The chemical element oxygen is in the second period of the VIth main group of the obsolete short version of the periodic table. According to the new numbering standards, this is the 16th group. The corresponding decision was made by IUPAC in 1988. The formula of oxygen as a simple substance is O 2 . Consider its basic properties, its role in nature and economy. Let's start with the characteristics of the entire group of the periodic system, which is headed by oxygen. The element differs from chalcogenes related to it, and water differs from hydrogen compounds of sulfur, selenium and tellurium. An explanation of all the distinguishing features can be found only by learning about the structure and properties of the atom.
Chalcogenes - elements related to oxygen
Atoms with similar properties form one group in the periodic system. Oxygen leads the chalcogen family, but differs from them in a number of properties.
The atomic mass of oxygen - the ancestor of the group - is 16 a. e. m. Chalcogenes during the formation of compounds with hydrogen and metals exhibit their usual oxidation state: –2. For example, in the composition of water (H 2 O), the oxidative number of oxygen is –2.
The composition of typical hydrogen compounds of chalcogenes corresponds to the general formula: H 2 R. When these substances are dissolved, acids are formed. Only the hydrogen compound of oxygen - water - has special properties. According to scientists, this unusual substance is both a very weak acid and a very weak base.
Sulfur, selenium, and tellurium have typical positive oxidation states (+4, +6) in compounds with oxygen and other nonmetals with high electronegativity (EO). The composition of chalcogen oxides is reflected in the general formulas: RO 2 , RO 3 . The corresponding acids have the composition: H 2 RO 3 , H 2 RO 4 .
The elements correspond to simple substances: oxygen, sulfur, selenium, tellurium and polonium. The first three representatives exhibit non-metallic properties. The oxygen formula is O 2 . An allotropic modification of the same element is ozone (O 3) . Both modifications are gases. Sulfur and selenium are solid non-metals. Tellurium is a metalloid substance, an electric current conductor, and polonium is a metal.
Oxygen is the most common element.
The total atomic content of an element in the earth's crust is approximately 47% (by weight). Oxygen is found both in free form and as part of numerous compounds. A simple substance, the formula of which is O 2 , is in the atmosphere, accounting for 21% of air (by volume). Molecular oxygen is dissolved in water, located between particles of soil.
We already know that there is another kind of existence of the same chemical element in the form of a simple substance. This is ozone - a gas forming a layer at an altitude of about 30 km from the earth’s surface, often called the ozone screen. Bound oxygen is included in water molecules, in the composition of many rocks and minerals, organic compounds.
The structure of the oxygen atom
Mendeleev’s periodic table contains complete information about oxygen:
- The element serial number is 8.
- The core charge is +8.
- The total number of electrons is 8.
- The electronic formula of oxygen is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4 .
In nature, there are three stable isotopes that have the same serial number in the periodic table, the identical composition of protons and electrons, but a different number of neutrons. Isotopes are designated with the same symbol - O. For comparison, we present a diagram reflecting the composition of three oxygen isotopes:
Properties of oxygen - a chemical element
There are two unpaired electrons on the 2p sublevel of the atom, which explains the appearance of oxidation states –2 and +2. Two paired electrons cannot separate, so that the oxidation state increases to +4, as in sulfur and other chalcogenes. The reason is the lack of a free sublevel. Therefore, in compounds of the chemical element oxygen does not show valency and oxidation state equal to the group number in the short version of the periodic system (6). His usual oxidative number is –2.
Only in compounds with fluorine does oxygen show an uncharacteristic positive oxidation state of +2. The EO value of two strong non-metals is different: EO (O) = 3.5; EO (F) = 4. As a more electronegative chemical element, fluorine more strongly holds its electrons and attracts valence particles at the external energy level of the oxygen atom. Therefore, in the reaction with fluorine, oxygen is a reducing agent and gives off electrons.
