The human organ of hearing includes three main parts. The first is the outer ear. It picks up sound vibrations. The task of the middle section is to transmit the sound wave to the inner ear. The middle section converts this irritation into a nerve impulse.
Inner ear: what is it and what is its composition?
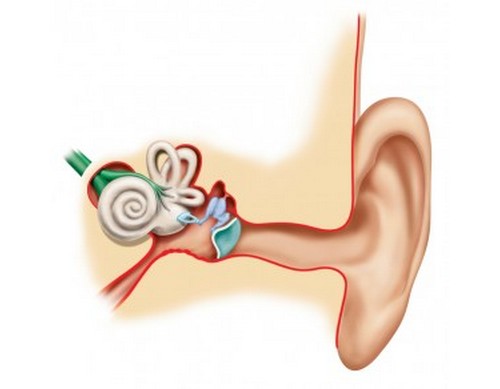
It is located in the cavity of the temporal bone, namely between the tympanic cavity and the internal auditory canal. The assumption that this organ performs only the function of hearing is misleading. Few people know that he has the responsibility to maintain balance when moving. The structure of the inner ear includes structures that are two labyrinths: bone and membranous (located inside the first). Between these formations there is a space that is filled with a specialized fluid that can transmit auditory vibrations - a perilymph.
Components
What is part of the inner ear? Each of the labyrinths has its own special structure. In the bone emit:
- vestibule;
- semicircular canals;
- a snail;
The first of these structures is an expanded intermediate part of the bone labyrinth. It is considered the connecting link between the cochlea (communicated at the back) and the semicircular canals (connected at the front). The lateral part of the vestibule has two openings: the vestibule window and the cochlea, and the medial part has two cavities resembling a sphere and an ellipse.
The back of the bone labyrinth is represented by semicircular canals. They are located in three mutually perpendicular planes (sagittal, horizontal and frontal). This is due to the fact that a person, moving in space, is also located in three planes. The channels are connected to the vestibule by means of extended legs.
In front is a snail. It has a spiral shape. Starting from the vestibule window, the cochlea makes two and a half revolutions around a core with a bone base. From the bone rod into the cochlear canal there is a spiral plate (consists of bone tissue) in order to divide this structure into two stairs: the vestibule and the tympanum. At the top of the cochlea they connect.
In addition to bone structures, the structure of the inner ear includes formations consisting of soft tissues. Such is the membranous labyrinth. It is filled with endolymphatic fluid and is divided into four sections:
- Spherical pouch.
- Elliptical bag
- Semicircular ducts.
- Cochlear duct.
The two pouches mentioned above can be called “queen cells”. They are in the recesses of the vestibule and communicate with each other. A bag in the shape of a sphere is connected with the channel of the cochlea (one of the parts of the bone labyrinth), and the elliptical one is connected to the ducts of the semicircular canals. If the channels ended with a leg, then the ducts with an ampoule. One duct can have only one ampoule.
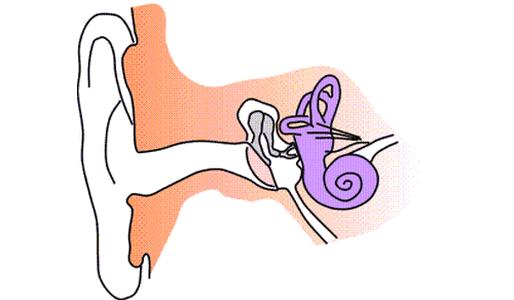
In turn, the channel of the cochlea has its own duct. If you make a cross section along it, you get a triangle. To understand how a sound wave is conducted, it is worth disassembling the main parts of the triangle. Two parts are distinguished in the duct: upper and lower. The function of the top is isolation from the staircase of the vestibule, the bottom - from the drum. Also on the bottom wall is a basilar membrane, on which fibrous formations lie, in order to perform a resonant function. The structure of the inner ear includes a formation that converts sound vibrations into nerve impulses. This is a Corti's organ. It is a group of membrane-coated hair cells.
Inner ear function
This organ of the human body serves to:
- Perception of sound.
- Balance and coordination in space.
In the absence of any of these functions, a full-fledged existence of a person will not be possible. In this case, he will not be able to reunite with the outside world. Receptor cells of the auditory apparatus are responsible for the perception of sound vibrations, and receptor cells of the semicircular canals and their formations are responsible for coordination.
Sound path through the auditory analyzer
The ear canal is the first in the path of the sound wave, which, due to its large area, captures vibrations. Then they, having hit the eardrum, cause it to oscillate, which allows you to transfer the wave to the system of auditory ossicles, which will amplify oscillatory movements many times and pass them to the vestibule window. The perilymph begins to move. Oscillations from the perilymph will be transmitted to the endolymph of the membranous labyrinth. Hair cells from fluid movement are excited and transform the mechanical energy of the movement into an electrical impulse, which is transmitted through the auditory nerve to the cerebral cortex, where the analysis takes place and the response is reproduced.
Vestibular analyzer
The composition of the inner ear also includes sensitive hair cells, together with a jelly-like substance, which are located in the membranous labyrinth. In ampoules, these groups of cells are called scallops. They capture various kinds of angular accelerations (acceleration of rotation). In queen cells, these cells are arranged in the form of spots and are represented by the otolith apparatus, since crystals of calcium salts are found in the jelly-like substance. This apparatus of the pouch and uterus reacts to changes in the position of the head, body turns and linear acceleration.
At the moment of movement of the body, cell receptors are excited by the movement of endolymph. As a result of this, a nerve impulse is generated, which is transmitted to the neurons of the vestibular node lying at the bottom of the ear canal, and then to the central nervous system: spinal cord and brain. When information on neurons enters the spinal cord, uncontrolled muscle contractions occur that regulate body coordination and movement.
To summarize
So, we examined the general information about the inner ear. This body has a complex device. As already mentioned, the structure of the inner ear includes a number of structures, both bone, and so consisting of other tissues. The two main functions of the inner ear are auditory and vestibular. In case of damage to the ear structures due to injuries or diseases, not only disturbance in the perception of sounds can occur, but also a perversion of the perception of the position of the body in space, loss of coordination. Therefore, it is worth paying attention to the state of the organs of the auditory and vestibular analyzer.