Cerebrospinal fluid (another name - cerebrospinal fluid) is a specific fluid that is in close relationship with the spinal cord and brain. It is produced by the plexuses of the vessels of the brain. In 24 hours, about 400-600 milliliters of cerebrospinal fluid are produced. In the presence of any pathology - up to 1000. Cerebrospinal fluid per day is completely updated from 6 to 8 times. In addition to cerebrospinal fluid, the membranes of the brain and spinal cord play an important role in the nervous system .
Cerebrospinal fluid function
1. Protective. It forms a water cushion that protects the spinal cord and brain from concussion, pressure changes, compression, and other negative mechanical influences.
2. Cerebrospinal fluid is a food source that is needed to increase the cellular mass of the brain. And even in the postnatal period, this fluid plays a crucial role in the processes of nervous tissue metabolism . Cerebrospinal fluid, filling the pericellular and perivascular spaces, comes into contact with the cells of the nervous system. Then it absorbs metabolic products and gives the cells the substances necessary for their functioning.
3. Regulation of osmotic pressure, maintaining its constant value in the brain tissues.
The number of cerebrospinal fluid:
- in newborns - from 30 to 60 milliliters;
- in children older than three years, from 100 to 150 milliliters (with about 50 percent of the cerebrospinal fluid located in the ventricles of the brain, 30-40 percent in the tanks of the brain of the head and in the subarachnoid spaces, the rest of the cerebrospinal fluid in the spaces of the subarachnoid spinal cord).
The composition of the cerebrospinal fluid includes hormones, vitamins, inorganic and organic compounds.
In young children, the study of cerebrospinal fluid plays a special role, since at this age there are often various disorders that were caused by birth trauma or asphyxia, and some inflammatory diseases have similar symptoms. Cerebrospinal fluid is examined for meningoencephalitis, meningitis, asphyxia, seizures, volumetric processes, hydrocephalus, diseases of a hereditary nature and before the introduction of contrasts into the spinal canal (ventriculography).
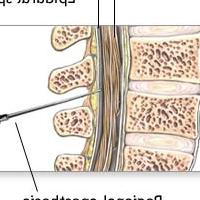
Liquor is obtained by ventricular or lumbar puncture. In young children,
lumbar puncture is performed in the supine position (approximately 2 hours after eating). The patient must be laid on his side, bent legs to the stomach so that the distance between the vertebrae increases. After that, the skin is treated and a puncture is made. Cerebrospinal fluid is collected in a special sterile tube. After taking the fluid, the needle is removed. The puncture site is carefully lubricated with iodine and a bandage is applied. Then the patient is laid on a bed in a horizontal position, without a pillow. Feed is allowed after about two hours. Within two days, the patient should observe bed rest and try not to make sudden head movements. Also, after a puncture, it is not recommended to use various physiotherapeutic procedures (gymnastics, exercise therapy, massage).