HIV is a dangerous disease of a viral nature that causes serious damage to the human immune system. About 8 thousand people a year get this virus. How to get tested for HIV, methods of infection and treatment methods will be discussed in the article.
What is HIV?
HIV is a disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus. Pathology affects the immune system to such an extent that the body can not fight any infections. This provokes the development of various diseases that cause significant harm to human health. HIV is dangerous because many years can pass from the moment of infection to the appearance of noticeable signs. In half of sick people, the asymptomatic period lasts about ten years.
The principle of the virus
When HIV enters the bloodstream, it attaches to its healthy cells, which are responsible for immunity. Inside these cells, the virus actively multiplies. This happens so quickly that HIV manages to spread throughout the body before a defensive reaction occurs. Since immune cells are already damaged and are not able to perform their functions normally, the virus does not receive a decent response from the immune system. Another feature of HIV infection is its rapid variability. In this regard, the body is difficult to recognize the virus and it continues to infect the body.
First of all, lymph nodes suffer, since it is in them that immune cells are produced to a greater extent. As they become infected with the virus, their numbers become critically low. This can be considered a sign of AIDS.
Types of HIV
Currently, there are 2 types of human immunodeficiency virus:
- HIV-1 or HIV-1. A very aggressive type of disease, characterized by pronounced symptoms, is the main causative agent of pathology.
- HIV-2 or HIV-2. Not as widespread as HIV-1. It is a less aggressive type of disease. Symptoms are slightly expressed.
Infection pathways
It is noted that in people with increased immunity, the risk of infection from contact with a sick person is significantly lower than in those who have a weakened immune response.
There are several main methods of infection.
- If you have sex without a condom.
- When using a syringe or any other medical instrument after an infected person.
- With a blood transfusion from an infected patient.
- From mother - to the child during fetal development, since the virus is able to penetrate the placenta, it can also be infected during childbirth and during breastfeeding. Breastfeeding an HIV-infected woman is contraindicated because the presence of the virus was also detected in colostrum and milk. If the child's HIV test is negative, this most likely indicates the absence of infection, but constant monitoring is necessary.
- From sick people - to medical personnel when injured with instruments on which infected blood could remain. This is a very rare way of infection.
- Use of personal hygiene products by strangers.
Developmental stages
HIV has several stages of development depending on the clinical manifestations.
- The incubation period. It lasts from the moment of infection until the first signs appear. In most cases, the duration of this stage is from 2 weeks to six months or more. Despite the fact that a blood test during this period is not yet able to show the presence of the virus in the blood, a person is already contagious.
- The acute stage (period of primary manifestations). This stage is characterized by certain symptoms that may be present for several weeks. The patient may be disturbed by such manifestations as swollen lymph nodes, fever, sore throat, in the eyes and head, general malaise and rashes and ulcers on the skin. But it is worth noting that in half of people this stage is absent and after the incubation period the asymptomatic stage immediately begins.
- Asymptomatic phase. The longest stage. Despite the fact that there are practically no signs of HIV infection, the reproduction of the virus in the blood continues. This stage can last about 10 years. Duration will depend on the spread of the infection.
- Secondary manifestations. Due to the fact that the virus is actively multiplying, and immune cells are not able to withstand this, various diseases begin to appear. For example, lesions of the skin, internal organs and others.
- Terminal - the last stage of HIV infection in which AIDS occurs. This is due to the fact that the number of T-lymphocytes reaches critically low values and they are not able to cope with infections. Bacteria deplete the body, affecting all organs and systems. A fatal outcome occurs within three years due to opportunistic diseases (pathologies caused by the influence of opportunistic organisms, which in the normal state do not pose a threat).
First signs
HIV has no symptoms characteristic of it and can be confused with other infectious diseases. But there are signs of HIV infection, the appearance of which is worth contacting a medical institution and taking an analysis.
These include:
- Enlarged and sore lymph nodes.
- Unreasonable increase in body temperature for a week or more.
- Fatigue.
- A sharp decrease in body weight.
- Violations of the stool.
- The appearance of oral candidiasis.
- Herpetic eruptions.
If you suspect an HIV infection, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Diagnostics
For successful treatment and increasing the life expectancy of people with HIV, early diagnosis of the disease is of great importance. How to get tested for HIV?
If you suspect a virus infection, you should contact the laboratory and take a blood test. Only in this way can you confirm or deny the presence of infection in the body. But you need to clarify how many days to take an HIV test after a possible infection, because antibodies to it do not begin to be produced immediately.
Diagnostics consists of special tests:
- IFA. The most common test with which you can detect the presence of antibodies to the virus. But it is worth remembering that their production occurs within three months from the moment of infection, so if a blood sample was taken earlier than this time, a negative HIV test is likely. The procedure must be repeated after a while. Doubtful value means that not all antibodies have been developed.
