Atlant is the first cervical vertebra in mammals with a full skeleton and ridge. In humans, this department is a fundamentally important part of the musculoskeletal system. The neck is not just a part of the body with which we tilt or turn the head, it is the most mobile segment of the spine through which the main blood vessels pass, transporting oxygen to the brain.
Structural features
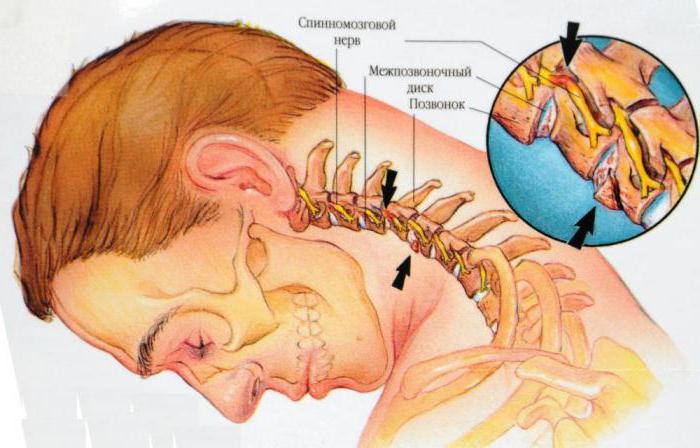
The cervical spine consists of several vertebrae that are interconnected, but each of them remains mobile. The neck is credited with the highest motor activity throughout a person’s life. Its vertebrae are small bodies with transverse processes, each of which received an opening for the passage of vital blood arteries and nerve endings.
The structure of the first cervical vertebra, the atlas, attracts the most attention. Due to the presence of this element, the articulation with the skull remains movable. By the way, the name "Atlas" he received in honor of the hero of ancient Greek mythology, holding the firmament on his shoulders.
About how many cervical vertebrae a person has, each of us knows from the course of school anatomy. There are seven of them, but the maximum load falls on the first. Throughout the day, when a person is awake, the head and cervical region are in constant dynamics. In this regard, some features of the anatomy of the first cervical vertebra (atlas) are distinguished:
- Unlike other elements, it does not have a body.
- Lateral masses, which to some extent perform the function of the body, are two symmetrical structures. They are connected due to the front and rear arches of Atlanta.
- The structure of the first cervical vertebra also implies the presence of two tubercles on the arches, front and back.
- The fossa of the tooth is a special recess on the posterior surface, which allows the atlas to connect to the tooth-like process of the axis - the second vertebra of the neck. At the same time, both retain their mobility.
- A movable joint is placed between the atlas and the axis. Thanks to this cartilaginous element, a person can rotate his neck or make high-amplitude movements.
Subluxation and displacement
Atlas, the first vertebra of the human cervical region, has the smallest size. Outwardly, it is similar to a ring thickened on the side. The slightest damage to the joint of the bones of the skull and neck can lead to serious consequences. For example, subluxation and dislocation are some of the most common injuries in this department, which are characterized by slipping of the tooth-like process of the axis. In this case, the first cervical vertebra (atlas) is displaced. How to eliminate such an injury?
In fact, it is not always possible to diagnose it in a timely manner. Most dangerous when subluxation occurs in newborns. Moreover, such damage may not manifest itself for many years, and at an older age, when certain complaints appear against the background of the development of the corresponding pathologies, doctors, as a rule, do not associate this with the displacement of the atlas. The first cervical vertebra, or rather anomalies of its structure or damage, can lead to various kinds of neurological symptoms.
So, you should understand the types of damage to Atlanta. Its displacement is diagnosed in patients of various age groups. The main groups of pathologies are distinguished:
- congenital;
- post-traumatic;
- postoperative;
- degenerative
- dysplastic.
Congenital changes in Atlanta structure
The Kimmerly anomaly should be attributed to the first category - an extra osseous arch above the vertebral artery is formed in the fetus . Often the formation is detected by chance during an X-ray examination. Meanwhile, with Kimmerley anomaly, patients have an increased risk of blood vessels being squeezed when the head is tilted, which, as a result, can lead to impaired cerebral circulation.
It is worth noting that this anomaly can be acquired. The most common cause of development is osteochondrosis, a degenerative process that occurs in the articular cartilage. In most cases, the treatment of this condition is conservative, they try to get rid of the problem with the help of a Shants collar and taking medications.
Post-traumatic disorders
The displacement of the atlas (first cervical vertebra) is accompanied by the development of instability. In most cases, as already noted, the cause is birth injury in babies. Intranatal damage to the ligamentous apparatus may be asymptomatic.
