The pelvic diaphragm consists of the muscles that raise the anus, the right and left coccygeal, the valve of the anus, as well as the connecting membranes. All of them form a single structure that has certain functions.
Muscle lifting the anus
It is a paired triangular apparatus of the iliac, coccygeal and pubic muscles. In combination with connective fibers, it creates a funnel-shaped plate of muscles that descend to the anus.
The coccyx-pubic part comes from the front of the tendon arch of the muscle that raises the anus. It looks like a sealed portion of the covering connective tissue. In addition, it relates to fascia, which cover the main muscle that raises the anus. Inside, the coccygeal-pubic area extends from the upper medial section of the closure opening. The search should be conducted from within the branches of the bone apparatus of the pubis. Then it descends to the coccyx and is fixed at the anal and sacral ligaments, as well as the front of the rectum. From bending between the anus and genitals, the coccygeo-pubic muscles are attached behind and are located under the muscles of the coccyx and rectum. Adjacent to the urine canal in front.
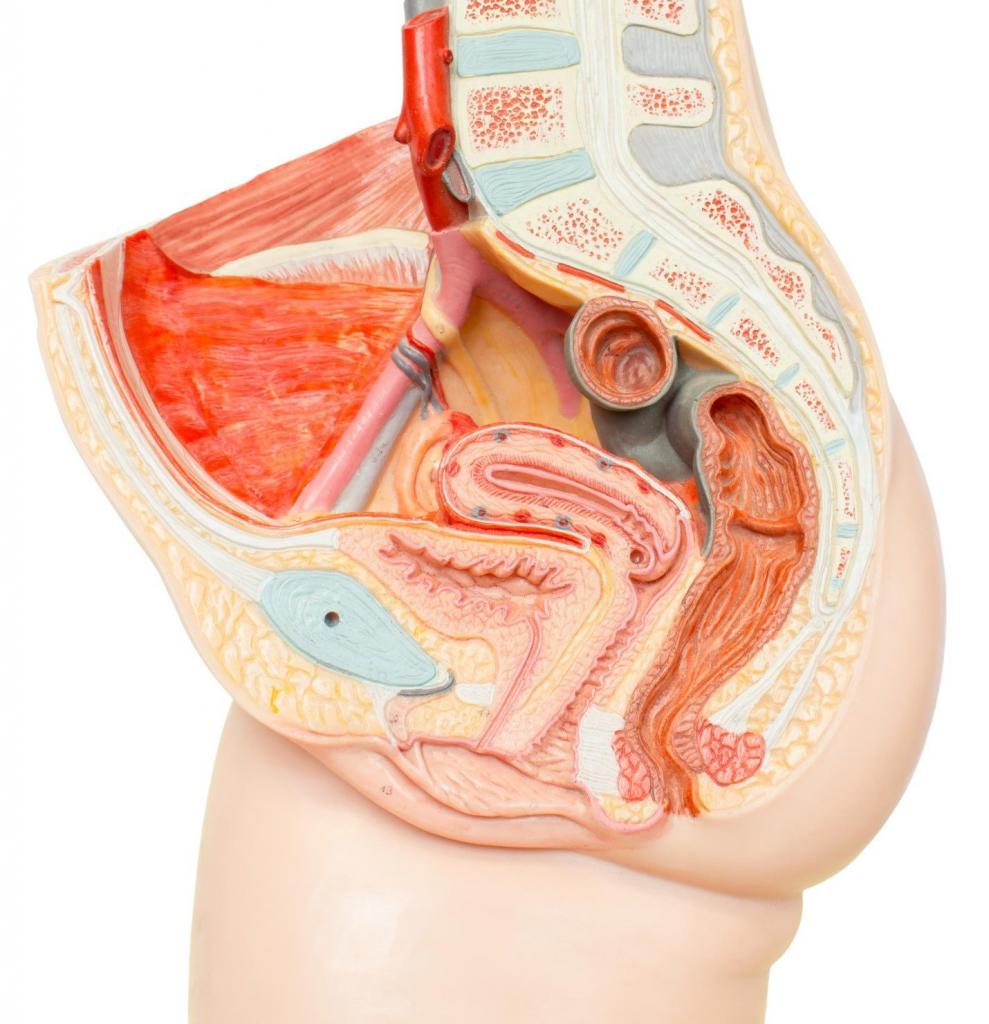
The muscle that lifts the prostate gland is part of the pubic-coccygeal. In the male, it is adjacent to the prostate. It is thanks to her that this organ can slightly lift up and squeeze during contraction. In women, these compounds form bundles of the pubis and vagina.
The recto-pubic muscle goes above and below the branches of the pubis. It connects to the opposite side of the front of the rectum, goes around the prostate or vulva, and is then woven into the muscles of the intestine. The main function of the pubic-rectal muscle is to contract. Compression of both coccygeo-pubic muscles brings the opposite intestinal walls closer together. This narrows the part of the intestine that is remote from the middle to the appearance of a narrow cross-member. That is, it raises it forward and up together with the pelvic floor. In the female, this muscle is also responsible for the compression of the vagina.
The iliac-coccygeal muscle extends from the semicircle of tendons and posterior to the coccygeal-pubic area. It is located behind, below and sideways. It is attached to the coccyx below the coccygeal-pubic processes. Together with its opposite part, the coccygeal-iliac fibers form a tendon that goes through the top of the coccyx and rectum. Outside it frames on the sides of the edge of the lower spine. Adheres to the tailbone fibers behind and covers it from above. The main functionality is to raise the bottom of the pelvis, making it stronger, but not depriving relative mobility.
Many are interested in the name of the muscle that raises the anus. However, no other term exists. In Latin, it sounds like m. levator ani.
Tailbone muscle
It looks like a triangle plate, which is located inside the ligaments of the osteum and sacrum. It originates from the spine of the seat, gradually expanding. It is attached to the sides of the bottom of the vertebrae of both the coccyx and sacrum. Before adjoins the back of the muscle responsible for raising the anus. Together they form a common muscle layer.
Anal valve
Frames a segment of the anus of the rectum, located further than the middle of the pelvic diaphragm. The upper muscles are adjacent to the fibers that raise the anus.
It has three parts:
- Subcutaneous. Contains the finest muscle filaments. Attaches directly to the skin of the anus.
- Superficial. Consists of strong arcuate joints.
- Deep. Contains large arched bundles, which frames the channel of the anus.
More powerful muscle rings are located inside. Outside, it looks sharp at the end of the upper section of the coccyx and skin. Go from the sides of the anus of the intestine. The front and outside are also pointed in the area of the tendons, cancellous-onion section and the cover between the genitals and the anus. The main function is to reduce the anus from the sides.
Associated disorders
There is such a thing as "muscle syndrome that raises the anus." It is expressed by spasmodic pain of the rectum. The reasons for this condition are not known until now. Treatment includes pain medication, physiotherapy, and sitz baths.