Rational decision making is very cool and interesting. Read our complete productivity guide here for more tips on improving productivity. But before we examine each step of this powerful process, let's look at what rational decision-making is and why it is important.
Questions and answers
To pinpoint your specific problem, collect as much data as possible in the desired area and analyze it to find any disturbing patterns or trends.
Example: “After analyzing our report on blog traffic, we now know why it has fallen sharply in recent years: our organic traffic is increasing slightly compared to the previous month, and electronic and social traffic are decreasing.”
Other solutions
Potential solution: “We could focus solely on growing email traffic: it is easier than growing social and organic at the same time. We also have 250,000 blog subscribers, so we could publish our posts for many readers.”

Potential result 1: “Increasing email traffic by sending two emails a day to our blog subscribers is a difficult task because we already send one email to subscribers daily and only 15% of our blog traffic falls on the channel. Focusing on email will give minimal results " Rational solutions to problems are very important. Without them, no company can work. In the same way, not a single person can exist without this ability, because this is a key success of our consciousness, which cannot be denied. In the future, throughout the article you will find real examples of how important and interesting this is. Without this, you can’t build a business. Thinking rationally is not only useful and necessary, but also pleasant in some ways. This can be confirmed by anyone who is either engaged in professional make-up-making or simply leads a very balanced life.
Potential Result 2: “Increasing organic traffic by targeting keywords with a large search volume for all of our new posts is the easiest way to increase the overall traffic of our blog. We have high domain authority, Google uses 80% of our total traffic, and we’ve just implemented a pillar cluster model. Focusing on organics would give most of the results. "
Example: "After a month of testing, our blog traffic grew by 14%, and organic - by 21%."
Important examples
People associate with brands the same personality traits as with people: choosing your favorite brand is choosing your best friend or another person. We come with an option that makes us feel something. Solving rational inequalities is the best way to study phenomena such as brand popularity, changing customer demands, and so on.
Why is that so?
The rational planning model is used in the planning and design of housing estates, cities and regions. It was central to the development of modern urban and transport planning. The model has many limitations related, in particular, to the lack of guidance for engaging stakeholders and the community affected by planning. Other planning models, such as collaborative planning, are now also widely used. Solving rational equations (Grade 8) is a very popular method at school.
Other models
A very similar model of rational decision making, as it is called in organizational behavior, is a very interesting process. A significant part of this article is devoted to him. In essence, it consists in making logical decisions. This is a multi-step model that seeks to be logical and follow an orderly path. Rational decision making is a multi-stage path to a logical choice.
The first step is to check, identify and detail the problem (identify the problem, determine the goal, collect information). It includes recognizing the problem, choosing the initial solution and starting the initial analysis. Examples of this are creative developments and ideas, inspiration, breakthroughs and brainstorming.
The very first step, which is usually ignored by top-level management, is to identify the exact problem. Although it is believed that the identification of the problem is obvious, in many cases it is not. A rational decision-making model is a group-based decision making process. If the problem is not identified properly, then one may encounter difficulties, since each member of the group may have their own definition of it.
This step includes two to three final solutions to the problem and the preliminary implementation of the site. When planning, examples of this are the planning units of development and revitalization in the city center.
This exercise is best done in groups, as different people may offer different ideas or alternative solutions. Without them, there is a chance to come to a non-optimal or rational decision. To learn alternatives, you need to collect information. Technology can help in its collection.
