For normal functioning of the body, you should lead a mobile lifestyle and have a balanced diet, using the necessary amount of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals and vitamins. If you systematically violate these principles, some organs begin to fail. Most women do not think about the concentration of sugar in the blood until the state of health does not cause any problems. And the level of health is determined by the level of sugar in the bloodstream. If its excess or deficiency is found, serious problems arise that could have been prevented in advance. This article will talk about the norm of blood sugar in women in different life periods and how to maintain it at an acceptable level.
Blood glucose
Blood sugar, or rather glucose, is the main source of nutrition for the tissues and cells of an individual’s body; it comes from eating carbohydrates. As a result of their splitting, glucose is formed. With excessive ingestion, it under the influence of enzymes turns into glycogen. It is stored in the liver. In the event of a lack of cell nutrition, the body spends reserve reserves. The concentration of glucose in the body is supported by a hormone called insulin, which is produced in the pancreas. In addition, the human nervous and autonomic systems, hormones of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland are involved in such a complex process. While all these organs work together, the blood sugar in women is normal. However, short-term changes in glucose levels during the day are possible due to:
- with the use of food;
- physical activity;
- prolonged lack of food;
- emotional state.
When is a blood test taken for sugar?
Checking the biomaterial for glucose is carried out at any routine examination for people diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. And also when diagnosing various diseases with the following clinical picture:
- excessive urination;
- rapid weight gain or weight loss;
- feeling of thirst;
- itching of the dermis;
- sweating
- dry mouth
- palpitations:
- bad breath of acetone from the oral cavity;
- loss of vision;
- constant general weakness.
Who else do the analysis:
1. Persons at risk:
- obese
- over forty years of age;
- whose relatives have diabetes.
2. All women registered for pregnancy.
3. Patients with pathologies:
- thyroid gland;
- adrenal glands;
- hypertension
- pancreatitis.
For analysis, blood is taken from the middle finger or from a vein and the glucose content is determined by two methods: on an empty stomach and under load.
Preparation for glucose analysis (mmol / L)
After obtaining the biomaterial for sugar, reliable results can be expected if the following conditions are met:
- stop eating twelve hours before blood donation;
- do not drink alcohol, carbonated drinks, flour, sweet, fried and spicy foods per day;
- in the morning before the delivery of the biomaterial, you can not use rinses, chewing gums, brush your teeth;
- if possible, refuse any medication per day;
- on the eve of the study, exclude sports training, as well as any physical activity;
- Do not visit the bathhouse and sauna;
- in acute conditions, postpone the date of analysis.
It was found that in women, the norm of blood sugar from a vein in the case of an analysis for an empty stomach is in the range from 3.5 to 6.05.
Sugar level in women
A standard amount of glucose in a woman’s blood ensures her well-being and ability to work. A prolonged deviation indicates the presence of abnormal changes in the body. It should be borne in mind that glucose readings fluctuate depending on hormonal disruptions that occur:
- with an interesting position;
- during menstruation. On critical days, it is undesirable to take biomaterial for blood analysis;
- with menopause. At this time, special control over the amount of sugar is required.
In addition, it is noted that after eating any food, indicators can grow by 1.5-2, and this will be the norm. Blood sugar levels in women differ by age. The smallest indicator is peculiar to girls of seven years of age. In the subsequent period, starting from 7 to 14 years, the glucose concentration gradually increases and approaches the norm in an adult woman. Already from 14 to 50 years, this value remains constant. And then, after a fifty-year milestone, the amount of sugar in the blood gradually increases. This is due to age-related characteristics of the body. After the age of sixty, the amount of sugar in the blood takes one of the largest values. During this period, women are recommended to carefully monitor their health and measure sugar with a personal glucometer several times a week. Medical observations found that the highest sugar rate is observed in the fair sex after ninety years. The body does not cope well with the digestibility of glucose, and there is a risk of developing diabetes. The following are the blood sugar rates for women in the table, depending on the age category.