- Immunoblot.
- PCR To detect the virus, its RNA is used, in this regard, it is possible to diagnose the disease at the earliest possible time - about 10 days should pass between the moment of infection and analysis.
- An HIV test purchased at a pharmacy. Using it, you can determine the presence of infection at home. This diagnostic method includes immunochromatographic tests, which are strips on which blood taken from a finger is applied. The presence of only the control line suggests that the HIV test is negative. But the manifestation of a colored line on a strip warns of the presence of a virus in the blood. OraSure Technologies1 is also one of the HIV tests available at the pharmacy. It has been approved by the FDA.
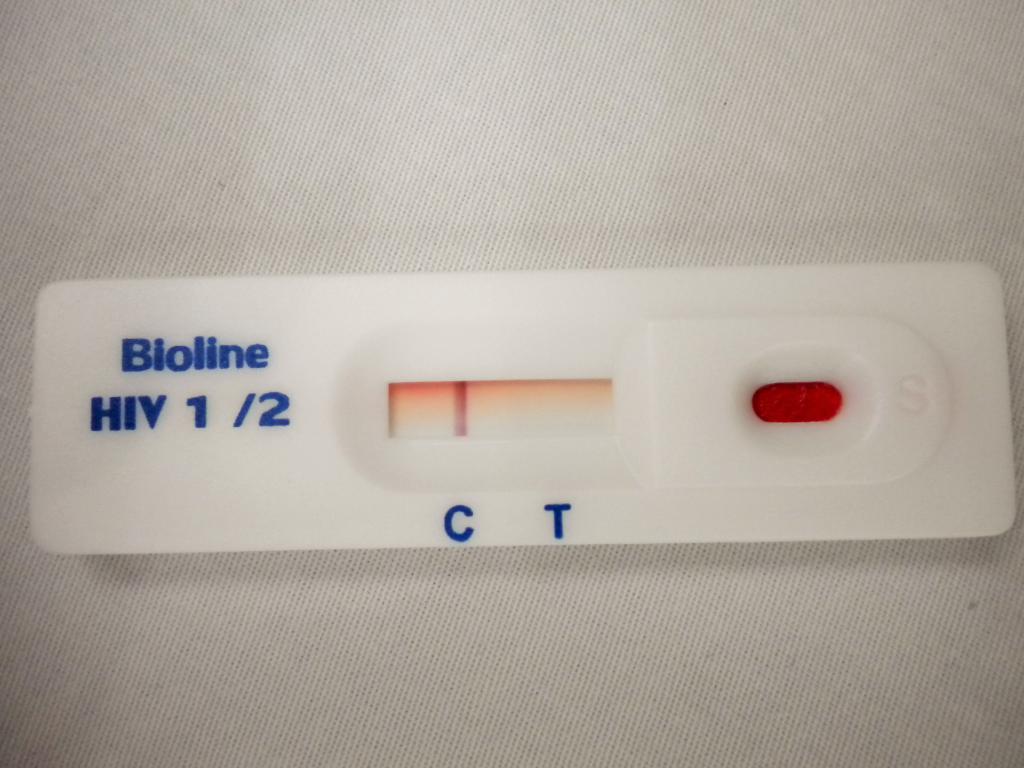
In laboratories, different tests are used to determine HIV infection, therefore, before donating blood, it is necessary to clarify which method is applicable in a particular laboratory. False negative HIV is often diagnosed. This is due to the untimely delivery of the analysis, when the antibodies have not yet developed in the quantity necessary for the analysis.
If HIV is negative, what does it mean? This can indicate both the absence of infection and the small number of antibodies produced.
Treatment and prognosis
No cure has yet been found for a cure for HIV. Therapy aims to relieve concomitant symptoms, treat diseases associated with the virus, and prevent complications.
Drug treatment includes taking the following drugs:
- Antiretrovirals (Retrovir).
- Didanosine. Used in the first stages.
- "Stavudin." It is used in the later stages.
- Nevirapine. With complications.
- "Nelfinavir". Can be used for children.
The treatment plan will be drawn up by the attending physician individually, depending on a large number of factors.
It is also very important to observe the correct lifestyle and psychological attitude. When treatment is started on time, the life expectancy of HIV-infected people can reach 20 years or more.
Conclusion
If the analysis showed that the person is HIV-negative, what does this mean? This question is asked by everyone who had to contact the laboratory for this reason. The answer to this question was given above. But in order not to fall into a situation in which this analysis may be required, it is necessary to observe preventive measures - not to engage in casual sexual intercourse, use contraception, or use other people's hygiene products. Medical instruments must be completely disinfected. An analysis of the presence of the human immunodeficiency virus is recommended to be given to all people once a year, even if the previous HIV test is negative.