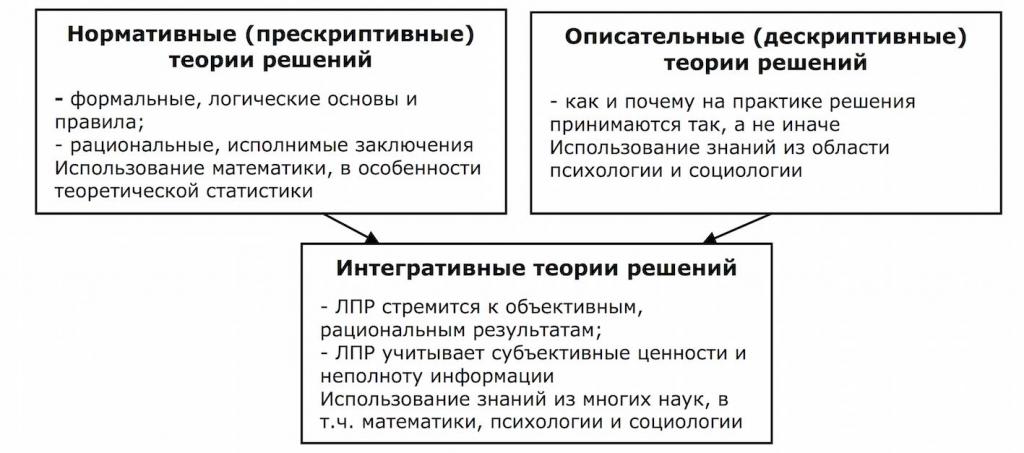
Evaluation criteria are measurements to determine the success and failure of alternatives. This step contains a secondary and final analysis, as well as secondary solutions to the problem. Examples of this are site suitability and sensitivity analysis. After carefully going through the process of identifying the problem, examining all possible alternatives for it and collecting information at this stage, it is proposed to evaluate the information and possible options in order to anticipate the consequences of each possible alternative in question. At this point, optional criteria for measuring the success or failure of a decision should be considered. A rational planning model relies mainly on an objective assessment.
Based on the evaluation and analysis criteria carried out in the previous steps, the best generated solution is selected. These four steps form the core of the Rational Decision Decision model, which is based on rational decision processes.
This stage includes the final implementation of the site and preliminary monitoring of the results. This step is part of the construction / repair process and contains secondary and final monitoring of the results. It takes place over a long period of time and allows you to change future decisions and actions taken based on the above assessment of results. This is a rational decision.
Some criteria, such as economic benefits, will be easier to measure or define, while others, such as environmental quality, will be more difficult to quantify. Ultimately, however, the set of decision-making criteria should include all policy objectives, and re-evaluating more easily defined or measurable criteria will have an undesirable effect on the shift of analysis to a subset of policy goals.
The process of defining a sufficiently comprehensive set of decision-making criteria is also subject to distortions due to pressure arising from political interaction. For example, decision-makers may tend to attach more weight to political influences that are concentrated, tangible, defined and immediate than influences that are diffuse, intangible, indefinite and delayed. For example, when using a carbon cap and carbon trading system, net financial costs in the first five years of policy implementation have a much easier impact on conceptualization than the more vague and uncertain effect of a country's improved position in influencing global climate change negotiations.
Modeling
Mapping the impact of policy alternatives can be done using a policy analysis matrix (PAM). PAM provides a summary of policy impacts for various alternatives, and matrix analysis can identify trade-offs associated with this. A sound management decision is very important.
After the policy alternatives have been evaluated, the next step should be to decide which policy alternative should be implemented. In one extreme case, comparing policy alternatives can be relatively simple if all of its goals can be measured using a single indicator and with the same weight. In this case, the decision-making method is BCA.
On the other hand, multiple goals will require the expression of political influences using various metrics that are difficult to compare. In such cases, the political analyst can rely on the concept of utility to combine various goals into a single assessment. According to the utility concept, each impact is assigned such a weight that one unit of each weighted impact is considered equally valuable (or desirable) in terms of collective well-being.
Weimer and Weining also suggested that the “don't go” rule might be a useful method for choosing among policy alternatives. In accordance with this decision-making regime, some or all of the political influences may be assigned thresholds that are used to eliminate at least some of the political alternatives. Thus, any policy alternative that does not meet this threshold can be excluded from consideration. If only one policy alternative satisfies all exposure thresholds, then it is precisely it that is considered a “move” for each impact. Otherwise, it may happen that all but a few political alternatives are excluded, and those that remain should be studied more carefully in terms of their compromises in order to make a decision.
