Why is hemoglobin in the blood reduced? Dizziness and skin and hair problems are just some of the symptoms of this condition.
Hemoglobin is the main component of red blood cells and provides oxygen transport from the lungs to all body tissues, as well as the transfer of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction. Human blood contains approximately 750 g of hemoglobin. With its lack, all cells of the body lack oxygen. This element provides the process of respiration of the cell, that is, the production of energy necessary for life. With oxygen deficiency, the functioning of all cells, tissues and organs is disrupted. Nerve tissue is especially sensitive to oxygen starvation. This is why hemoglobin decreases in the blood, and dizziness and fatigue disturb patients.
Red blood cells form in the red bone marrow, hemoglobin begins to accumulate here. Its molecule contains iron atoms, and some vitamins are needed to form red blood cells. With a lack of iron, a small amount of hemoglobin is formed, and with a lack of vitamins (cyanocobalamin (B 12 ) and folic acid), the normal formation of red blood cells is disturbed. Iron deficiency is the most common cause of hemoglobin decline. It can be caused by insufficient food intake. But there are other reasons. In some conditions, iron deficiency occurs even when it is sufficiently ingested with food. This element, like all other substances, is absorbed from food in the small intestine. Diseases of this department will lead to a decrease in the intake of all substances in the blood, including iron. Next, all situations will be considered in more detail, why hemoglobin in the body may decrease.
Classification of Anemia
The condition of the body caused by insufficient hemoglobin in the blood is called anemia. Following WHO recommendations, the following criteria for anemia were adopted:
- hemoglobin level for women ≤ 120 g / l (for pregnant women - less than 110 g / l);
- for men, Hb ≤ 130 g / l;
- for children Hb ≤ 110 g / l.
In Russia and the CIS countries, a classification of anemia is used according to the hemoglobin content in one red blood cell (by color index):
- hypochromic (CPU <0.8);
- normochromic (CPU 0.8 - 1.05);
- hyperchromic (CP> 1.05).
The spread of this classification is easily explained. You can determine the CPU in a normal clinic using a portable hemoglobin analyzer for a minute, and capillary blood (from the finger) is suitable for analysis.
In other countries (and recently in our country), a classification based on measuring the volume (size) of red blood cells (MCV) is also used. Both classifications of anemia overlap and can be combined:
- microcytic (MCV <80 fl) hypochromic;
- normocytic (MCV 80-100 fl) normochromic;
- macrocytic (MCV> 100 fl) hyperchromic.
MCV is now on the regular list of general blood count indicators and can be determined in any laboratory that has an automatic analyzer.
Microcytic hypochromic anemia
This group of anemia is determined by a number of indicators, the main of which is the volume of red blood cells (MCV). To establish why blood hemoglobin decreases when MCV falls, it is necessary to determine the content of serum iron.
If the iron content is normal or even increased, the patient is sent to a hematologist. If the gland is less than normal, then in order to find out why hemoglobin has decreased, a differential diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia and anemia of chronic conditions is carried out. For this, the level of blood transferrin is determined.
Iron deficiency anemia
Iron deficiency is recorded in 30% of the world's population and in 6% of the European population. Almost half of these people have iron deficiency anemia (IDA). This type of anemia is the most common and accounts for 41.5% of all such conditions according to world data, and according to Russian scientists - 93%. Most often, IDA is recorded in women, with almost half of the patients aged 15 to 30 years, with age, pathology is less common.
Iron deficiency anemia is a syndrome that is characterized by a violation of hemoglobin production due to iron deficiency, developing against a background of various physiological and pathological conditions.
IDA is manifested in two groups of symptoms: anemic and sideropenic.
Anemic symptoms:
- flies in front of the eyes, dizziness, tinnitus, darkening of the eyes when rising quickly, headaches;
- weakness, fatigue, decreased performance, fatigue;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, palpitations, shortness of breath under exertion, pulsation in the neck and temples.
Sideropenic symptoms:
- Dry skin, dull, split ends.
- Cracks in the feet, fingertips.
- Fragility, layering, waviness of nails, nails become concave, in shape resemble a spoon.
- Dark tooth enamel, caries.
- Distortion of taste and smell. Often patients take signs of iron deficiency for their quirks or character traits. Eating earth, lime, chalk, raw meat, potatoes, paints, a constant desire to eat something cold - ice or ice cream, a love of the smell of kerosene, exhaust gases, soaps - are symptoms of low hemoglobin.
- Glossitis (inflammation of the tongue), dysphagia (violation of swallowing), angular stomatitis ("jams", fissures in the corners of the mouth).
- Decrease in intellectual abilities.
- Tachycardia, diastolic myocardial dysfunction.
