In the article, we will consider what protein and white blood cells in urine mean.
A general urine test along with a blood test is perhaps the most common type of study. Due to this, various diseases are determined, and not only the genitourinary system. The study of urine takes into account parameters such as quantity, transparency, color, smell, pH. Each of these properties has its own norm. White blood cells and protein in the urine are symptoms of the presence of various pathologies. But it must be understood that when they say that these components are absent in urine, this does not always mean that there are no diseases. Even a completely healthy person can have traces of them.
The mechanism of the appearance of protein in urine
So, we will understand when there are elevated white blood cells and protein in the urine.
Through the basal glomerular membrane, the vast majority of proteins do not normally penetrate. This is due to the large size of the protein units, as well as because of their charge and shape. If at least a small disturbance appears in the membrane, then albumin without leukocytes comes into the urine first, if the defect is more significant, the molecules are larger. Epithelial tubular tissue, even in a healthy person, forms a certain proportion of proteins, some penetrates from the ureters and urethra.
When does protein and white blood cells appear in urine?
Proteinuria: classification
A pathology such as proteinuria (the appearance in the urine of protein in amounts available for detection by analyzes) has two classifications. Consider them.
At the site of origin, proteinuria is divided into:
- renal (due to renal impairment);
- prerenal (due to increased tissue breakdown);
- postrenal (the pathology process is located in the urinary tract).
Renal proteinuria has two varieties:
- glomerular (if the filtration system of the renal glomerulus is damaged);
- tubular (based on a change in the normal mechanism of reuptake of protein low molecular weight units).
If protein and white blood cells are elevated in the urine, it is important to find out the causes.
Protein in the urine: causes
There are several ways to detect protein in the urine. A value of 0.033 g and above is considered pathological. Urine collected in the morning should not have more than 0.002 g per liter. The protein concentration per day in a healthy body is not higher than 50-150 mg.
Its excessive content in urine more than the permissible norm is called proteinuria.
Many people wonder where the protein and white blood cells come from in the urine. The reasons for the appearance of protein can be very different. The most common among them are:
- glomerulonephritis;
- diabetic nephropathy (diabetes mellitus);
- nephrotic syndrome;
- kidney sclerosis;
- inflammation of the urethra and bladder;
- myeloma and other paraproteinemic disorders;
- oncology of the urinary tract;
- a defect in the normal supply of blood to the renal tissue against a background of heart failure;
- intoxication of the body with heavy metals;
- sarcoidosis;
- sickle cell anemia;
- connective tissue diseases (kidney damage with red systemic lupus erythematosus);
- amyloidosis of the kidney;
- renal tuberculosis.
Does this always indicate pathology?
When are white blood cells and protein in urine considered normal?
However, there are cases in which the increased content of these elements in urine is not a symptom of the disease. This happens when consuming excess amounts of protein-containing food, severe physical exertion, a change in body position, under the influence of low and high temperatures. It is very interesting that proteinuria can be a consequence of a stress factor.
What other causes of protein and white blood cells in urine are possible?
Hemoglobinuria
The presence of such a protein in the urine as hemoglobin needs special attention. It is not normally contained in this fluid. Its presence in urine indicates a serious violation in the tissues of the kidneys. There are two ways to penetrate urine. The first is based on the ongoing processes of destruction in red blood cells, hemolytic anemia develops.
So, elevated leukocytes and protein in the urine are due to:
- allergies
- spleen diseases;
- intoxication of the body with toxic substances.
At the same time, a large amount of hemoglobin is released from red blood cells, part of it passes through the glomerular membrane.
The second mechanism is manifested in violation of bleeding or defects in the urinary organs. This situation is possible with:
- oncology;
- kidney stones;
- glomerulonephritis.
In this case, the urine acquires a bright red hue. With this value in the analyzes, remember the false hemoglobinuria that occurs when the timing of the study is violated.
Protein and white blood cells in the urine must be alert.
Leukocyturia
Urine normally contains up to three white blood cells in the field of vision in men, up to five in women. A large number of these elements in urine indicates inflammation either in the urinary tract or in the kidney tissue. The increased content of leukocytes in chronic processes is more informative in comparison with bacteria. It is not always possible to detect the latter.
With an increased concentration of leukocytes in the urine, purulent clots become noticeable. A similar phenomenon is called pyuria. It is also often accompanied by discoloration and an unpleasant odor.
