The intervertebral openings of the spinal canal play an important role in the human body, so it is important to know what they consist of, where and how they form. Read about this and much more in the article.
Spinal canal
It consists of the intervertebral foramen of the vertebrae, which, in turn, are formed by bodies, arches, and also ligaments. The diameter of the canal is much larger in the region of such departments as the lumbar and cervical, as they are more mobile compared to the thoracic.
The spinal canal has a very important function: it is the location of the spinal cord. The channel formed by the vertebrae reliably protects its delicate tissue. The central nervous system is formed from the spinal cord and brain , the purpose of which is to regulate all functions in the human body. Therefore, in order to ensure normal functioning of the spinal cord, it is important to maintain the integrity and anatomical structure of the canal.
What is the intervertebral foramen?
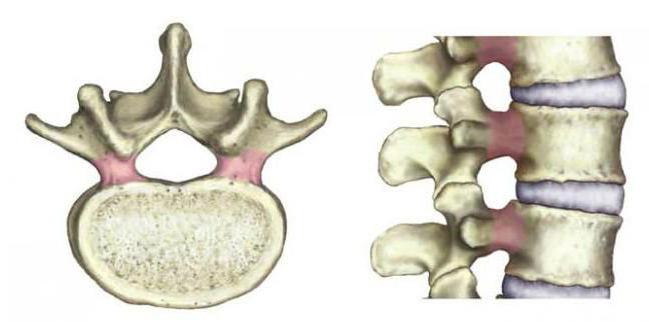
This is a narrow funnel-shaped opening through which the nerve roots and veins exit from the spinal canal. Arteries, on the contrary, enter it, supplying the nerve structures with blood. Where are the intervertebral openings? Their location is the lateral parts of the spinal column, that is, between each two vertebrae forming a pair, one on each side. Simply put, the body and bone processes when connecting the vertebrae form holes, which are called intervertebral. Nerves that exit through these openings are called spinal nerves.
As for the functional relationship, the size of the holes between the vertebrae is not as important as their shape, as well as the size of the channel through which the spinal nerves pass. The parameters of this channel are affected by:
- The size of the lateral depression in the spinal canal.
- The shape and size of the processes of the joints.
- Yellow ligament (its condition).
- The edge of the body of the vertebra and the disc between the vertebrae.
Where are they formed?
Intervertebral openings are formed by the upper and lower vertebral notches, which appear in the process of connecting the vertebrae. Frontal restriction occurs due to intervertebral discs and vertebral bodies located in the neighborhood. Above and below, the limitation for the holes is the legs of the arches, and behind the yellow ligaments, as well as joints that have grown in arcs. Thanks to the front and rear joints, the formation of a movable intervertebral joint occurs. When the intervertebral foramen is narrowed, it means that a change has occurred in one of the joints, which can lead to compression of the nerve.
The holes between the vertebrae along the entire length of the spine are only 23 pairs. They increase in size from top to bottom. Cervical holes between the vertebrae - four millimeters, in the region of the fifth vertebra of the lower back - 10.2.
What are vertebrae?
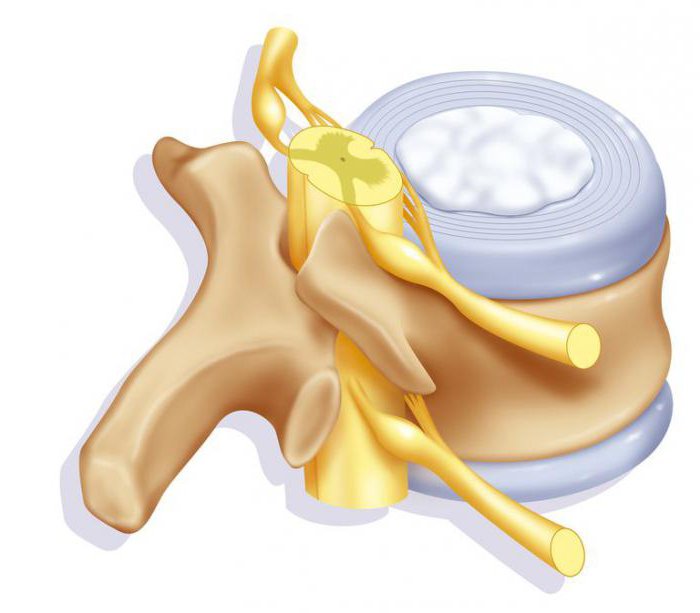
It is impossible to examine the intervertebral foramen separately from the vertebrae, so it is important to know what they are. The vertebrae are the bones due to which the formation of the spinal column occurs. The vertebrae have a cylindrical body, which is called their front part. The main supporting load falls on him. This is due to the fact that in the distribution of the weight of a person on the spine, the bulk of it goes to the front. Behind the body there is a half-ring-shaped arch, from which processes in the amount of seven pieces depart. The bow is attached to the vertebral body with legs.
