The femoral muscles surrounding the femur, depending on the location, are divided into several groups: anterior, posterior and medial. The back group is responsible for upright and straightening the body, hip extension in the hip joints and flexion of the legs in the knee joints.
The back group consists of the following muscles:
Location
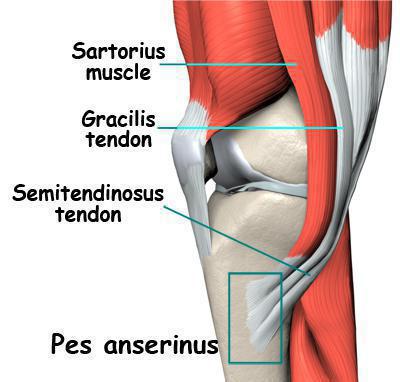
The semi-membranous muscle of the thigh is located under the semi-tendon muscle. Muskulus semimembranosus (semi-membranous muscle) begins with the lamellar tendon, which makes up its entire upper part, attaching its upper part to the sciatic tubercle, and then descends along the medial (inner) edge of the thigh. The final (distal) tendon of the semi-membranous muscle breaks up in the area of the lower attachment into three tendon bundles, forming deep crow's feet on each of the thighs.
One of the bundles is attached to the fascia, which covers the popliteal muscle, the second to the internal condyles of the tibia (tibia) on both legs, while the third, turning to the back wall of the knee joint, is part of the posterior oblique popliteal ligament.
Where the tendon of the muscle is divided into several bundles, a synovial bag (bursa muskulus semimembranosi) of the semimembranous muscle is located.
Functions
Semi-membranous muscle performs a number of important functions, providing movement of the lower limb in the hip and knee joints:
- Bends the tibia in the knee joints.
- Rotation (rotation) of the lower legs inward with bent knees (the muscle protects the synovial membrane from pinching by pulling the capsule of the knee joints).
- Hip extension in the hip joints.
- Tonic muscle.
- If the legs are fixed, then the semi-membranous muscles, together with the gluteus maximus muscles, are responsible for the extension of the body.
Nutrition and innervation
The blood supply to the semi-membranous muscle is an artery that wraps around the femur, the popliteal and perforating arteries.
The innervation of the muscle is carried out by the tibial nerve.
Semi-membranous muscle diseases
- Injuries - sprain of three degrees of severity, including partial and complete rupture.
Tendopathy is a pathology that is manifested by painful sensations in the posterior sections of the knee joint, aggravated after climbing up inclined surfaces, prolonged running, and bending of the knee joints with resistance. In this case, the maximum pain is determined at the places of attachment of the tendons on the posterior medial surface of the tibia slightly below the border of the joint. Between the capsule of the knee joint, the medial part of the calf muscle and the tendon, there is a bag inside which chronic bursitis can develop. It is necessary to conduct differential diagnosis with intraarticular pathologies. They treat tendonopathy of the semi-membranous muscle similarly to tendopathies of other localizations.
Insectinitis in the goose paw area manifests itself with increased external rotation or with an attempt to turn the knee inward with a fixed lower leg (gymnastics, football, skiing). Clinical manifestations: increasing local swelling, pain during palpation, which intensifies when trying to remove the lower leg from its forced position of internal rotation. Most often, injuries of the goose foot are combined with damage to other stabilizing structures of the knee joint. Differential diagnosis of this pathology must be carried out with damage to the inner meniscus (its horn) and bursitis in this area.
Popliteal fossa cysts (Becker cyst) is an inflammatory process in the area of the mucous bag of the semimembranous and calf muscles (the presence of such bags is found in 60% of healthy people and is not a deviation from the norm). Clinically, a cyst manifests itself in the form of a densely elastic tumor in the upper part of the popliteal fossa, swelling, an increase in size (due to which compression of the surrounding structures occurs), discomfort, pain, and limitation of movement. More often, a cyst occurs a second time as a result of overstretching of the bag with fluid in chronic inflammation of the knee joint, which has a different etiology (rheumatism, tuberculosis, various injuries, osteoarthritis, and others).