If white blood cells are of increased importance, then there may be the following reasons:
- inflammation in the bladder, urethra, renal tissue;
- inflammation of the prostate;
- urolithiasis disease;
- nephritis of tubulo-interstitial origin;
- glomerulonephritis and chronic and acute pyelonephritis.
We examined the causes and symptoms of protein in the urine and white blood cells in the urine. How to treat this pathology?
Treatment
When urine has a high concentration of white blood cells, then you need to determine the cause of this phenomenon and prescribe treatment. Such symptoms alone are only signs of certain diseases. It happens that in the urine deviations from the norm are due to non-compliance with recommendations for its collection. In such a situation, it is worth retaking the analysis. The doctor, as a rule, prescribes another study to the patient. If the indicators deviate from the norm a second time, then an ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys is used. It is also necessary to assign an analysis of urine for the presence of epithelial tissue in it, as well as to identify ketone bodies. What does protein and white blood cells in urine mean? The presence of these elements indicates damage directly to the kidneys.
Determine exactly what the cause of the changes in urine is, its analysis according to Nechiporenko, as well as the Reberg and Zimnitsky test will help.
Taking antibiotics and other medicines
If the root cause is infectious inflammation, then antibacterial medicines are necessarily prescribed. In addition, a plentiful drink and a diet that excludes salted, fried and spicy are desirable.
With tuberculosis of the urinary system, therapy with special drugs is required. With urolithiasis, a specialist prescribes medications that can remove sand if the stones are large, prompt removal or crushing of stones is indicated.
All the methods listed above are also relevant for the elimination of nitrites in urine, because they also act only as a symptom, and not an independent disease.
Urinalysis: transcript, norms, indicators
Urinalysis occurs in several ways.
Organoleptic properties of urine.
- Color. Varies normally from light straw to deep yellow. With an admixture of other shades, the patient should be wary.
- Smell. The urine of a healthy person has a specific unsharp smell, which can become stronger with cystitis and have an ammonia hue.
- Transparency. Precipitation or turbidity of urine indicates the possible presence in it of salts, fats, pus, mucus, bacteria, red blood cells and other substances that should not be normal. Urine should be transparent.
- Foaminess. When shaking normally, the urine foams little, and the foam settles quickly. If it is stable, then this indicates the presence of protein.
Physical and chemical indicators. This category includes only two parameters that are currently determined by special test strips.
- Acidity. This indicator normally allows values from 4 to 7 pH in the form of a general analysis of urine in adults, that is, from moderately acidic to moderately alkaline. This is not a deviation. If the acidity is slightly reduced, this is characteristic of chronic renal failure, increased potassium in the blood, increased activity of the parathyroid gland, cancer of the bladder or kidney, ureaplasmosis. This indicator can be high with starvation or dehydration, frequent consumption of meat for food, intake of a number of drugs, and elevated body temperature. It can also be a sign of diabetes.
- The density of urine. Normally, this indicator for children after twelve years of age and adults ranges from 1.010 to 1.022 grams per liter. If foreign cells or substances are contained in large quantities due to an impaired metabolism or infection, the density increases. It also occurs during dehydration. Low density can be observed as a result of the use of diuretics, diabetes insipidus, and kidney failure.
Biochemical properties of urine
To evaluate these parameters, resort to special reagents and analyzers.
- Protein. Its normal content in urine is approaching zero - 0.033 grams per liter (no more).
- Sahara. The maximum permissible value of their content in the urine of an adult patient is 0.8 mmol per liter. With an increase in this indicator, there may be physiological reasons such as excessive consumption of sweets, pregnancy, and the release of adrenaline as a result of stress. However, most likely we are talking about one of the following disorders: renal dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, Cushing's syndrome, acute pancreatitis, adrenal gland damage.
- Ketone bodies. The presence of ketone bodies in the urine may indicate endocrine diseases: acute inflammatory process of the pancreas, diabetes mellitus, Cushing's syndrome, thyrotoxicosis. You also need to keep in mind the likelihood of ketone bodies appearing in urine during alcohol intoxication, starvation, traumatic brain injuries, and low-carb diets.
- Bile pigments (urobilinogen, bilirubin) are the products of hemoglobin breakdown, appear in the urine with lesions of the biliary tract and liver, as well as as a result of the destruction of red blood cells in malaria, sickle cell anemia, toxic hemolysis, hemolytic disease.
- Indican. The presence of such a substance in urine indicates the processes of decay and fermentation in the intestine. It should not be normal in a urinalysis.
