combined management structure as exemplified by an apatite-nepheline ore mining and processing enterprise
Consider this form of organizational structure on the example of an organization having branches in different regions of the country, as well as engaged in several types of activities. The following is a diagram of a combined organizational structure.
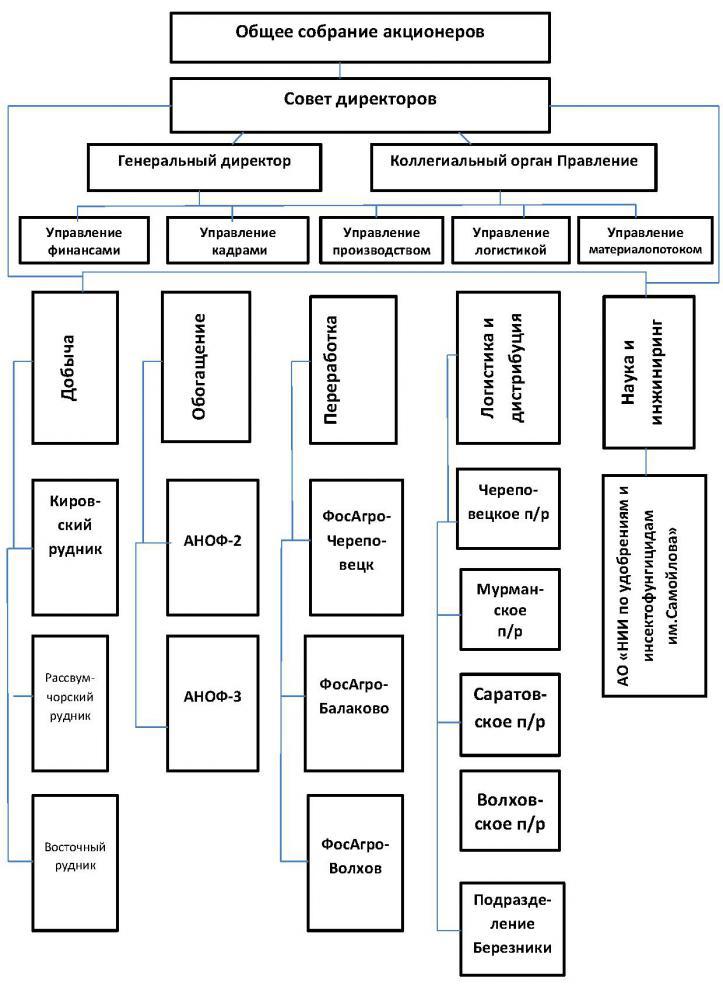
The management is carried out by the general meeting of shareholders, which stands above the board of directors. The Board of Directors appoints the General Director and the composition of the collegial body of the Management Board, whose responsibilities include managing the strategic development of the enterprise. The Management Board and the General Director are linearly subordinate to the Department of Finance, Human Resources, Basic Production, Logistics and Material Flows. The functional units of the Complex are enterprises engaged in mining, beneficiation, processing, transportation of ore, as well as a research group. The organizational structure of organizational units operating in different regions is also made up of linear and functional services.
Regardless of the form, the organizational structure should perform the functions of dividing tasks between the services of the organization, determining the competence of each of them in achieving the final result of activities, and also control the inviolability of interconnections between departments.