Chickenpox, or, more correctly, chicken pox, is familiar to almost every inhabitant of the Earth. It is awarded to us by viruses with the melodic name varicella-zoster, discovered in 1911. More than a century has passed since that distant time. Varicella has already been studied far and wide, but so far man has no power to defeat it. The diseases caused by this virus do not seem particularly serious, because mortality from them is 1 in 100 thousand cases, and even then not from themselves, but from the complications caused by them. It is in these complications that his insidiousness lies. The varicella-zoster virus is able to penetrate the blood, lymph, and many body systems. It is impossible to expel him from there. Once in our body, the parasite remains with us forever.
Virus portrait
Varicella zoster belongs to the genus Varicellovirus, numbering 17 species. Among them, there are those that affect only certain animals or birds, and there are purely human ones. These include the type of “zoster” considered by us. This word means “belt” in Greek, which reflects the picture of rashes that is observed most often.
It is impossible to infect them from pigs, chickens, dogs and other animals. In the international taxonomy of infectious pathogens, it is called Human alphaherpesvirus type 3. All viruses are microscopically small, but each has its own unique "face." The microscope shows us that the varicella-zoster is round or slightly oval in shape, has a core consisting of DNA and a shell studded with spikes made of complex proteins. Once in the body of the victim, the virus causes chickenpox.
Infection pathways
The varicella-zoster virus infects only people, mostly pre-school children and primary school children. A particularly high number of infections in schools, kindergartens, in any large number of teams. The distribution paths are airborne (sneezing, coughing) and contact. On the body of a sick child, bubbles always form in which thousands of thousands of viruses can be counted. When these bubbles burst, pathogens with exudate enter the environment and can enter the body of a healthy person through dirty hands, objects, or through bodily contact, such as shaking hands. Viruses can exist favorably only in the cells of their victim, therefore, once outside, they become defenseless. They can be easily killed with disinfectants, boiling, any detergents.
Symptoms
Penetrates into our body varicella-zoster through the mouth, where it settles on the mucous membranes. Having conquered the first “bridgehead”, viruses invade the lymph vessels, blood, lungs, nervous and autonomic systems, and spinal cord cells. Having penetrated into these organs, they begin to multiply, and already having mastered in the body, they cause a disease. From the moment of infection to the first symptoms, 14 or more days may pass. The main sign of chickenpox is the appearance of blisters in the form of a rash throughout the body. At first they look like reddish nodules, but quickly increase to the size of a match head or a little less. In them under a thin skin is a transparent exudate. When the bubbles burst, the exudate flows out, and sores remain on the skin, which, when dried, turn into crusts.
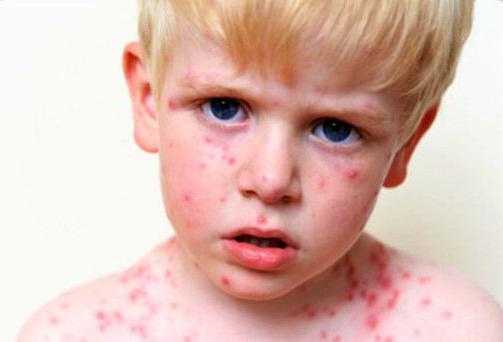
The temperature in sick preschoolers rarely rises to high values, and, as a rule, keeps around 37.5 ° C, signs of intoxication are most often not observed, but the child may be capricious, refuse to eat, and be lethargic. Older children (7-12 years old) tolerate chickenpox a little more difficult, although their disease can occur in a fairly mild form with a low temperature and satisfactory well-being.
With chickenpox, a rash is a problem, which in patients of any age is very itchy. Children itch and peel off, leaving lifelike pock marks on their skin.
In adults, primarily with chickenpox, the disease is more severe. They noted:
- weakness;
- headache;
- high temperatures;
- body aches;
- sleep disturbance;
- sometimes nausea before vomiting and impaired stool.
Chickenpox in pregnant women and newborns
Among pregnant women, chickenpox is rarely diagnosed (no more than 5%), since most expectant mothers have had it in childhood, and the body is able to develop antibodies to varicella-zoster. In a newborn, they also provide protection against this virus for up to 6 months. Therefore, babies with chickenpox practically do not get sick.
Unfortunately, if the primary infection with smallpox virus occurred during pregnancy, there is a risk of infecting it with the fetus (8%). If the disease occurred in the first trimester, 5% of babies may have various congenital malformations (convulsive syndrome, paralysis, rudimentary fingers, anomalies in appearance and organs). With a disease in the second trimester with deviations, 2% of children are born, and with a disease in the third trimester, cases are isolated.
But if mom got chickenpox five days before birth or within two days after them, chickenpox is very difficult in newborns, even deaths are possible.
Diagnosis of varicella-zoster, IgG, IgM and other antibodies
Previously, the diagnosis of chickenpox was made visually. Now doctors are conducting a series of tests to find out exactly which virus caused the disease and which antibodies are produced in the body. Modern diagnostics include:
- A smear from the oral cavity.
- A blood test to determine the type of virus.
- Analysis of exudate from the bubbles.
- Test for antibodies of the IgM group, which are formed almost immediately after the onset of the disease in pre-B lymphocytes, and are detected in the blood on the 4th day of the disease. Subsequently, antibodies of other groups are also found in patients. IgG antibody values grow slowly, but also slowly and decrease after the disappearance of visible symptoms and the attenuation of the disease. This property of them is used to diagnose the chronic forms of certain ailments.
Treatment
As a rule, patients with chickenpox are not hospitalized. At home they are given a course of antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Brivudin, Gerpevir), antipyretic, antihistamines are prescribed, and all rashes are lubricated with green or fucorcin. To enhance immunity, doctors also attribute vitamins and diet.
