Ensuring the needs of mankind with sufficient energy is one of the key tasks facing modern science. In connection with the increase in the energy consumption of processes aimed at maintaining the basic conditions for the existence of society, acute problems arise not only in generating large volumes of energy, but also in the balanced organization of its distribution systems. And the topic of energy conversion is key in this context. The coefficient of generating useful energy potential, as well as the level of costs for servicing technological operations within the framework of the infrastructure used, depends on this process.
Conversion Technology Overview
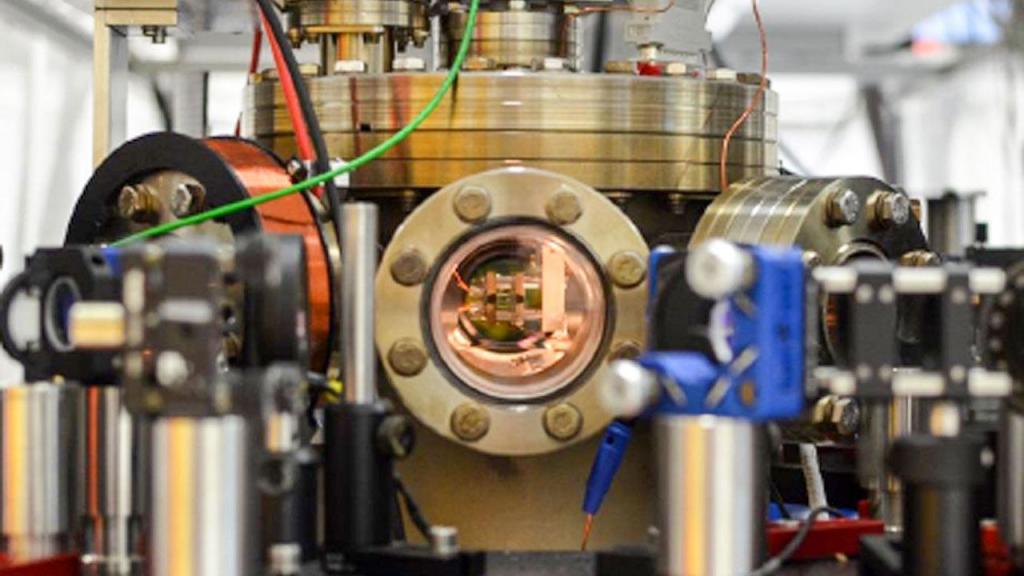
The need to use different types of energy is associated with differences in the processes for which a feeding resource is required. Heat is required for heating, mechanical energy - for power support of the movement of mechanisms, and light - for lighting. Electricity can be called a universal source of energy both from the point of view of its transformation, and in terms of possibilities of application in various fields. Natural sources, as well as artificially organized processes that contribute to the generation of the same heat or mechanical force, are usually used as the initial energy. In each case, a certain type of equipment or complex technological structure is required, which, in principle, allows for the conversion of energy into the form necessary for final or intermediate consumption. Moreover, not only transformation is distinguished among the tasks of the converter as the transfer of energy from one type to another. Often this process also serves to change some parameters of energy without its transformation.
The conversion as such can be single-stage or multi-stage. In addition, for example, the operation of solar generators on photocrystalline cells is usually regarded as the transformation of light energy into electricity. But along with this, the conversion of thermal energy, which the Sun gives to the soil as a result of heating, is also possible. Geothermal modules are placed at a certain depth in the ground and, through special conductors, fill batteries with energy reserves. In a simple conversion scheme, the geothermal system provides the accumulation of heat energy, which is given to the heating equipment in its pure form with basic training. In a complex structure, a heat pump is used in a single group with heat condensers and compressors that provide heat conversion and electricity.
Types of electrical energy conversion
There are various technological methods for extracting primary energy from natural phenomena. But accumulated energy resources give even more opportunities for changing the properties and forms of energy, since they are stored in a form convenient for transformation. The most common forms of energy conversion include radiation, heating, mechanical and chemical effects. In the most complex systems, molecular decay processes and multilevel chemical reactions are used, in which several stages of conversion are combined.
