A star named the Sun is the only one in our system. Other objects revolve around it, including the planet Earth, where we live. And given the disparate importance of this celestial body for the existence of all living things, including man on Earth, it is also important to know what the Sun consists of and how many more years it can shine.
Sun worship and study
Since ancient times, people have noticed the dominant role that this star plays for all living things. Many ancient cultures deified the Sun; there was a cult of worshiping it. It was revered as a deity in ancient Egypt, in pre-Columbian America. And some of the greatest constructions of mankind are dedicated to the Sun: Stonehenge in England, Chichen Itza in Mexico, for example. And given the sunny location, Egyptian pyramids were built. It is interesting that the ancient Greek astronomers considered the Sun to be one of the planets, on a par with the Earth. Of course, in those days no one knew what the sun was made of. So, for example, the Greek philosopher Anaxagoras considered it to be made of metal (for which, incidentally, he was thrown into prison and sentenced to death). And the idea that all the planets revolve around the center, which this star is, was expressed by scientists of Ancient India (and almost simultaneously - Greece), and was revived and developed by Copernicus in the 16th century.
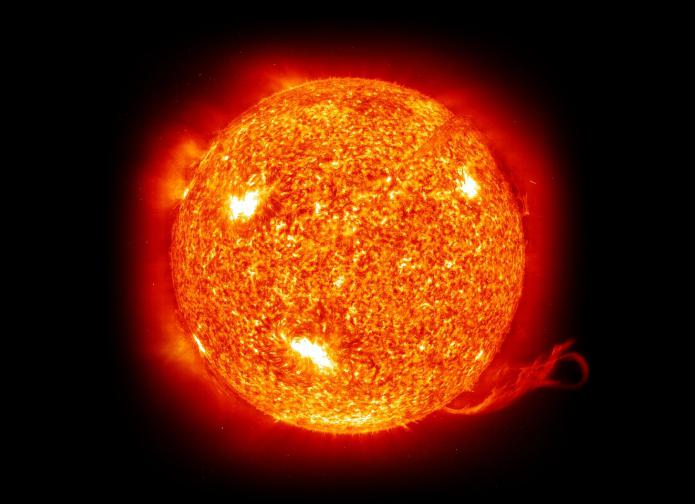
Modern science
Modern science, of course, has gone far ahead. Scientists have calculated and the mass of this celestial body, and its estimated volume, and the distance to the Earth. Observations are carried out visually with the help of the most powerful modern telescopes capable of magnifying so that everything is visible in the palm of your hand. With the help of artificial satellites launched into their respective orbits, priceless materials are extracted that contribute to a more detailed study. Now it is already known with precision what the sun consists of. And it also became clear to scientists "solntsevedov" and its qualitative and configurational composition.
Internal structure
Our star has a layered structure. It should be noted that its mass is more than 99% of the total mass of the entire solar system (for comparison, this is 330,000 times the mass of the Earth). According to the spectral classification, the Sun is of the yellow dwarf type. The core is the central part where thermonuclear processes take place (radius over 150 thousand kilometers). There is a very high temperature - over 14 million degrees, and the substance reaches a huge density. Energy and heat in the core are generated through this reaction, and the rest of the sun is heated by them. What is the core of the sun made of? Since a thermonuclear reaction occurs in the center of the star, and the hydrogen, which occupies the largest part in the composition, burns out, then, according to scientists, there is more helium (64%) and less hydrogen (up to 36%).
What the sun consists of
Well, this is with regards to the kernel. And the sun itself is mainly composed of hydrogen. Its 92% by volume, and by mass - 73%. The next element is helium (7% of the volume). Other elements are also present: iron and nickel, oxygen and nitrogen, sulfur and magnesium, calcium and chromium, and some others - these are the substances that make up the sun.
Two main layers
Two main layers can be distinguished: internal and atmospheric. The inner consists of three parts: core, energy transfer zone, convection zone. The atmosphere of the sun consists of three parts: the photosphere, chromosphere and corona.
Energy transfer through rays and convection
In the zone following the core, thermonuclear energy produced by the star’s core is transferred to the upper layers of the Sun. The temperature decreases gradually, and the wavelength increases. This segment occupies from 0.3 to 0.7 of the total radius from the center. The convection zone located next to it transfers energy through the convection process.
Atmosphere of the sun
The photosphere is the visible surface of the sun. She sends out spectral rays into the surrounding space. Its thickness is only 200 kilometers. And above it is a layer of the chromosphere, which is many times thicker - up to 20,000 kilometers. There continuously lower and rise gases, carrying out movement. Prominences sometimes appear in the chromosphere, protruding beyond the surface of up to 250,000 kilometers, visible even from the Earth. Sometimes the substance collected in a prominence overcomes solar attraction and breaks into open space. The solar corona, as it were, completes the construction of the Sun itself, rising 2 million kilometers. The appearance of the corona is not always the same and is associated with periods of activity of the star.
sunny wind
From the corona constantly flows a stream of particles that are ionized. These are mainly protons and electrons called the solar wind. They spread to the very borders of the solar atmosphere. Radiation reaches a myriad of particles per second. And their loss for a yellow dwarf in millions of years is a mass equivalent to the mass of a planet such as, for example, Earth. Phenomena such as northern lights or geomagnetic storms on Earth are directly related to the effects of the solar wind.
The sun and life on earth
For people, animals and plants that live on Earth, the Sun and the light emitted by it is an extremely important thing. In those places where rays fall in a limited number, a small variety of biological forms, shortening of the growth season for plants, and stunted species are noted. Sunlight is the basis for photosynthesis. And the chlorophyll contained in the leaves of plants is one of the main conditions for the emergence of life on Earth, according to most scientists. And many species of animals (and humans) exist due to the eating of plants and the accumulation of solar energy in organisms. Another important factor for the existence of all living things is the ultraviolet radiation of the Sun, with the help of which vitamin D. from the waters of the World Ocean.

To explain what the Sun consists of for children is not particularly difficult. But in order to understand the structural features of a huge star, such as this one, it is necessary to imagine that infinite amount of gas volume, which is concentrated in one place of the solar system. But to put it simply, the Sun consists, for the most part, of both hydrogen and helium. These gases are very light, but the star itself is very heavy and weighs like 330,000 planets identical to Earth. And the temperature to which these and other elements included in the composition are heated reaches up to 15 million degrees. Many data on the composition of the star by modern scientists were obtained using spectral analysis of the sunlight that reaches the Earth, and are quite accurate.