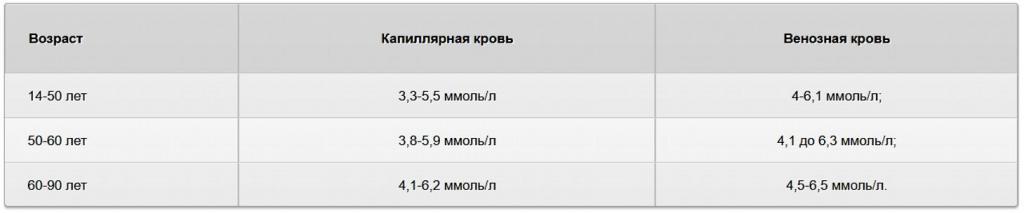
Obviously, venous blood sugar is slightly higher than capillary.
Sugar Rates for Diabetic Women
A slight increase in blood sugar in a woman does not mean that she has developed diabetes. Initially, the doctor suggests impaired glucose tolerance, in which fasting sugar from a finger is in the range of 5.6 to 6.1 mmol / L. However, after a certain period this can cause illness. Subsequent excess of the blood sugar level in women leads to a pre-diabetes state, in which the concentration of glucose in the blood is in the range of 5.6-6.9 mmol / L. This condition borders on health and disease, but unlike diabetes, it can be easily adjusted by diet and exercise. With a further increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood, type 2 diabetes mellitus develops. This disease is chronic and requires constant therapy in order to prevent serious complications.
Signs of diabetes in women at 50
At this age, hormonal restructuring of the body is already beginning, which is preparing for menopause. Against the background of a weakening of the defenses, a disease can occur. The norm of blood sugar in a woman at the age of 50 when delivering biomaterial on an empty stomach from a finger is from 3.3 to 5.5. If the pancreas malfunctions and the protein hormone (insulin) is not sufficiently produced, blood glucose increases and diabetes develops. In order to prevent its development, you need to know the signs of the disease, which are manifested in the following:
- dry mouth and thirst appear;
- a large volume of drunk fluid causes frequent urination;
- weight loss or weight gain;
- constant weakness, not passing after rest;
- poorly healing lesions on the dermis;
- itching in the perineum;
- frequent hunger;
- visual impairment;
- gum bleeding and dental problems.
If any of these symptoms are found, a woman of fifty years of age should consult a doctor and check her health. If, when deciphering the analysis, the woman’s blood sugar from the finger (the norm is 5.5 mmol / l) will be higher, then the doctor will prescribe a therapy that includes diet food and physical activity.
Causes of diabetes in the elderly
According to statistics, the majority of people with diabetes are elderly people, whose age is 60 or more. Age-related changes in the human body lead to a deterioration in the functions of the pancreas and metabolic disorders, and this often contributes to the onset of the disease. People of retirement age often suffer from type 2 diabetes. In the treatment of this disease in elderly people often have problems due to other chronic pathologies, so you need to know the reasons and try to prevent or prevent the rapid development of the disease. It is known that as early as 60 years, the blood sugar norm in women on an empty stomach increases and ranges from 3.8 to 5.9 mmol / L. This orientation will continue. With increasing age, blood glucose levels will increase. Reasons that provoke the disease in old age:
- Deposition of fat on the abdomen. It occurs due to malnutrition. To eliminate it, the pancreas begins to produce more insulin, but over time it is depleted and ceases to produce hormone.
- After 60, the norm of blood sugar in women is in the range from 4.1 to 6.2 mmol / L. This phenomenon is associated with aging and a decrease in insulin production.
- The lack of the hormone incretin produced by the digestive tract, which activates the production of insulin.
- Restructuring after menopause.
- Failure to observe proper nutrition.
- Low physical activity.
- Smoking.
- The use of alcohol-containing drinks.
To prevent the disease, you should be tested twice a year for blood sugar or measure it with a personal glucometer.