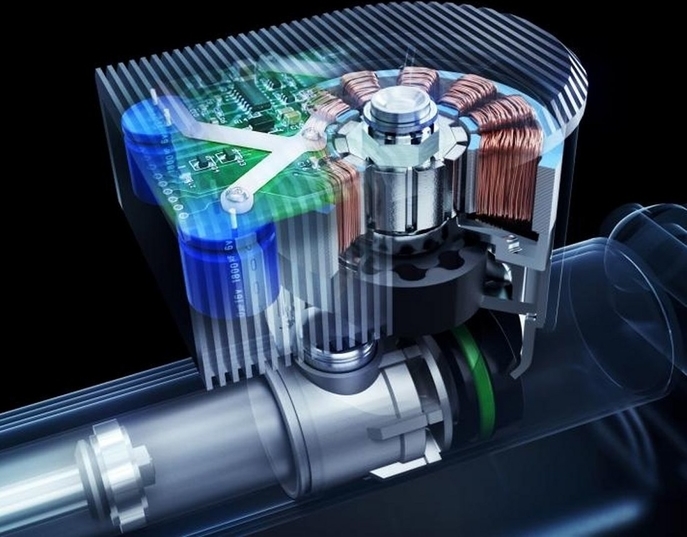
The choice of a specific method of transformation will depend on the conditions of the organization of the process, the type of initial and final energy. Among the most common types of energy that, in principle, participate in the conversion processes, one can distinguish radiant, mechanical, thermal, electrical and chemical energy. At a minimum, these resources are successfully exploited in industry and households. Special attention is paid to indirect processes of energy conversion, which are derivatives of a particular technological operation. For example, in the framework of metallurgical production, heating and cooling operations are required, as a result of which steam and heat are generated as derivatives, but not target resources. In essence, these are waste products of processing that also find application, undergo transformation or use within the framework of the same enterprise.
Heat energy conversion
One of the oldest in terms of development and most important for maintaining human life energy sources, without which it is impossible to imagine the life of modern society. In most cases, heat is converted into electricity, and a simple scheme of such a transformation does not require the connection of intermediate stages. However, in thermal and nuclear power plants, depending on the conditions of their work, the preparation stage can be applied with the conversion of thermal into mechanical energy, which requires additional costs. Today, thermoelectric generators of direct action are used to convert thermal energy into electricity.
The transformation process itself takes place in a special substance that is burned, generates heat and subsequently acts as a source of current generation. That is, thermoelectric plants can be considered as sources of electricity with a zero cycle, since their work starts even before the appearance of basic thermal energy. The main resource is fuel cells - usually gas mixtures. They are burned, as a result of which the heat-distributing metal plate is heated. In the process of heat removal through a special generator module with semiconductor materials, energy is converted. Electric current is generated by a radiator unit connected to a transformer or battery. In the first version, energy is immediately supplied to the consumer in a finished form, and in the second - it is accumulated and given as needed.
Generation of thermal energy from mechanical
It is also one of the most common ways of generating energy through conversion. Its essence lies in the ability of bodies to give off thermal energy in the process of doing work. In its simplest form, this example of energy transformation is demonstrated by the example of the friction of two wooden objects, resulting in a fire. However, to use this principle with tangible practical benefits, special devices are required.
In the household, the conversion of mechanical energy takes place in heating and water supply systems. These are complex technical constructions with a magnetic core and a lined core connected to closed electrically conductive circuits. Also, heating pipes pass through the working chamber of this design, which are heated by the work performed by the drive. The disadvantage of this solution is the need to connect the system to the mains.
In industry, more powerful converters with a liquid coolant are used. The source of mechanical work is connected to closed reservoirs of water. In the process of movement of the executive bodies (turbines, blades or other structural elements), conditions for vortex formation are created inside the circuit. This occurs at the time of sharp braking of the blades. In addition to heating, in this case, the pressure rises, which facilitates the processes of water circulation.
Electromechanical energy conversion
Most modern technical units work on the principles of electromechanics. Synchronous and asynchronous electric machines and generators are used in transport, machine tools, industrial engineering units and other power plants for various purposes. That is, the electromechanical types of energy conversion are applicable to both generator and motor modes of operation, depending on the current requirements of the drive system.
In a generalized form, any electric machine can be considered as a system of mutually moving magnetically coupled electrical circuits. These phenomena also include hysteresis, saturation, higher harmonics and magnetic losses. But in the classical view, they can be attributed to analogues of electric machines only if we are talking about dynamic modes when the system operates within the framework of the energy infrastructure.
