Studying geography and topography, we come across a concept such as terrain. What is this term and what is it used for? In this article we will understand the meaning of this word, find out what types and forms of reliefs are, as well as much more.
Relief concept
So what does this term mean? The relief is a set of surface irregularities of our planet, which are composed of elementary forms. There is even a separate science that studies its origin, development history, dynamics and internal structure. It is called geomorphology. The relief consists of individual forms, that is, natural bodies of nature, representing its individual parts and having their own dimensions.
Variety of shapes
According to the morphological principle of classification, these natural bodies can be both positive and negative. The first of them rise above the horizon, representing a rise in the surface. An example is a hillock, a hill, a plateau, a mountain, and more. The second, respectively, form a lowering relative to the horizon. These can be valleys, beams, hollows, ravines, etc. As mentioned above, the shape of the relief consists of individual elements: surfaces (faces), points, lines (edges), angles. The complexity of distinguish between complex and simple natural bodies of nature. Simple forms include tubercles, hollows, hollows, etc. They are separate morphological elements, the combination of which forms a shape. An example is a hillock. It is divided into such parts: sole, slope, top. The complex form consists of a number of simple ones. For example, the valley. It includes a channel, floodplain, slopes and more.
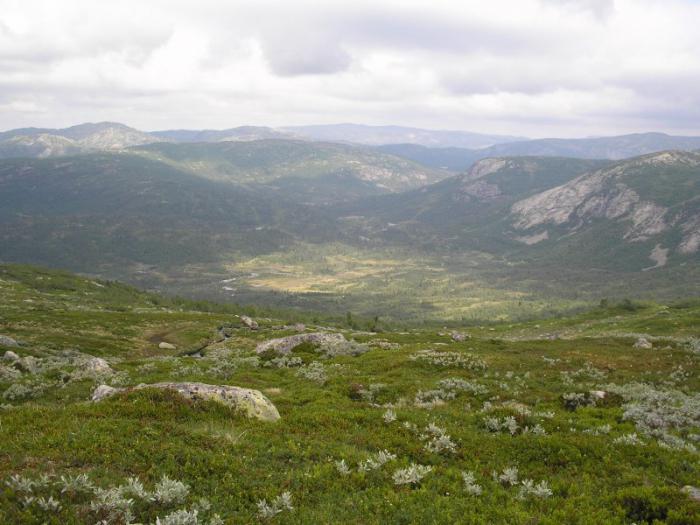

The degree of slope distinguish subhorizontal surfaces (less than 20 degrees), sloping and slopes (more than 20 degrees). They can have a different shape - straight, convex, concave or stepped. By the degree of stretching, they are usually divided into closed and open.
Types of reliefs
The combination of elementary forms, which have a similar origin and extend over a certain space, determines the type of relief. In significant areas of our planet, it is possible to combine several separate species on the basis of a similar origin or difference. In such cases, it is customary to talk about groups of relief types. When the union is made on the basis of their formation, then they talk about the genetic types of elementary forms. The most common types of land relief are flat and mountainous. In terms of height, the former are usually divided into depression, elevations, lowlands, plateaus and plateaus. Among the second, the highest, highest, medium and low are distinguished.
Flat terrain
This is a terrain characterized by insignificant (up to 200 meters) relative elevations, as well as a relatively low slope slope (up to 5 degrees). The absolute heights here are small (only up to 500 meters). These sections of the earth's surface (land, bottom of the seas and oceans), depending on the absolute height, are low (up to 200 meters), elevated (200-500 meters), upland or high (over 500 meters). The relief of the plains depends primarily on the degree of ruggedness and land cover. It can be loamy, clay, peat, sandy loamy soils. They can be cut by river beds, beams and ravines.
Hilly terrain
This is a terrain with a wavy nature of the earth’s surface, forming bumps with absolute heights of up to 500 meters, relative elevations of up to 200 meters and a steepness of no more than 5 degrees. The hills are often composed of hard rocks, and the slopes and peaks are covered with a thick layer of loose rock. The lowlands between them are flat, wide or closed basins.
Elevations
The mountainous terrain is a terrain representing the surface of the planet, significantly elevated relative to the surrounding territory. It is characterized by absolute heights of 500 meters. Such a territory has a diverse and complex relief, as well as specific natural and weather conditions. The main forms are mountain ranges with characteristic steep slopes, which often turn into cliffs and rocks, as well as gorges and hollows located between the ranges. The mountainous areas of the earth's surface are substantially elevated above sea level, while they have a common base, which rises above the plains adjacent to them. They consist of many negative and positive landforms. According to the height level, they are usually divided into low mountains (up to 800 meters), mid mountains (800-2000 meters) and high mountains (from 2000 meters).
Landforming
The age of elementary forms of the earth's surface is relative and absolute. The first establishes the formation of a relief relative to any other surface (sooner or later). The second is determined using a geochronological scale. The relief is formed due to the constant interaction of exogenous and endogenous forces. So, endogenous processes are responsible for the formation of the main features of elementary forms, and exogenous, on the contrary, tend to align them. In relief formation, the main sources are the energy of the Earth and the Sun, do not forget about the influence of space. The formation of the earth's surface occurs under the influence of gravity. The main source of endogenous processes can be called the thermal energy of the planet, which is associated with radioactive decay occurring in its mantle. So, under the influence of these forces a continental and oceanic crust was formed. Endogenous processes cause the formation of faults, folds, the movement of the lithosphere, volcanism and earthquakes.
Geological observations
The study of the surface shape of our planet is carried out by geomorphologists. Their main task is to study the geological structure and terrain of specific countries, continents, and the planet. In compiling the characteristics of a particular area, the observer must determine what caused the surface shape in front of him, to understand its origin. Of course, it will be difficult for a young geographer to independently understand these issues, so it is better to turn to books or a teacher for help. Composing a description of the relief, a group of geomorphologists must cross the study area. If you want to draw up a map only along the route, then you should maximize the lane of observation. And in the process of research periodically move away from the main path to the sides. This is especially important for poorly visible terrain, where the forest or hills interfere with the review.
Mapping
When writing down general information (the terrain is hilly, mountainous, rugged, etc.), it is also necessary to map and describe each element of the relief separately - a steep slope, ravine, ledge, river valley, etc. Determine dimensions - depth, width, height, tilt angles - often, as they say, by eye. Due to the fact that the relief depends on the geological structure of the terrain, when conducting observations, it is necessary to describe the geological structure as well as the composition of the rocks that make up the studied surfaces, and not just their appearance. It is necessary to note in detail karst craters, landslides, caves, etc. In addition to the description, schematic sketches of the study area should also be carried out.
By this principle, you can explore the area near which your home is located, or you can describe the relief of the continents. The methodology is one, only the scales are different, and the time for a detailed study of the continent will require much more. For example, in order to describe the relief of South America, you will need to create many research groups, and even then it will take more than one year. After all, the aforementioned mainland is characterized by an abundance of mountains stretching along the entire continent, Amazonian virgin forests, Argentinean pampas, etc., which creates additional difficulties.
Note to the young geomorphologist
When compiling a relief map of the area, it is recommended to ask local residents where it is possible to observe the places where the layers of rock and groundwater exit. These data should be entered on the map of the area and describe them in detail and sketch. On the plains, rock is most often exposed in places where rivers or ravines cut through the surface and form coastal cliffs. Also, these layers can be observed in quarries or where a highway or railway passes through a cut-out recess. The young geologist will have to consider and describe each layer of rock, it is necessary to start from the bottom. Using a tape measure, you can make the necessary measurements, which should also be entered in the field book. The description should indicate the size and characteristics of each layer, their serial number and exact location.