Chorionic biopsy is a study that allows you to identify congenital and hereditary pathologies in early pregnancy. With him, samples of the chorion are taken, which subsequently forms the placenta.
It is worth noting that no manipulation of the fetus itself is carried out, so a chorionic biopsy is considered quite safe. After the procedure, the risk of spontaneous abortion is only 2%. This study gives accurate results, but it is painful and capable of causing a sharp malaise to the pregnant woman, therefore, it is carried out strictly according to indications. This takes quite a bit of time, and the results are ready in 3-4 days.
There are 2 main types of this manipulation:
• Vaginal biopsy of chorionic villi - performed between 8 and 12 weeks of gestation. Under the control of ultrasound, a special instrument is inserted through the vagina into the uterus, which is placed between the endometrium and the chorion (it is the fruit membrane). With this manipulation, the villi on the chorion are cut off or absorbed. Further they are subject to laboratory research. Such a procedure is absolutely painless.
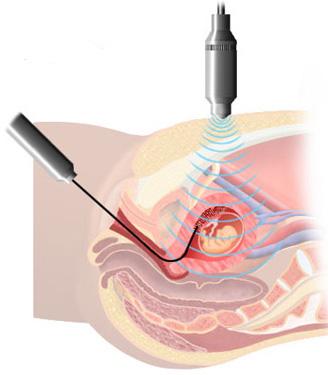
• Abdominal biopsy of chorionic villi - done between 9 and 11 weeks of pregnancy. Sometimes this manipulation can be used in the second and third trimester, as it allows you to quickly get results, especially when there is little amniotic fluid, so amniopuncture is impossible. To perform the manipulation, the patient lies on his back. The doctor using an ultrasound machine determines the position of the placenta, the uterine walls, and also finds out a future safe place for a puncture. To take the necessary material, one needle is used to puncture the abdominal and uterine walls, and the other, a cell sample is taken for further investigation. It is worth noting that the puncture site must be treated with a local anesthetic with good analgesic properties.
A chorionic biopsy is most often prescribed to pregnant women who are at increased risk of having a child with genetic disorders, although any woman can undergo this examination if she wishes to bear the fetus.
What pathologies can be detected using this diagnostic technique? This is primarily
Down syndrome, trisomy 13 and 18 of the chromosome,
Turner syndrome, cystic fibrosis and
sickle cell anemia, as well
as Klinefelter syndrome. In addition, a chorionic biopsy reveals approximately 100 chromosomal and genetic abnormalities.
It is worth noting the important advantage of this diagnosis - it can be used much earlier than amniocentesis (already at 10 weeks of gestation). In addition, the results can be obtained quickly enough - in most cases in the first week after the examination.
I must say that a chorionic biopsy can also reveal placental mosaicism, when some cells have a normal chromosome set, while others are formed with certain abnormalities.
After the examination, spotting spotting and cramping abdominal pain may appear. Amniotic fluid (in small amounts) can also be released from the vagina. If any unusual symptoms appear, consult a doctor who is pregnant.