Mushrooms are unique living creatures. Their amazing variety and ability to form symbiosis with a wide variety of species of animals and plants provides them with a wide range. How do fungi differ from other living organisms and why do they stand out in an independent kingdom of the living world? Indeed, by external signs, higher fungi resemble plants. And the yeast belonging to unicellular fungi is very similar to bacteria. So how do mushrooms differ from plants and animals?
Classification Brief
Scientists divide all living things on our planet into five kingdoms:
- kingdom animals;
- the kingdom of the plant;
- the kingdom of Mushrooms;
- the kingdom of Bacteria;
- kingdom Viruses.
How do mushrooms differ from representatives of other kingdoms and why are they distinguished into a separate category? Scientists know more than 100 thousand species of mushrooms. They, in turn, are classified into three departments:
- real mushrooms;
- oomycetes;
- lichens.
The study of the question of how fungi differ from plants and animals is the science of mycology.
The difference between mushrooms and plants
The mycelium of higher fungi occupies a significant surface. Many species live in symbiosis with the roots of trees, forming mycorrhiza. The outer part of the fungus - the fruiting body - bears the function of reproduction.
And how do mushrooms differ from plants? The answer lies primarily in the way mushrooms get
nutrients.
- Unlike plants, fungi lack chlorophyll - they are not able to produce organic matter from inorganic matter. By type of nutrition, mushrooms, like animals, belong to heterotrophs. Among the fungi there are parasites that cause diseases of animals and plants. Such diseases are called mycoses. There are saprophytes that process dead organics - the remains of plants and animals. Of particular importance are xylophytes that break down living and dead wood. The symbionts that benefit the "master" benefit from cooperation for themselves. There are even predator fungi that live in a layer of the earth and feed on small soil worms.
- The metabolism of mushrooms is similar to that of animals. Proteins, unlike vegetable ones, are complete, and urea is the final product of their breakdown. When decomposing a dead fungus, proteins are broken down into ptomains, cadaveric poison. Mushrooms receive energy by splitting glucose, and plants - carbon dioxide. Metabolism contains lecithin and glycogen, which is not found in plants.
- The chemical structure of mushroom poisons is similar to that of animals (snakes), not plants.
- The cell wall of fungi is well defined and consists of proteins and chitin, less often, as in plants, of cellulose.
So mushrooms only look like plants. The fundamental differences between fungi and animals are much smaller.
How mushrooms differ from animals
Still, mushrooms have something that makes them related to plants.
- Mushrooms absorb nutrients all over the surface - they do not have a digestive apparatus.
- Like plants, fungi have a rigid cell wall - animal cells have a slightly different membrane.
- Cell mitosis and the formation of new cells in fungi are similar to those in brown algae.
- Mushrooms cannot move independently.
Another thing that mushrooms differ from animals and plants is that their cells can have two nuclei, and special formations - thalli - contain many nuclei. Neither in plants nor animals is this noted - a cell always contains one nucleus.
Fungi and bacteria
What is the difference between fungi and bacteria? First of all, among bacteria there are both autotrophs and heterotrophs. Other differences:
- In the cells of bacteria there is no nucleus.
- Bacteria are exclusively unicellular organisms.
- Bacteria are microscopic in size, and most fungi can be seen with the naked eye.
- Some types of bacteria are able to move independently with the help of flagella.
Another important factor that distinguishes fungi from bacteria is the development of living space. Despite the fact that mold (which is nothing more than mycelium of the fungus) is recognized by scientists as one of the most tenacious organisms, bacteria remain leaders in capturing the habitat. The range of temperature and other environmental indicators in bacteria is immeasurably higher than in all other living things.
What is the difference between mushrooms and lichens
The Lichen Division is the nomenclature unit of the kingdom of mushrooms. The difference between mushrooms and lichens is that the latter are nothing more than a symbiosis of algae and fungus. The interwoven threads of the mycelium form the body of the lichen, and between the threads live blue-green or green algae - unicellular. Lichen lives wherever there is light. Mycelium of the fungus absorbs water and mineral elements from the environment, and algae receive carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and synthesize organics from these substances. Thus, the type of nutrition is auto-heterotrophic, which gives lichens undoubted advantages over both fungi and plants.
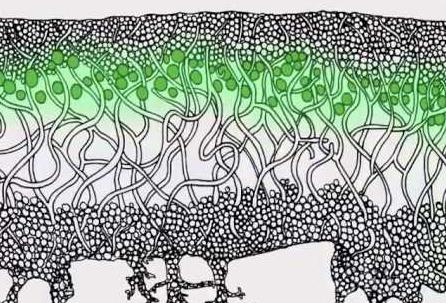
Scientists still have not come to a consensus on what principle the interaction of fungus and algae is based on. According to one theory, we are talking about mutually beneficial cooperation. According to another version, lichen is a fungus parasitizing on algae. Due to the fact that the algae multiplies rapidly, its complete destruction does not occur. And in the third version, the interaction of the fungus and algae is presented as mutual parasitism, completely obeying the law of the struggle of opposites.
Uniqueness of mushrooms
Mushrooms are very diverse in structure and habitat. They bring a person both benefit and harm. The main purpose of mushrooms in the cycle of substances is the processing of dead organics, especially wood, and the formation of the soil layer.
Mushrooms produce a large number of biologically active substances and are the subject of technological developments in microbiology and biotechnology.
The reproduction of mushrooms occurs in a variety of ways. This is another way mushrooms differ from plants and other living creatures, usually using 1-2 methods of reproduction. In fungi, reproduction is possible:
- Vegetative - part of the mycelium, budding or special formations.
- Asexual - with the help of spores (conidia or sporangia).
- Sexual - by the fusion of two primary mycelia.
The method of propagation is based on the classification of fungi within the kingdom.
Mushroom variety
A variety of forms and methods of reproduction and the nutrition process - this is how fungi differ from other organisms. The most famous among mushrooms was hat mushrooms, due to the fact that people use their fruiting body for food. Protein in its usefulness is comparable to animal meat. In the world there are more than 8000 species growing around the globe. White mushroom, raincoat and champignons are especially appreciated, which, among other things, have medicinal properties.
Parasite fungi cause significant damage to agricultural activities. Smut fungi cause diseases of grain plants, rust mushrooms look like brown spots, and polypore dwellers settle on tree trunks. The lower unicellular fungus mucor damages food products, forming a white coating on them. In nature, this fungus plays a positive role, but it often causes damage to bread, vegetables and fruits.
Fungi from the genus penicillum and aspergillus belong to higher fungi, but act on food as destructively as mucor. In addition to decomposition of the substrate, mycelium secretes mycotoxins that can cause poisoning in humans and animals. People also use this property for positive purposes: some types of mushrooms produce drugs - antibiotics, with which they treat bacterial diseases. Lower mushrooms cause numerous diseases of fruits and vegetables: late blight, “black leg”, “potato cancer”.
Yeast is also a mushroom. These oval-shaped small multicellular organisms breed in a sugar-rich environment.
With their help, a person produces wine, beer and other alcoholic products, butter bread, they feed animals. Parasitization of yeast on plants leads to a disease called "powdery mildew," and in humans and animals they cause thrush.
Mushrooms have signs related to animals and plants. In appearance, they are closer to plants, and in metabolism and type of nutrition - to animals. Many unicellular fungi are very similar to bacteria in many respects, however, they also have significant differences, primarily in the method of reproduction. So scientists rightfully distinguish these amazing creatures into a separate kingdom - the kingdom of mushrooms.