Oxygen is a simple substance
The English researcher D. Priestley in 1774 during the experiments released gas during the decomposition of mercury oxide. Two years earlier, C. Scheele received the same substance in its pure form. Only a few years later, the French chemist A. Lavoisier established what kind of gas is part of the air and studied the properties. The chemical formula of oxygen is O 2 . We will reflect in the record of the composition of the substance the electrons involved in the formation of a nonpolar covalent bond - O :: O. We replace each connecting electron pair with one feature: O = O. This oxygen formula clearly shows that the atoms in the molecule are connected between two common pairs of electrons.

We perform simple calculations and determine what the relative molecular mass of oxygen is: Mr (O 2 ) = Ar (O) x 2 = 16 x 2 = 32. For comparison: Mr (air) = 29. The chemical formula of oxygen is different from the ozone formula per oxygen atom. So Mr (O 3 ) = Ar (O) x 3 = 48. Ozone is 1.5 times heavier than oxygen.
Physical properties
Oxygen is a gas without color, taste or smell (at ordinary temperature and pressure equal to atmospheric). The substance is slightly heavier than air; soluble in water, but in small quantities. The melting point of oxygen is a negative value and is –218.3 ° C. The point at which liquid oxygen again turns into gaseous is its boiling point. For O 2 molecules, the value of this physical quantity reaches –182.96 ° C. In the liquid and solid state, oxygen takes on a light blue color.
Obtaining oxygen in the laboratory
When heated, oxygen-containing substances, such as potassium permanganate, produce a colorless gas that can be collected in a flask or test tube. If you bring a lighted torch into pure oxygen, then it burns more brightly than in air. Two other laboratory methods for producing oxygen are the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide and potassium chlorate (bertholta salt). Consider a diagram of a device that is used for thermal decomposition.
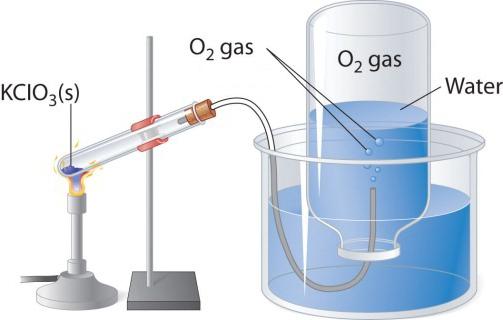
In a test tube or round-bottom flask, pour a little bit ofertol salt, close the cork with a gas outlet tube. Its opposite end should be directed (under water) into the flask overturned upside down. The neck should be lowered into a wide glass or mold filled with water. When the test tube is filled with bertholite salt, oxygen is released. Through a vent pipe, it enters the flask, displacing water from it. When the flask is filled with gas, it is closed under water with a cork and turned over. Obtained in this laboratory experiment, oxygen can be used to study the chemical properties of a simple substance.
Combustion
If the laboratory is burning substances in oxygen, then you need to know and comply with fire regulations. Hydrogen instantly burns in the air, and mixed with oxygen in a ratio of 2: 1, it is explosive. The burning of substances in pure oxygen is much more intense than in air. This phenomenon is explained by the composition of the air. Oxygen in the atmosphere is slightly more than 1/5 part (21%). Combustion is the reaction of substances with oxygen, resulting in the formation of various products, mainly oxides of metals and non-metals. Mixtures of O 2 with flammable substances are flammable; in addition, the resulting compounds may be toxic.
The burning of an ordinary candle (or match) is accompanied by the formation of carbon dioxide. The following experiment can be carried out at home. If you burn the substance under a glass jar or a large glass, then combustion will cease as soon as all oxygen is consumed. Nitrogen does not support breathing and burning. Carbon dioxide, an oxidation product, no longer reacts with oxygen. Transparent lime water can detect the presence of carbon dioxide after burning a candle. If combustion products are passed through calcium hydroxide, the solution becomes cloudy. A chemical reaction occurs between lime water and carbon dioxide, and insoluble calcium carbonate is obtained.