- Inability to hold urine when laughing or coughing. Patients note the syndrome of "restless legs" - the need to move your legs due to the sensation of discomfort that occurs, mainly in the evening.
Causes of Iron Deficiency
Blood loss. The most common reason why hemoglobin is reduced in women is considered to be long and heavy menstruation. It is the cause of a decrease in the iron content in the blood of women in 30% of all cases. If menstruation lasts more than 5 days or more often than every 26 days, the body will lose more than 60 ml of blood per month. Given the loss of iron with this volume of blood and the moderate intake of this trace element with food, after 10 years the body will lose half of its total iron supply. That's why blood hemoglobin decreases in women predominantly young - before the onset of menopause.
In 5% of cases, a low iron content is caused by donation, in 1% by nosebleeds, and in another 1% by loss in urine, for example, with urolithiasis.
The main reason hemoglobin in men and women is reduced is bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract. Such pathologies occur with ulcers, erosions, polyps, tumors, hemorrhoids, taking aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (increase blood permeability of the small intestine wall).
Congenital iron deficiency. It is registered in newborns in case of iron deficiency from the mother during pregnancy.
Malabsorption. In 5% of cases, low iron levels are recorded due to intolerance to cereal gluten protein. This disease is called celiac disease, it leads to atrophy of the intestinal mucosa and, as a result, to impaired absorption of substances, including iron. In Russia, this ailment is often detected. In addition, negative taste preferences lead to malabsorption. Tea, coffee, calcium-rich foods (cheese, cream, cottage cheese, walnuts) - this is why hemoglobin can decrease.
Iron deficiency in food with strict diets or vegetarianism. A lack of iron in mother's milk is a common cause of low hemoglobin in newborns.
Increased iron consumption is noted during:
- puberty, mostly in girls;
- pregnancy
- lactation;
- premenopausal period in women.
The following standards and minimum indicators of hemoglobin content during pregnancy have been adopted:
- in the first trimester: 112-160 110 g / l;
- in the II trimester: 108-144 105 g / l;
- in the III trimester: 112-140 110 g / l.
Why does hemoglobin decrease in women during pregnancy?
The first reason is an increase in blood volume. This happens due to an increase in the mainly liquid part of the blood, so the concentration of all blood substances decreases. This is physiological anemia.
The second reason why hemoglobin decreases during pregnancy is an increased consumption of iron. It is necessary for the formation of the hematopoietic system of the fetus, for the synthesis of its hemoglobin, the formation of other tissues of the child, as well as for building the placenta and uterine growth. The highest iron consumption occurs in 16-20 weeks of pregnancy. This explains why hemoglobin decreases in pregnant women in the second trimester.
In addition, various pathological conditions that can lead to an even greater drop in the hemoglobin content in the blood of the future mother should not be ruled out.
Iron deficiency anemia treatment
The basic principles of treatment:
- It is impossible to cure iron deficiency anemia with a diet. If the diagnosis is made, then treatment is carried out only with iron preparations. Hoping for proper nutrition is not worth it. From food, only 2.5 mg per day can enter the body, with drugs - ten times more. It will be necessary to use products containing this microelement after its content in the blood normalizes.
- It is necessary to use drugs for oral administration.
- Parenteral administration of drugs is prescribed only in severe cases of anemia, with impaired absorption of iron or intolerance to oral drugs.
- The effectiveness of treatment is determined by restoring the level of hemoglobin and iron (and not by the number of drugs taken).
- Ferric iron preparations are used to treat iron deficiency anemia. Currently, ferrous and ferric iron preparations are on the market. The latter are much more efficient and safer.
Chronic disease anemia
This is the second most common type of anemia after iron deficiency. The reasons more often are:
- chronic kidney disease;
- chronic heart failure;
- liver disease
- autoimmune diseases;
- endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism);
- oncological diseases.
All of the above pathologies lead to a reduction in the life of red blood cells, inhibition of their synthesis and deposition of iron in the cells of the reticuloendothelial system. This explains why hemoglobin levels are reduced in chronic diseases.
For the treatment of anemia in chronic diseases, it is necessary to eliminate the underlying ailment. Iron preparations will not help.
Normocytic anemia
If a decrease in the hemoglobin content is established in the blood, and the red blood cell volume indicator is normal, then normocytic anemia is indicated. To find out the reason why hemoglobin is reduced in this case, it is necessary to determine the content of reticulocytes. These are erythrocyte precursor cells, they must mature in the red bone marrow, and then in the bloodstream into the red blood cells themselves. Normally, their blood contains 1% of all red blood cells. You can count them in a smear under a microscope. A high content of reticulocytes in the blood is caused by increased production of red blood cells in the red bone marrow and indicates the presence of posthemorrhagic or hemolytic anemia.