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) during pregnancy
GDM disease occurs when blood sugar in pregnant women (normal - 5.8 mmol / L) is too high. Most often this happens at the beginning of the second trimester. An earlier detection of the disease in a pregnant woman indicates that the woman had diabetes before pregnancy. This pathology after delivery passes by itself without treatment. However, after suffering gestational diabetes, there is a risk of an increase in the amount of glucose in the blood in the future. The reasons that affect the development of GDM during pregnancy depend on the genetic characteristics of the woman and are as follows:
- failure of carbohydrate metabolism;
- weight is higher than normal;
- parturient age over 30 years;
- genetic predisposition;
- severe toxicosis;
- circulatory system diseases;
- spontaneous miscarriages that were earlier;
- delivery by a large baby during a previous pregnancy;
- transferred in the past GDM.
Excessively detected blood sugar in pregnant women in the early stages provokes:
- spontaneous abortion;
- malformations of the fetus associated with the structure of the brain and heart.
If GDM occurs in the second and third trimester, the fetus will most likely have a lot of weight or hyperinsulinemia. After giving birth, the baby may have breathing problems, increased blood viscosity and body imbalance. To prevent all troubles, pregnant women regularly take tests when they are registered and are under strict medical supervision.
Signs of gestational diabetes and treatment
Often at the very beginning, diabetes during pregnancy does not manifest itself. After a short period, a woman may experience:
- dry mouth even when drinking a large amount of liquid;
- fatigue that does not correspond to the energy expended;
- weakening of visual acuity;
- frequent urination
- itchy skin;
- increased appetite;
- loss or, conversely, rapid weight gain.
The signs of the disease are very similar to those that occur during pregnancy, so you need to visit a doctor and undergo appropriate examinations. The fasting blood sugar rate for women in an interesting position should be in the range of 3.3-5.8 mmol / L. To clarify the situation, the doctor recommends testing with a glucose load. When confirming the diagnosis at the first stage of GDM, a diet with constant monitoring of blood sugar levels is used. In this case:
- meal up to six times in small portions;
- eat a lot of vegetables, herbs, unsweetened fruits and berries;
- exclude instant foods;
- use foods only boiled and stewed;
- increase the consumption of lean meat, poultry, fish, cereals;
- use vitamins and minerals on the recommendation of a doctor.
It is necessary to increase physical activity, walk more, engage in swimming. Medicines, namely insulin, are used when the concentration of sugar in the bloodstream is not corrected by diet and exercise. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor.
Prevention of diabetes and recommendations for maintaining normal blood sugar in women
It is known that diabetes in mortality takes third place after oncology and diseases of the cardiovascular system. Moreover, it should be noted that women are diagnosed more often than men. To prevent the disease, you need to know the factors leading to the onset of diabetes:
- Overweight. Each woman can determine the body mass index; for this, her body weight is divided by the square of growth. If the resulting number is more than 30 and the waist circumference is more than 81 cm, then the risk of the disease increases several times.
- Inactive lifestyle.
- Smoking, frequent overeating and stressful conditions.
- Hereditary predisposition.
In the presence of the above symptoms, close attention should be paid to proper nutrition. In order to maintain blood sugar in women, normal dietary monitoring is necessary. To do this, it is recommended:
- Refuse digestible carbohydrates. Do not eat jam, sugar, condensed milk, products from premium flour, limit rye bread, using one piece for food intake.
- Increase the intake of foods containing protein: fish, poultry, lean meat, as well as vegetables and fruits.
- Reduce the intake of fatty foods: meat, sausages, sour cream, mayonnaise.
- For a snack, use a cucumber or an apple.
- Eat often, but in small portions.
In addition, it is desirable for all representatives of the fair sex to know what the norm of blood sugar in women is and how it changes depending on the age category.
Physical activity for diabetes
The most useful load for diabetes is considered to be associated with the rhythmic motor activity of the upper and lower extremities. Suitable for this are walking, cycling, swimming, jogging.
First of all, you can go hiking, it is very useful for diabetics: a good mood appears, weight is reduced and special equipment is not required. Responsible activities include work on a summer cottage, cleaning the premises, daily climbing stairs, dancing and many other events. In order not to harm your health, you need to consult with your doctor about the size of the possible load on the body. It is advisable to constantly check in both men and women the blood sugar rate after and before the start of vigorous work.