Industrial oxygen production
The cheapest process, resulting in air-free O 2 molecules, is not related to chemical reactions. In industry, say, in metallurgical plants, air is liquefied at low temperature and high pressure. The most important components of the atmosphere, such as nitrogen and oxygen, boil at different temperatures. Separate the air mixture while gradually warming to normal temperature. First, nitrogen molecules are released, then oxygen. The separation method is based on different physical properties of simple substances. The formula of a simple oxygen substance is the same as it was before cooling and liquefying the air - O 2 .
As a result of some electrolysis reactions, oxygen is also released, it is collected over the corresponding electrode. Gas is needed by industrial and construction enterprises in large volumes. Demand for oxygen is constantly growing, especially the chemical industry needs it. The obtained gas is stored for industrial and medical purposes in steel cylinders provided with marking. Oxygen tanks are painted blue or blue to distinguish them from other liquefied gases - nitrogen, methane, ammonia.
Chemical calculations by the formula and equations of reactions involving O 2 molecules
The numerical value of the molar mass of oxygen coincides with another quantity - the relative molecular weight. Only in the first case are units of measure present. Briefly, the formula for the oxygen substance and its molar mass should be written as follows: M (O 2 ) = 32 g / mol. Under normal conditions, a mole of any gas corresponds to a volume of 22.4 liters. So, 1 mol of O 2 is 22.4 liters of substance, 2 mol of O 2 is 44.8 liters. According to the reaction equation between oxygen and hydrogen, you can notice that 2 moles of hydrogen and 1 mole of oxygen interact:
If 1 mol of hydrogen is involved in the reaction, then the volume of oxygen will be 0.5 mol • 22.4 l / mol = 11.2 l.
The role of O 2 molecules in nature and human life
Oxygen is consumed by living organisms on Earth and has been involved in the circulation of substances over 3 billion years. This is the main substance for respiration and metabolism, with its help, the decomposition of molecules of nutrients occurs, the energy necessary for organisms is synthesized. Oxygen is constantly consumed on Earth, but its reserves are replenished due to photosynthesis. The Russian scientist K. Timiryazev believed that thanks to this process, life on our planet still exists.
The role of oxygen in nature and the economy is great:
- absorbed in the process of respiration by living organisms;
- participates in photosynthesis reactions in plants;
- part of organic molecules;
- processes of decay, fermentation, rusting occur with the participation of oxygen acting as an oxidizing agent;
- used to produce valuable products of organic synthesis.
Liquefied oxygen in cylinders is used for cutting and welding metals at high temperatures. These processes are carried out at machine-building plants, at transport and construction enterprises. For work under water, underground, at high altitude in an airless space, people also need O 2 molecules. Oxygen pillows are used in medicine to enrich the composition of the air inhaled by sick people. Gas for medical purposes differs from technical gas in the almost complete absence of impurities and odors.
Oxygen is an ideal oxidizing agent
Oxygen compounds with all chemical elements of the periodic table are known, except for the first representatives of the noble gas family. Many substances directly react with O atoms, excluding halogens, gold and platinum. Of great importance are phenomena involving oxygen, which are accompanied by the release of light and heat. Such processes are widely used in everyday life, industry. In metallurgy, the interaction of ores with oxygen is called firing. Pre-ground ore is mixed with oxygen enriched air. At high temperatures, metals are reduced from sulfides to simple substances. So get iron and some non-ferrous metals. The presence of pure oxygen increases the speed of technological processes in various branches of chemistry, technology and metallurgy.
The emergence of a cheap method of producing oxygen from air by the method of separation into components at low temperature stimulated the development of many areas of industrial production. Chemists consider O 2 molecules and O atoms to be ideal oxidizing agents. These are natural materials, they are constantly renewed in nature, do not pollute the environment. In addition, chemical reactions involving oxygen most often result in the synthesis of another natural and safe product - water. An important role is played by O 2 in the neutralization of toxic industrial wastes and the purification of water from pollution. In addition to oxygen, its allotropic modification, ozone, is used for disinfection. This simple substance has a high oxidative activity. During ozonation of water, pollutants decompose. Ozone also has a detrimental effect on the pathogenic microflora.