Antibodies to varicella-zoster virus, which are protection against repeated infections, remain in the body of patients who have been ill for life. These are mainly IgG antibodies, although IgA, IgM groups may also be present. The level of IgA antibodies drops significantly by the 4th month after the disease. Basically, they protect the mucous membranes of the internal organs and make up 20% of all antibodies. IgM of the total number of immunoglobulins is 10%, and IgG is 75%. They are the only ones able to pass through the placenta (due to their compact size), and give immunity to the fetus in the womb.
Complications
Since, after chickenpox, people have antibodies to the varicella-zoster IgG virus in the body, they get lifelong immunity. Complications of the disease in ordinary children can be infections entered in the comb of papules. In very weak children, the following complications are possible:
- pneumonia (symptoms: cough, fever, skin cyanosis, shortness of breath);
- encephalitis (symptoms: headache, fever, cramps, impaired coordination, nausea);
- bursitis;
- arthritis;
- thrombophlebitis.
In adults, against the background of chickenpox, they may develop:
- laryngitis;
- tracheitis;
- meningitis;
- encephalitis;
- hepatitis;
- arthritis;
- erysipelas;
- abscesses, phlegmon, streptoderma.
Shingles, causes
This disease is also called "herpes zoster." Once in the body, the zoster varicella remains to live in a latent (inactive) state in the nerve cells in the spinal cord, in the cranial nerves, in the ganglia (clusters of neurons) of the nervous system. While the human immunity is strong, they sit quietly and do not cause trouble. But as soon as the body weakens, viruses are instantly activated. As a result, there is no new chickenpox, but a person begins another ailment - herpes zoster, which belongs to the category of infectious diseases, and manifests itself with characteristic rashes on the body.
Causes:
- transfer of operations, injuries, other diseases, including acute respiratory infections, flu;
- nervous stress;
- poor nutrition;
- hard work, exhausting the body;
- poor living conditions;
- chronic diseases that have relapsed;
- pregnancy;
- hypothermia;
- organ transplantation;
- some drugs that suppress the immune system;
- elderly age.
Symptoms
Shingles is more commonly seen in adults, but in debilitated children who have had chickenpox, it can also be diagnosed. Its main visual sign is a rash on the body, mainly located where the nerve trunks pass. This ailment has nothing to do with herpes near the nose and lips, as it is caused by another virus, as the analysis shows. The varicella-zoster virus, having received freedom from immunity that held them in check, leaves the nerve cells and rushes along their axons to the tips of the nerves. Reaching the target, it causes a skin infection. Symptoms of the Harbingers:
- temperature;
- unexplained fatigue and malaise;
- prostration;
- loss of appetite;
- pain and itching (sometimes incomprehensible tingling) in places of future rashes.
Symptoms at the peak of the disease:
- rash in the form of vesicles with a transparent exudate;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- neuralgic pains (may be moderate or severe);
- temperature is higher than subfebrile;
- signs of intoxication.
The disease lasts from a week to a month.
Rash Type Classification
Varicella-zoster are able to affect different parts of the body, and therefore distinguish these types of shingles:
- Ophthalmic (the optic branch of the trigeminal nerve is affected, which can lead to damage to the cornea). It is manifested by pain in the eyes, a decrease in vision, a rash on the temples and under the eyes.
- Ramsay-Hunt syndrome (mimic muscles are affected, rashes are noted in the oral cavity and ear canal).
- Motor (myotomas and dermatomes are affected, patients complain of severe pain in the muscles of the limbs, forearms).
According to the course of the disease, these types are distinguished:
- abortive (without pain and rashes);
- cystic (rashes are very large);
- hemorrhagic (in the exudate of the vesicles there is blood);
- necrotic (in place of papules, necrosis of the skin occurs);
- generalized (rash throughout the body).
Diagnostics
Clinically and visually, shingles before the rash appears are often mistaken for appendicitis, angina pectoris, pleurisy, and other ailments. If necessary, laboratory analysis is performed. Varicella-zoster is detected by express diagnostics, consisting in the study of samples under a microscope. Immunofluorescence and serological methods are also used. Complex laboratory tests are carried out in cases:
- infants
- immunodeficient children;
- atypical herpes;
- the complex course of the disease.
In babies infected in the womb, a large number of IgG antibodies and IgM antibodies are found in large numbers. Differentiation is performed by PCR. This reaction also helps to detect viruses in the absence of a skin rash and its presence on internal organs.
Shingles Treatment
If the analysis turned out to be positive, the varicella-zoster is diagnosed with 100% certainty. After that, the doctor determines the treatment algorithm. I must say that in young people, shingles passes without drugs, but with a sparing diet and bed rest. Medicines can speed recovery and prevent complications, as well as relieve pain and fever, if any.
Antiviral drugs are prescribed for patients older than 50 years old, severely debilitated, having suffered injuries and operations, suffering from chronic ailments, and children. The prevailing drugs are Acyclovir, Famciclovir, Valaciclovir, and among the painkillers Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Naproxen and analogues. Also, according to indications, anticonvulsants, antidepressants, corticosteroids are prescribed. When infected with varicella-zoster, the patient's eyes and / or brain are hospitalized.
Complications
It is noted in 28% of cases of shingles. Patients complain of:
- visual impairment;
- hearing loss;
- frequent and unreasonable headaches;
- spontaneously appearing dizziness;
- body soreness after the rash disappears.
In some patients, the development of heart and / or kidney failure, complication of the course of cancer, blindness or deafness, damage to the tissues of the brain and / or spinal cord is possible.
As a prophylaxis, the Zostavax vaccine has been developed. Its effectiveness, established experimentally, is 50%.