Demonstration
To demonstrate the rational analysis process, as described above, let's look at the program document “Promoting the Use of Biofuels in the European Union: Implications for Climate Change Policies” by Lisa Ryan, where the European Union proposed replacing fossil fuels with biofuels from 2005-2010 to as part of a strategy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from road transport, improve energy security and support rural community development. The rational decision-making method is very advanced and is used in almost all areas of life.
Nevertheless, there are many assumptions, requirements, without which a rational decision-making model fails. Therefore, they should all be considered. The model assumes that we either have, or should, or can obtain adequate information in terms of quality, quantity and accuracy. This applies both to the main situation and to alternative technical ones. It is further assumed that you either have, or should, or can gain substantial knowledge of causal relationships related to evaluating alternatives. In other words, this assumes that you are well aware of all the alternatives and consequences of the selected options. It is further assumed that you can rank them and choose the best one. Solving rational fractional numbers is a popular method in mathematics.

While the rational planning model was innovative in concept, the concepts themselves today are controversial and dubious processes. The rational planning model has gone out of mass use in the last decade. Lucy Suchman argues that instead of interpreting human agents as rational planners, they can be better understood as being involved in local actions. Going further, Guy Benveniste argued that a rational model cannot be implemented without taking into account the political context. Rational problem solving is an important and interesting task.
Other models
Rational decision-making models include a cognitive process, where each step follows a logical order compared to the previous one. Cognitive implies that it is based on thinking and weighing alternatives to get the best potential result.
There are various types of rational models, and the number of steps used and even the steps themselves will differ in different models.
Some people assume that making decisions is equivalent to solving problems. Some solutions, however, are not problem-oriented.
Comparisons are often made by filling out forms or diagrams that have many names. Decision matrix, Pugh matrix, selection matrix, criteria rating form, and others. Relative importance is given to each criterion, and options are evaluated according to each criterion and the largest “winnings”. The solution of fractional rational inequalities is very popular in mathematics.
A rational decision-making model assumes that there is one better outcome. Because of this, it is sometimes called an optimizing decision-making model. The search for excellence is often a factor in the actual delay in decision making.
Such a model also assumes that each option can be considered, as well as the future consequences of each. Although many would like to think that they know what will happen, the universe often has other plans.
It is also limited by the cognitive abilities of the decision maker. How good is their memory? How good is their fantasy? The criteria themselves, of course, will be subjective, and it will be difficult to compare them. These models require a lot of time and a lot of information. And, of course, a rational decision-making model is trying to negate the role of emotions in the process.
Decision makers are said to show limited rationality when they consider fewer options than are actually available, or when they choose an option that is not the best overall, but the best in the current environment. For example, someone pours coffee on a shirt in a restaurant, goes to a store next door and buys a tight-fitting shirt to change clothes immediately. In this regard, the solution of rational inequalities is very effective.
Obviously, it would be best to buy a suitable shirt. But if a person is in a hurry and cannot wear wet, stained coffee clothes, then it is appropriate to buy a poorly suitable item. This is called a satisfactory rational solution.
When you think about it, most of our decisions are partly because we save time by not considering every opportunity we have. We select only the most useful. Rational examples of solutions are also popular in schools, because the benefits from them are very great.
History
This model was originally created by Vroom and Yetton in 1973, and then modified by Vroom and Iago. In fact, there are five situations for making decisions, from one decision maker to a person with different amounts of information compared to the rest of the group and to the entire group.
The Vroom-Jago decision-making model contains a series of seven questions with yes or no answers that identify important criteria and indicate which of the five decision-making processes is most appropriate.
Conclusion
Decision making is a very important process in every sense of the word. Without it, the existence of a modern political and social reaction is impossible, because the will-core of a person strives for his total expression through the matrix of choice. In computer science, mathematics, and mixed fields, however, this phrase is used to name a slightly different phenomenon, and this article is devoted to this meaning. It is very important to understand and realize it to everyone who read it, especially to people who are often going to make rational decisions, the methods and features of which are very diverse. This can be seen from the information stated in the article.
It is also important to understand how important the decisions are. In modern companies, a huge responsibility lies with the job-makers, who determine a significant part of the activities of media holdings. Therefore, this topic is so interesting to all young and ambitious specialists.
, , , .