A striking representative of unsaturated hydrocarbons is ethene (ethylene). Physical properties: colorless flammable gas, explosive in a mixture with oxygen and air. In significant quantities, ethylene is obtained from oil for the subsequent synthesis of valuable organic substances (monohydric and dihydric alcohols, polymers, acetic acid and other compounds).
Homological series of ethylene, sp 2 hybridization
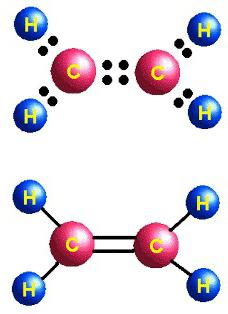
Hydrocarbons, similar in structure and properties to ethene, are called alkenes. Another term historically entrenched for this group is olefins. The general formula C n H 2n reflects the composition of the entire class of substances. Its first representative is ethylene, in the molecule of which carbon atoms form not three, but only two õ bonds with hydrogen. Alkenes - unsaturated or unsaturated compounds, their formula is C 2 H 4 . Only 2 p- and 1 s-electron clouds of a carbon atom are mixed in shape and energy; in total, three õ bonds are formed. This condition is called sp2 hybridization. The fourth carbon valency is conserved; a π-bond appears in the molecule. In the structural formula, the structural feature is reflected. But the symbols for designating different types of communication on the schemes are usually used the same - dashes or dots. The structure of ethylene determines its active interaction with substances of different classes. The addition of water and other particles occurs due to the breaking of a weak π-bond. The released valencies are saturated due to electrons of oxygen, hydrogen, and halogens.
Ethylene: physical properties of a substance
Ethene under normal conditions (normal atmospheric pressure and a temperature of 18 ° C) is a colorless gas. It has a sweet (ethereal) smell, its inhalation has a narcotic effect on humans. It hardens at –169.5 ° C and melts under the same temperature conditions. Ethene boils at –103.8 ° C. It ignites when heated to 540 ° C. The gas burns well, the flame is luminous, with weak soot. Ethylene is soluble in ether and acetone, much less in water and alcohol. The rounded molar mass of the substance is 28 g / mol. The third and fourth representatives of the homologous series of ethene are also gaseous substances. The physical properties of the fifth and the following alkenes differ; they are liquids and solids.
Obtaining and properties of ethylene
The German chemist Johann Becher accidentally used ethyl alcohol in experiments with concentrated sulfuric acid. So, ethene was first obtained in laboratory conditions (1680). In the middle of the XIX century A.M. Butlerov gave the compound the name ethylene. Physical properties and chemical reactions have also been described by a famous Russian chemist. Butlerov proposed a structural formula that reflects the structure of matter. Ways to get it in the laboratory:
- Catalytic hydrogenation of acetylene.
- Dehydrohalogenation of chloroethane in a reaction with a concentrated alcohol solution of a strong base (alkali) with heating.
- Cleavage of water from ethanol molecules (dehydration). The reaction takes place in the presence of sulfuric acid. Its equation: 2 – 2 – OH → 2 = 2 + 2
Industrial receipt:
- oil refining - cracking and pyrolysis of hydrocarbons;
- dehydrogenation of ethane in the presence of a catalyst. H 3 C – CH 3 → H 2 C = CH 2 + H 2
The structure of ethylene explains its typical chemical reactions - the addition of particles by C atoms, which are located at a multiple bond:
- Halogenation and hydrohalogenation. The products of these reactions are halogenated.
- Hydrogenation ( hydrogenation), ethane production .
- Oxidation to ethylene glycol dihydric alcohol. Its formula: OH – H2C – CH2 – OH.
- Polymerization according to the scheme: n (H2C = CH2) → n (-H2C – CH2-).
Ethylene Applications
When fractional distillation of oil in large volumes receive ethylene. The physical properties, structure, and chemical nature of the substance make it possible to use it in the production of ethyl alcohol, halogen derivatives, alcohols, oxide, acetic acid and other compounds. Ethene is a monomer of polyethylene, as well as the starting compound for polystyrene.
Dichloroethane, which is obtained from ethene and chlorine, is a good solvent, used in the production of polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Film, pipes, utensils are made from low and high pressure polyethylene, cases from CDs and other details are made of polystyrene. PVC is the basis of linoleum, raincoats. In agriculture, ethene processes fruits before harvesting to accelerate ripening.