The bones of the upper limb and shoulder are referred to the skeleton of a person’s arm. In anatomy, in addition to the bones of the arm, joints and ligaments are also distinguished as their constituent parts. The upper limbs consist of: bones of the shoulder, forearm, hands (wrists, metacarpals and phalanges of the fingers).
Humerus characteristics
This limb element is a long tubular bone. Its composition includes the so-called body and 2 epiphyses: the upper proximal and lower distal. The upper section of the
shoulder girdle has a rounded shape, and the lower is trihedral. The shoulder joint is the connection of the superior epiphysis with the articular fossa of the scapula. All bones of the skeleton of the upper extremities are composed of the body and pineal glands and are connected to each other.
Structure and function of the ulna
According to the anatomical structure, the ulnar and radius bones are referred to the forearm. The ulnar consists of many long tubular bones and two ends (proximal and distal pineal glands). The base of the bone is presented in the form of a trihedron, it has certain edges that bear the following names: anterior (palmar), posterior (dorsal), interosseous (external). The front edge of the bone is round. The back goes a little back. The interosseous edge has a pointed shape and faces the radius.
Unlike the distal, the proximal pineal gland is more thickened. The block-shaped notch that is in it is completely covered by articular cartilage. This is necessary so that the edges of the bone are not erased with constant movement of the upper limb. At the ends of the block cut, the processes are located : coronoid and ulnar. The front surface of the bone, located below the coronoid process, has a tuberous structure.
The upper and lower epiphyses of the radial and ulnar parts of the arm interact with each other through joints. Any connection of the bones of the upper extremities is a complex mechanism, especially in the elbow. If an injury occurs and the elbow joint is damaged or the bones are broken in it, many actions and operations will be done by specialists before the elbow can work again.
The lateral side (outer surface) of this element of the upper limb includes a radial notch, a notch for the entry of the radial head. This cavity for the anterior part of the bone and the bone itself form the proximal joint of the forearm.
Like the lateral side of the distal pineal gland, the posteromedial has a styloid process, which is necessary for a better ligament of limb elements. We see that the ulnar bone is very complicated, which together with the beam forms the bones of the upper limb. Human anatomy - the structure of all organs and systems, including the bones and joints of his limbs - is generally not elementary.
Radius of the upper limb
The difference between the two components of the forearm is that the distal end of the radius is much thicker than the proximal end. This ending forms a rounded head, in which there is an epiphysis with a flat recess. Due to this, the correct connection of bones occurs. This head is the surface of the joint. On the front side of the radius there is a part that is responsible for the attachment of the biceps of the shoulder joint. The structural elements of the wrist are connected to the radius via a massive distal pineal gland. The lower epiphyses of the radial and ulnar bones, when combined, form a radicular ulnar joint.
Wrist characteristics
The bones of the upper limbs of a person consist of short elements arranged in 2 rows (proximal and distal), and have an unusual shape. At the wrist, it is presented in the form of a curved groove, the convexity of which is turned to the back of the palm.
In the proximal row are small bones, which were named according to their shape: lunate, scaphoid, trihedral. In addition, there is still a pea-shaped bone, which adjoins the palmar surface to the trihedral element. The distal row is formed by the trapezoid, capitate, and hook-shaped bones. To perform their functions, all of the structural components listed are ordered so that they are not in the same plane. The carpal bones of the upper limbs of a person of the proximal series form an ellipsoidal bulge. It connects to the distal epiphysis of the radial part of the upper limb. And in the distal row, the bones are articulated with the metacarpal.
Bones of the upper limb
The metacarpal phalanges of the fingers are formed by tubular bones (with one epiphysis), which have a body, a base, a head. They are curved, convex side to the back of the hand. The distal row of the carpal bones is connected to their bases, and the heads to the beginning of the phalanges. The heads of the metacarpal bones are adjacent to the bases of the proximal phalanges, and their head part is articulated with the beginning of the distally located phalanges. Each finger has 3 phalanges: proximal, middle, distal. However, the thumb has only two.
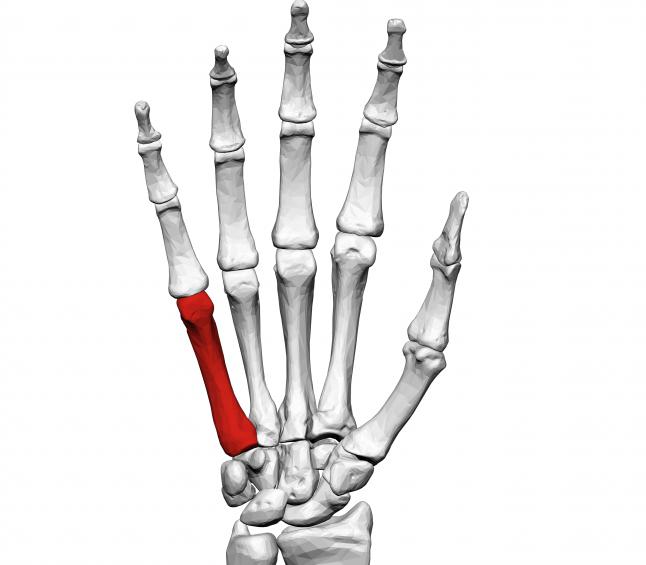
Each phalanx, like all other bones of the upper limbs, the anatomy of which is described above, also has a base, body and head. But their feature is that they are built one after another. At the same time, all three phalanges account for only one true pineal gland. The proximal parts of the wrist have one fossa in which they connect to the next bone. The middle and distal phalanges are slightly different from the proximal, as they have two pits for the formation of a joint. These recesses have a flat shape, they are separated by small scallops. Each last phalanx in the finger above is slightly narrowed, flattened and roughened.