The electromechanical energy conversion system is based on the principle of two reactions with two-phase and three-phase components, as well as the method of rotating magnetic fields. The rotor and stator of the motors perform mechanical work under the influence of a magnetic field. Depending on the direction of movement of the charged particles, the operating mode is set - as a motor or generator.
Generation of electricity from chemical energy
Aggregate chemical energy source is traditional, but methods for its conversion are not so common due to environmental restrictions. Pure chemical energy itself is practically not used, at least in the form of concentrated reactions. At the same time, natural chemical processes surround a person everywhere in the form of high- or low-energy bonds, which appear, for example, during combustion with the release of heat. However, the conversion of chemical energy is purposefully organized in some industries. Usually conditions are created for high-tech combustion in plasma generators or gas turbines. A typical reagent of these processes is a fuel cell, which contributes to the production of electrical energy. In terms of efficiency, such transformations are not so advantageous in comparison with alternative methods of generating electricity, since part of the useful heat is dissipated even in modern plasma systems.
Solar Energy Conversion
As a way of converting energy, the processing of sunlight in the near future may become the most popular in the energy sector. This is due to the fact that even today, every homeowner can theoretically purchase equipment for converting solar energy into electrical energy. A key feature of this process is the free storage of sunlight. Another thing is that this does not make the process completely cost-free. First, the costs will be required for the maintenance of solar cells. Secondly, generators of this type themselves are not cheap, so few can afford the initial investment in organizing their own mini-power plants.
What is a solar energy generator? This is a set of photovoltaic panels that convert the energy of the sun's rays into electricity. The principle of this process is in many ways similar to the operation of a transistor. As the main material for the manufacture of solar cells, silicon is used in different versions. For example, a device for converting the energy of the Sun can be poly- and single-crystal. The second option is preferable in terms of performance, but costs more. In both cases, the photocell is illuminated, in which the electrodes are activated and an electrodynamic force is generated during their movement.
Steam conversion
Steam turbines can be used in industry as a way of transforming energy into an acceptable form, or as an independent generator of electricity or heat from specially directed flows of conventional gas. Not many turbine machines are used as devices for converting electric energy in combination with steam generators, but their design is optimal for organizing this process with high efficiency. The simplest technical solution is a turbine with blades, to which nozzles with supplied steam are connected. As the blades move, the electromagnetic installation rotates inside the apparatus, mechanical work is performed, and current is generated.
Some turbine designs have special extensions in the form of steps, where the mechanical energy of the vapor is converted into kinetic. This feature of the device is determined not so much by the interests of increasing the generator energy conversion productivity or by the need to develop precisely the kinetic potential, but by providing the possibility of flexible regulation of the turbine operation. The expansion in the turbine provides a control function, which enables efficient and safe regulation of the generated energy volumes. By the way, the working expansion area, which is included in the conversion process, is called the active pressure stage.
Energy transfer methods

The methods of energy transformation cannot be considered without the concept of its transfer. To date, there are four ways of interacting bodies in which the transfer of energy occurs - electrical, gravitational, nuclear and weak. In this context, transmission can also be considered as a method of exchange, therefore, fundamentally separate the completion of work during energy transfer and heat transfer function. What energy conversions do work do? A typical example is a mechanical force at which the movement of macroscopic bodies or individual particles of bodies takes place in space. In addition to mechanical force, magnetic and electrical work are also distinguished. The key unifying property for almost all types of work is the ability to complete quantitative transformation among themselves. That is, electricity is transformed into mechanical energy, mechanical work into magnetic potential, etc. Heat transfer is also a common way to transfer energy. It can be non-directional or chaotic, but in any case, the movement of microscopic particles occurs. The amount of activated particles will determine the amount of heat - usable heat.
Conclusion

The transfer of energy from one form to another is normal, and in some industries a prerequisite for the production of the energy process. In different cases, the need to include this stage can be explained by economic, technological, environmental and other factors of resource generation. Moreover, despite the variety of natural and artificially organized methods of energy transformation, the vast majority of plants that provide conversion processes are used only for electricity, heat and mechanical work. Means for converting electrical energy are the most common. Electric machines that provide the transformation of mechanical work into electricity by the principle of induction, for example, are used in almost all areas where complex technical devices, assemblies and devices are involved. And this trend does not decrease, since humanity needs a constant increase in energy production, which forces us to look for new sources of primary energy. At the moment, the most promising areas in the energy sector are systems for generating the same electricity from mechanical energy produced by the Sun, wind and water flows in natural nature.