Microscopic characteristics. An examination of urine under a microscope is required additionally if violations are detected.
- Epithelium. The urine of a healthy person can include individual epithelial cells (under a microscope up to ten in the field of view), however this is most likely a rarity. The increased content of epithelium in the urine indicates, for example, diseases such as cystitis and certain types of nephropathy.
- Slime. It occurs in urine during genital infections and inflammation of the genitourinary system.
- Hyaline cylinders are formations that consist mainly of tubule cells in the kidneys and proteins. If there are more than twenty of them in one milliliter of urine, this may indicate pyelonephritis, hypertension, glomerulonephritis. It is also the result of diuretics.
- Blood cells (white blood cells, red blood cells). May be present in urine in small concentrations. Normal values of red blood cells: for women - from 0 to 3, for men - from 0 to 1; for leukocytes: in women, from 0 to 6, in men, from 0 to 3. If red blood cells are elevated, this may be a sign of urolithiasis, kidney infarction, nephrotic syndrome, cancer of the genitourinary system, acute glomerulonephritis.
If the protein in the urine and white blood cells are elevated, what this means should be determined by the doctor. Most likely, this is the result of urinary tract pathologies.
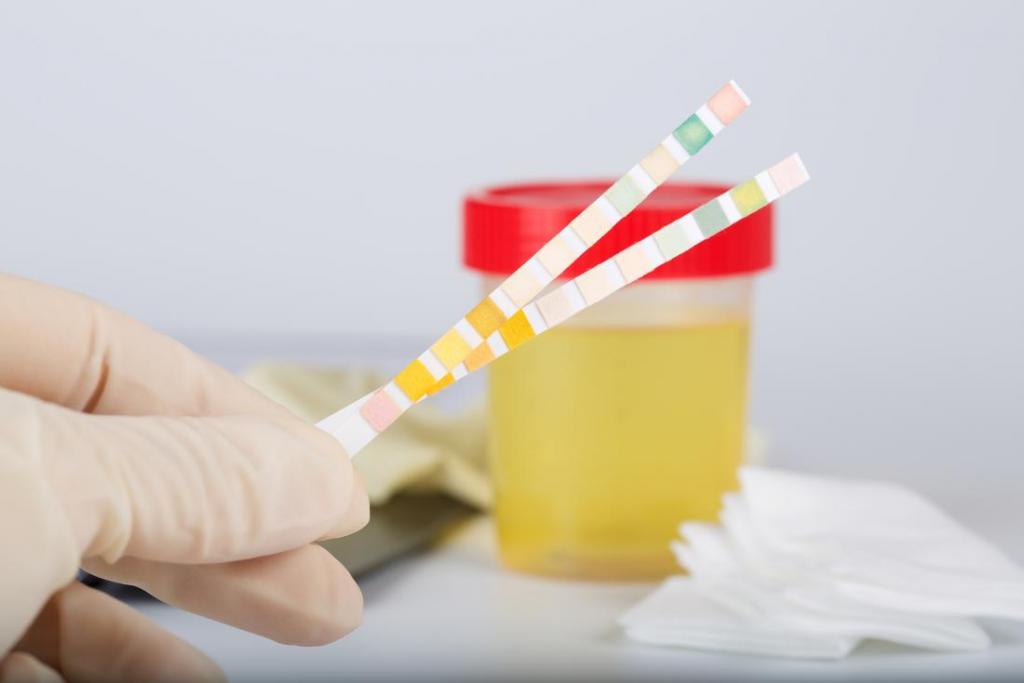
- Bacteria. The urine of a healthy person is sterile. Bacteria are found with insufficient hygiene before obtaining biomaterial or with an infection of the genitourinary system.
- Mushrooms are not detected normally. Their presence indicates the occurrence of an infection.
- Parasites. The presence of any amount of parasites in urine is unacceptable, urgent additional diagnosis and treatment is required.
- Granular cylinders. They are a mixture of cells of the tubules of the kidneys and red blood cells that appears in the urine with lead poisoning, the inflammatory process of the urinary system, and viral infections.
- Salt. The urine is not normally contained, their presence may indicate urolithiasis.
- Wax cylinders are formed if a granular or hyaline cylinder gets stuck in the lumen of the tubule of the kidney. This happens with chronic kidney failure, nephrotic syndrome, renal amyloidosis.
We found out what protein and white blood cells in urine mean.