Bones of the free upper limb, their connection
All bones are connected by joints, this allows a person to move unlimitedly. The connection of the bones of the upper extremities, clavicle and scapula is represented by the combination of two paired joints: the articulation of the sternal ends of the clavicle with the handle of the sternum and its acromial ends with the acromions of the scapula. The next ligament of the scapula is the upper transverse, in the form of a short thin bundle, thrown over the notch of the scapula. The hole for the advancement of nerves and blood vessels is formed by a transverse ligament with a notch and very often ossifies. In humans, the structure of the bones of the upper limbs is very diverse.
The acromioclavicular joint can move in any direction, but the frequency of movements is small. They are prevented by the coraco-clavicular ligament. It is divided into quadrangular and triangular ligaments. Quadrangular has the shape of a trapezoid, and triangular - a cone. Both ligaments towards each other are located at an angle.
Description of the shoulder joint
In the movement of the bone of the upper limb, the shoulder joint plays an important role. The shoulder joint is formed by the head of the humerus and the articular cavity of the scapula. This cavity has an oval shape, occupies one quarter of the head area, slightly concave. The articular lip present in it increases the congruence of the connecting tissues covered with hyaline cartilage. The joint capsule has freedom of movement, therefore, when the bone is lowered, it can be folded. It is strengthened by muscles, ligaments located in the shoulder joint. The head of the shoulder is tightly fixed with muscles and ligaments in the articular cavity. There are no muscles in the front-lower part of the shoulder joint. It is surrounded by mucous bags that interact with the joint cavity.
Blood approaches the shoulder joint through the anterior and posterior arteries located around the shoulder bone. This connection of bones is very mobile, it is characterized by the following actions: rotation, circular motion, extension, bending, abduction, mixing. In humans, the bones of the upper and lower extremities are slightly different, but the connections are the same in structure.
Elbow Complexity
The joint of the elbow is formed by the connection of the humerus, ulna and radius. Inside this large joint there are three small joints:
- shoulder-elbow;
- brachioradial;
- ray elbow.
Due to the presence of a joint capsule and a common cavity, they are combined into a complex joint covered with hyaline cartilage.
The shoulder-elbow and brachioradial joints, working together, cause flexion and extension, and the ray-elbow joint is involved in the movements of the forearm. Various movements are due to the presence of a large number of muscles. Such a complex mechanism cannot exist without support. And this joint support is in the form of an ulnar and radial ligament. They clasp the bone heads of the upper limb. The human anatomy is designed in such a way that by doing this the joint bends in the opposite direction.
How do forearm bones connect?
The radius and ulna are located nearby, and their ends are connected in the joint. The epiphyses of these structures are connected by the distal and proximal joints. For the strength of the connection between these bones there is a membrane, which is the beginning of the deep muscles of this part of the upper limbs. The upper joint (proximal) is an integral part of the elbow joint, and the lower one acts independently. The distal radiopulmonary joint is separated from the wrist by a small articular disc. It has the shape of a triangle with concave plate surfaces.
The structure of the wrist joint
The bones of the wrist are connected to the radius using the articular disc and the surfaces of all participants in the joint. The proximal rows of the bones of the wrist are strongly interconnected, so the articular surface is one area on the side of the wrist. Naturally, it is smaller than the radius of the radius, therefore, a disk in the shape of a triangle helps to connect two articular areas of different sizes. In addition, it helps to separate the ulna from the joint, which is surrounded on all sides by ligaments.
What joints are involved in connecting the bones of the hand and fingers?
The bones of the hand are interconnected using three joints:
- Mid-carp. It is located between the bones of the first and second row of the wrist. On the two surfaces of the wrist (palmar and dorsal) there are many ligaments. This is due to the fact that the hands are actively functioning, they must perform small movements, bend, unbend. This strong ligamentous apparatus is called the radiant ligament of the wrist.
- Metacarpal. Four metacarpals have one capsule and articular plane. The joint of the thumb is separated from the rest.
The bones of the fingers are interconnected using the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. In addition to them, there is still a large number of strong ligaments on each finger, which allows a person to bend and unbend fingers. As you can see, the structure of the upper limbs of a person is quite complex, but because of this, they are distinguished by mobility.