The human body is one of the most complex structures, which consists of many elements. In addition to internal organs, there are a huge number of connecting parts, one of which is tissue fluid. It performs many important functions and is vital for every person.
Biological definition
What is tissue fluid? This is the question many people ask when they learn about the existence of this element. A sufficiently detailed answer was given by scientists who identified the definition of this part of the human body. Tissue fluid is one of the parts of the internal environment of the body, which is similar in composition to plasma and fills all the distances between cells. It includes cerebrospinal fluid and certain elements of the heart bag.
Education and Deletion
For the most complete understanding of what tissue fluid is, it is necessary to study the process of its appearance. This component occurs in the process of converting blood plasma, which through the walls of the capillaries penetrates into a special external space. It is during this period that the formation of tissue fluid occurs, which remains between the cells. The unspent part of the plasma returns back to the circulatory system.
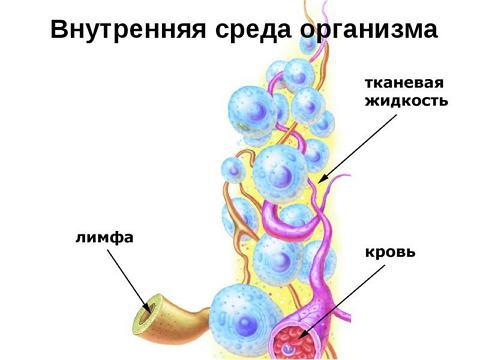
In the normal course of the life-support process, tissue fluid accumulates in the lymphatic capillaries, from which it gradually passes into the vessels and serves as the main part of the lymph. After passing through all stages, it flows through the lymph nodes and is involved in the process of blood circulation. This course occurs throughout a person’s life, supporting the work of all internal organs, enriching them with nutrients. Removal of this fluid occurs naturally, as described above, but if this process slows down and it begins to accumulate, disturbances in the form of edema of various parts of the body may occur. It all depends on the localization.
Disorders in tissue fluid removal
If tissue fluid is not excreted from the body at certain times, it stagnates. In the course of this, internal and external edema is formed, which can be detected as follows:
- At the initial stages of local edema, it is detected by clicking on the problem area, a hole is formed in it, which disappears for a long time.
- At the advanced stage, the swelling is visible to the naked eye.
- Accumulation of fluid in the internal organs can be detected by systematic weighing.
Types of local edema:
- Allergic - occurs as a result of the body's reaction to various pathogens, expressed as subcutaneous formations (urticaria, etc.), less often the larynx is affected, causing suffocation.
- Edema caused by venous congestion.
- Lymphatic stasis is the cause of the most dangerous edema. Initially, it is mild, but if treatment is not started on time, the development of elephantiasis is possible.
General edema is formed with a large number of sodium and water ions in the body and is divided into the following types:
- cordial;
- hypoproteinemic;
- renal;
- fluid congestion in the lungs ;
- cerebral edema.
Composition
For the most complete answer to the question of what tissue fluid is, it is necessary to consider its chemical composition:
- water;
- dissolved sugar, salt, amino acids, enzymes, etc .;
- oxygen;
- carbon dioxide;
- residual effects of cell work.
Tissue fluid contains very little protein - only 1.5 grams per 100 milliliters.
Function
What is the function of tissue fluid? It is a connecting element between the cells of the body and blood vessels. Tissue fluid is located directly around the cells, providing timely dissolution of the membranes. Cells that come in contact with tissue fluid receive from it all the necessary elements for nutrition and oxygen. In this case, the processed substances return back to the circulatory system and continue to circulate throughout the body. What is tissue fluid? First of all, this is the most important element that acts as a link in the process of life support of the whole organism.