Posthemorrhagic anemia can develop as a result of acute bleeding, which requires surgical intervention.
Hemolytic anemia is a pathological condition of the body caused by increased destruction of red blood cells. It can be hereditary and acquired, in half the cases, the cause of anemia is not established. Red blood cells can be destroyed by the following factors:
- mechanical damage to the erythrocyte membrane (prosthetic heart valves, heart-lung machine);
- chemical damage to red blood cells (snake bites, lead poisoning, benzene, pesticides);
- hypersensitivity to certain drugs;
- parasitic infections (malaria).
For successful treatment, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of anemia. In addition, appoint:
- preparations of vitamin B 12 and folic acid;
- in special cases - transfusion of "washed" red blood cells;
- glucocorticoid hormones, since the disease is often accompanied by an increase in the size of the spleen and liver (in some cases, the spleen is removed);
- cytostatics in autoimmune etiology.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn
GBN refers to congenital hemolytic anemia.
It is impossible to confuse GBN with physiological jaundice of newborns. Such jaundice appears in most premature and half full-term infants without any pathology. The fact is that in the blood of a child before birth, special fetal hemoglobin prevails, which has an increased ability to attach oxygen. While the baby is in the womb, his mother’s blood supplies him with oxygen, it is not enough. Under conditions of oxygen deficiency, normal hemoglobin would not have been able to cope with its delivery to each cell of the fetal body. After birth, the baby begins to breathe on its own, oxygen becomes more, fetal hemoglobin is already unnecessary and is replaced by the usual "adult". After childbirth, “baby” hemoglobin begins to gradually break down in the vascular bed with the formation of the final product - bilirubin, which has a red-yellow color. That is why the child's hemoglobin decreases in the first two months of life from 200 to 140 g / l. Usually such jaundice passes by itself, sometimes treatment with lamps is necessary. In more rare cases, jaundice is caused by pathological causes that must be diagnosed and treated.
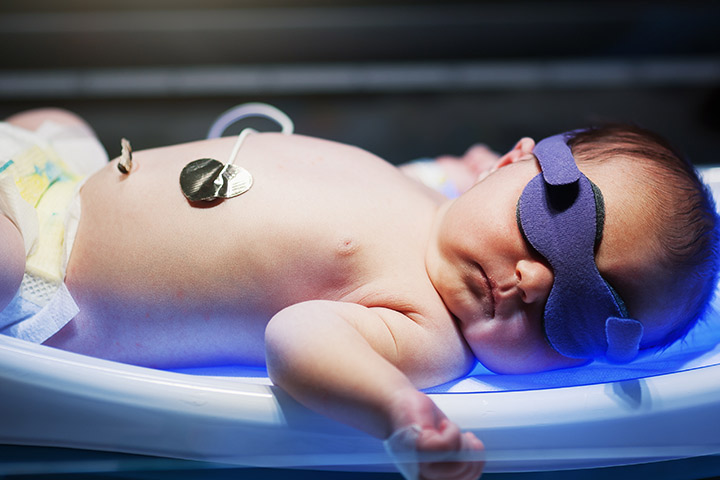
One of these causes is hemolytic disease of the newborn, which is recorded in 0.5% of children. It occurs due to the incompatibility of the blood of the mother and the fetus. The reason may be a negative Rh factor of the mother and a positive child or their different blood groups. As a result, antibodies are produced in the female body that destroy the red blood cells of the fetus. Despite the name - “disease of the newborn,” the ailment can affect the child even in the womb and even lead to his death. The destruction of red blood cells leads to a state of anemia of the newborn and, in some cases, severe jaundice. This explains why hemoglobin decreases after HDN.
Macrocytic anemia
It is characterized by a violation of the hematopoiesis process and the appearance in the vascular bed of large cells called macrocytes. If such cells are found in a blood smear, they suggest B12-deficient, folic acid deficiency or drug toxic anemia. Of these, B 12 is more often found to be deficient, registered mainly in the elderly. A deficiency of this vitamin occurs during strict vegetarianism, after operations on the stomach, small intestine, stomach cancer, helminthic invasion. To treat this type of anemia, B- 12 drugs are prescribed at a dose of 500-1000 g / day and treatment of pathology that causes a vitamin deficiency.
Folic acid deficiency anemia develops mainly in young people. Vitamin deficiency may be due to insufficient intake of plant foods, as well as inflammation of the small intestine or removal of part of it. An increased need for vitamin occurs during pregnancy. For treatment, folic acid is prescribed in a dosage of 5-15 mg / day.