In adulthood, a stronger mechanical effect will be required to displace Atlanta. In the presence of strong ligaments, an injury to the first cervical vertebra can provoke:
- a fall from a height or, for example, a header to the bottom when diving in shallow places;
- traffic accident causing a whiplash;
- a blow to the neck or head in a fight;
- sports training;
- incorrect performance of the headstand;
- wrong flip;
- sharp turn of the neck after sleep or prolonged stay at rest.
Another cause of Atlas displacement may be a spinal fracture. In this case, not the number of cervical vertebrae in a person is damaged, but whether the ligaments remain integral. The chances of restoring all the functions of the cervical spine depend on this. Meanwhile, even with the most favorable scenario, instability will remain in the spine for a long time.
Postoperative complications
After surgery, pathological changes can also occur at the level of the first cervical vertebra. Atlas often moves after a bilateral laminectomy.
It is also important to note that intervertebral hernia and protrusion operations at the level of the first two cervical vertebrae are performed in exceptional cases. Such interventions have a huge risk of complications due to the passage of the major blood arteries and spinal structures.
Degenerate and dysplastic displacement
This pathology is quite rare, since the atlas does not have a fibrous intervertebral disc. Osteochondrosis most often affects the third and lower vertebrae.
With dysplastic syndrome, disorders occur throughout the spinal column, which is manifested by instability in all departments. With the underdevelopment of Atlant or its individual structures, its fusion with the axis can be observed.
Symptoms of Atlas Displacement
For this kind of complications, specific manifestations are characteristic. If they occur and suspected bias, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis. The research results will allow you to accurately determine whether the correction of the first cervical vertebra is really needed. Atlas, changing its position, can provoke the appearance of such symptoms:
- soreness in the neck and shoulder girdle, especially after heavy physical exertion;
- cramping
- Dizziness
- fainting conditions;
- tilt your head to one side;
- cephalgia;
- cramps
- sleep disturbances;
- discomfort, tingling and burning of the neck muscles;
- mild swelling of the soft tissues;
- hypertonicity of the upper back;
- acute torticollis (at an early age);
- uncertainty when turning the head, tilting.
Conservative therapy
If the pathology has been confirmed in the diagnostic results, but the moment of displacement itself is unknown, treatment should be started without delay. With a slight displacement of the first vertebra (up to 3 mm), conservative methods are used:
- physiotherapy;
- regular wear of the fixing collars;
- medicines that relieve inflammation and reduce muscle tone;
- analgesic blockade with severe pain;
- physiotherapy and massage.
If this treatment does not bring results after two to three months, the patient is recommended to consult a neurosurgeon. The risks of complications and the appropriateness of the operation are determined individually.
What to do immediately after an injury?
The tactics used in the treatment of bias are practically independent of the patient's age. If changes in the position of the atlas are detected immediately after the injury, three stages of therapy are performed:
- First aid. The cervical region is immobilized with a splint or collar. It is important to achieve maximum immobility of the first cervical vertebrae and atlas.
- Direction. This manipulation should only be performed by a specialist! Under no circumstances should you do this yourself! Injury to blood vessels or nerves ending there can lead to disability.
- Rehabilitation. For the recovery period, the patient may be prescribed wearing an orthosis, massage and gymnastics for the first cervical vertebra.
Treatment and rehabilitation in a medical facility
Atlas is set in a hospital setting. A traumatologist or chiropractor, depending on the complexity of each particular case, can perform the procedure manually or using the Glisson loop. Reducing Atlanta for babies is often carried out according to the method of Rüsche-Guether. In children, the vertebra often falls into place without any manipulation after eliminating puffiness and muscle spasm.
The rehabilitation period after reduction is of fundamental importance to exclude repeated subluxation of the vertebra. In addition, it is extremely important to maximize the load on the cervical spine. It is worth constantly remembering that any sharp and careless movement will lead to repeated displacement. It may take about six months to fully recover. The chances of recovery are inversely proportional to the patient’s age: the older the person, the slower and more difficult the tissue repair will be.
What are the risks and consequences?
A subluxation, or displacement, of the atlas is serious damage to the upper spine. Leave it unattended. In itself, without the intervention of doctors, this condition will not pass. In children, untreated subluxation or displacement of the atlant is fraught with serious consequences that may occur after a few years. In particular:
- decreased visual acuity;
- lag in psychomotor development;
- development of scoliosis, osteochondrosis;
- torticollis;
- flat feet, clubfoot;
- high intracranial pressure;
- cerebral edema and frequent migraine attacks;
- chronic fatigue, fatigue;
- irritability;
- moodiness;
- rapid excitability;
- bad memory;
- hyperactivity and lack of concentration;
- cramps
- violations of the digestive tract.
In most cases, the consequences of an injury received at birth are significant changes in the well-being of the child during adolescence. Increased blood pressure, fatigue, headaches and weakness - all these manifestations are characteristic of a very common diagnosis of “vegetovascular dystonia”. By the way, its cause is often subluxation of the atlas.