A human skull is a bone box of a complex configuration for placing the brain and sensitive receptors directly connected with the brain: vision - eyes, hearing - two external sound receivers combined with the inner middle ear, smell - nose with two channels and maxillary cavity, taste - receptors located on the tongue. The tactile, or tactile, information is received by the brain indirectly.
Functional separation
The structure of the human skull is rational, like everything in nature. The brain chamber occupies the entire upper part of the cranium, and the lower part is designed to accommodate visceral organs. The brain part consists of several single and paired bones, connected by means of sutures. These are the frontal, parietal and occipital bones, paired bones - sphenoid and temporal. The visceral part includes the upper jaw, lower nasal concha, palatine and zygomatic bones, lower jaw and hyoid bone.
Visceral part
The entrance sections of the digestive and respiratory tract open in the skull. The moving part of the skull, the lower jaw, ends with a pharynx passing into the esophagus and larynx. Thus, the structure of the human skull is focused on the vital activity of the whole organism. These two receivers of food and air are separated and each performs its function. The base of the skull rests on the vertebral column, it is supported by seven cervical vertebrae, they also play the role of a frame support for the cervical muscles, arteries and veins. Many nerves pass through the lower part, each of them carries to the brain its own piece of information, receiving the necessary impulses in response. The rather complex structure of the human skull is justified by many useful functions.
Vault
The upper part is the so-called arch, the front part of the arch is the forehead, which passes into the superciliary arches, between which there is a recess. On the sides of the cranial vault, the temporal bone, parietal and sphenoid bones are closed. Down from the line of closure of the listed bones, the base of the skull begins. The shape of the base is complex, characterized by a large number of tunnels through which nerve fibers and blood vessels go. In the back of the base is the occipital bone. In many ways, the structure of the human skull is subject to life support tasks.
Front part
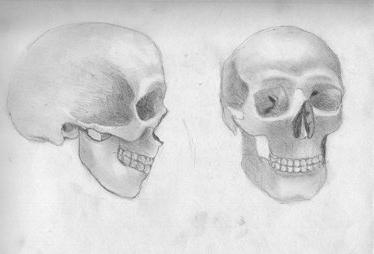
The front part of the skull consists of three tiers, distinct from each other, not interconnected and performing independent functions. This eye socket is a paired formation in the form of a horizontally located pyramid with the base outward, the apex inward. The bones of the human skull , the structure of the internal segments - everything is carefully thought out and interconnected. An eyeball, a gland producing tear fluid, and a certain amount of fatty tissue are placed in the orbit. Below the eye is the nasal cavity located in the center. In the middle, the cavity is divided by a bone septum, and outward it opens with a pear-shaped hole. All this can be seen if you look at the structure of the human skull in pictures. Below the nasal cavity is the oral cavity, which is bounded by the alveoli and the dentitions from the sides and the bony palate from above. The oral cavity is the most mobile part of the skull, performing a chewing function. In addition, a speech apparatus is located in the oral cavity.