Any novice athlete who has set himself the goal of losing weight or gaining muscle mass, regardless of gender, is faced with a metabolic process called catabolism. What it is, what effect it has on the body, how to start or stop it, this article will help to figure it out. It is always important to remember that all processes in the body were originally laid down by nature, and interference with them without the initial stages of preparation can only do harm. Therefore, before rushing to extremes, you need to read more than one material. Only by comparing the facts from several sources, you can take the first step.
From the course of physiology
Everyone has heard about the metabolism, which in the scientific community is called metabolism. In turn, it is divided into anabolism and catabolism. What it is, it will be easier to understand if you literally translate the names from Latin - growth and destruction, respectively. If the athlete is faced with the task of gaining muscle mass - anabolism will be his prerogative. For a person who wants to lose excess fat - catabolism. Everything is quite simple at the level of body weight and calories burned. However, delving into physiology, and without understanding the biochemical processes, it is impossible to achieve results, one may encounter the concept of “complex organic substances”, which include proteins, carbohydrates and fats, which are directly involved in the metabolism and are responsible for building the figure of any person.
Starting the process of losing weight
It is known for certain, thanks not only to numerous reviews of professionals, but also to many research institutes of the world that to start the process of catabolism it is enough to consume less calories and spend more. Moreover, the difference between consumed and consumed calories should not exceed 15% of the daily norm, otherwise catabolism will develop into complete destruction of the body. The ways of catabolism, in a understandable language, for any athlete include the oxidation of complex organic matter, the transport of oxidation products to the mitochondria of cells for burning, and the release of energy. Here at this stage for a person, the main thing is that fats, and not protein, participate in the oxidation, otherwise muscle mass will also go away in the process of losing weight, which is much more difficult to restore than the fat layer.
Proper nutrition
Muscle catabolism during weight loss is inevitable, no matter what athletes and coaches say. But it can be minimized by supplying the necessary amount of proteins, carbohydrates and fats to the body. It is impossible to completely cut fats and carbohydrates from the diet, and diets where this is advertised should be bypassed. The human body is able to extract the amount of energy it needs from the muscles, and at the slightest opportunity, saving energy, it will make itself such a reserve of fat that it will be very difficult to get it.
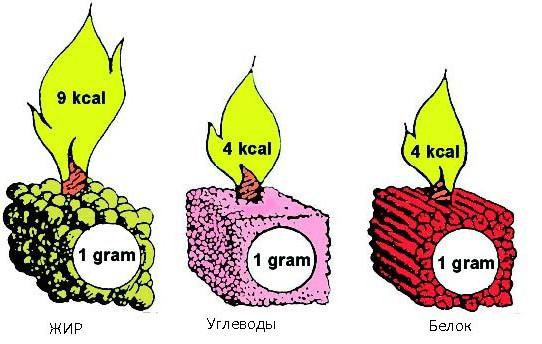
Power calculation is simple. On average, the calorie requirement of the body is 33 kcal per kilogram of weight. The need for protein and carbohydrates is 3 and 4 grams per 1 kg of human weight, respectively. The rest is fats. In one gram of protein and carbohydrates - 4 kcal, and in a gram of fat - 9 kcal. That is, for an athlete weighing 80 kg, you need to consume 2640 kcal. After mathematical calculations, in order not to start muscle catabolism, you need 240 g. protein, 320 gr. carbohydrates and 44 grams of fat. You need to cut fats and carbohydrates at 3-5% per day, and if you feel unwell, stop.
Chemical trigger catabolism
Most athletes, in search of a quick solution, resort to drugs that trigger purely fatty catabolism. What it is, it will be easier to understand if you imagine a program that can be loaded into the human body by setting parameters - take energy only from fat cells, send all incoming protein to build muscle, and in no case put off excess carbohydrates in reserve, and excreted naturally. This is quite possible when taking hormonal drugs or using special herbal ingredients. For many people, such an “intervention in the system” will be painless. Having completely stopped protein catabolism, the athlete quickly says goodbye to fat deposits. And some can harm the cardiovascular system, disrupt metabolism, develop allergies, become infertile, etc. In any case, first you need to do a general blood test, and only after finding out your predisposition to diseases, consume chemicals.
Biologically active additives
Muscle catabolism can be overcome by taking special nutritional supplements called protein, non-essential and essential amino acids. A lot of articles and reviews have been written about them, and specialized sources of information (as well as a trainer) will help the novice athlete make the right choice. It remains only to clarify that in the process of burning muscles for energy, when a prepared protein enters from the outside, the muscle can recover. As you know, the protein in the body is synthesized into amino acids, and those, in turn, are involved in the synthesis of building protein for muscles. Therefore, many athletes and resort to completely harmless, synthesized from plant or animal proteins, proteins and amino acids.
Active lifestyle
Having learned about catabolism, what it is and how to use it correctly, it remains to find out what other external factors affect the metabolism and can trigger the destruction of protein in the body.
- Lack of sleep. In a dream, the body does not rest, as half the population of the planet believes , but redistributes resources. After a hard workout, it restores and strengthens the muscles. Or continues to extract energy from fats according to a previously launched program. Accordingly, lack of sleep violates important processes and leads to stress.
- Stress. The body is so arranged that in the event of stress, the hormone cortisol is produced, which, by destroying the protein, is involved in the synthesis of glucose. And unused glucose is synthesized into fat cells.
- Support metabolic rate . No wonder many trainers strongly recommend drinking 3-4 liters of water per day and consume food in small quantities, breaking it into several receptions. All this forces the body to continuously carry out the synthesis of complex substances. The necessary elements are quickly delivered to their destinations, and all toxins are excreted from the body naturally.