In their structure, the vertebrae are spongy bones, the upper layer of which is bone beams, interconnected by cells. They contain red bone marrow. Thanks to the body and the arch, the vertebral intervertebral foramen is formed. Relative to the spinal column, their location is determined strictly symmetrically one above the other, resulting in the formation of the spinal canal, which is the location of the spinal cord, nerve roots, blood vessels, adipose tissue.
The connection of the vertebrae and their bodies
To understand how the intervertebral foramen is formed, it is important to know how the vertebrae connect. This process occurs with the help of synchondrosis, that is, intervertebral discs. The vertebral columns connected by them, or rather their bodies, are fastened with the help of two longitudinal ligaments that run along the midline from the front and back. Connections of all vertebrae provide the spine with high mechanical strength, mobility, as well as flexibility.
Intervertebral discs
These are dense formations that have a rounded shape. Their location is the space formed by the connection of neighboring vertebrae. The structure of the disk is very complex. The pulpous nucleus with its elastic properties is allocated a place in the center. It is a shock absorber for vertical loads. The fibrous ring in many layers is located around the nucleus. Thanks to the ring, it is held in the center and does not allow the vertebrae to move. The intervertebral discs of adults do not have blood vessels, and the vessels of the vertebral bodies supply their cartilage. For this reason, many drugs cannot get into the cartilage of the disc, which greatly complicates the treatment of many diseases of the spine.
Layers and fibers of the fibrous ring have the ability to cross in several planes. Normally, without any pathologies, ring formation occurs with fibers of high strength. But if a disc disease occurs, for example, osteochondrosis, then the fibers of the fibrous ring are replaced by scar tissue. In turn, the fibers of the fabric do not have such elasticity and strength, as a result of which the disk weakens. If the intradiscal pressure rises, a rupture of the fibrous ring may occur.
Throughout life, the structure of the disks, as well as their size, changes. At the age of 13 years, the growth and development of all tissues occurs in width and height. The process later slows down and stops completely in adults. Prior to adolescence, the discs have blood vessels, but by the age of 25 they disappear. In adults, they do not.
Ligaments
The posterior longitudinal and yellow ligaments are considered the most significant. The first serves as a heavy, with its help all the bodies are connected from behind. The yellow ligament, which is so called thanks to the pigment, has a different purpose: thanks to it, all arcs are connected. Ligaments perform a specific function. If the intervertebral discs and joints are destroyed, the task of the ligaments is to compensate for the instability, which in this case is the pathological mobility of the joints.
The result of the work of the ligaments is their hypertrophy, and this leads to the fact that the lumen in the spinal canal decreases. Therefore, the formation of bone growths or hernias, even the smallest in size, leads to a narrowing of the intervertebral openings, which causes compression of the spinal cord and roots.
What is stenosis?
This disease is usually a chronic form in which the pathological process progresses. It is characterized by the fact that the central canal and intervertebral foramen (photo presented for review) are narrowed. This is due to the fact that bone and cartilage tissue grows. Pathology is observed in diseases such as osteoarthritis, spondylosis and others.
Spinal canal stenosis is a common pathology that affects older people who have crossed a 60-year threshold in 21% of cases. But it is noteworthy that only 30% of patients showed symptoms of the disease. Usually it is diagnosed during the examination for a completely different reason. In most cases, narrowing in the spinal canal occurs in the lumbar region.
The diagnosis of stenosis is made when, after a full examination, tests show that the distance between the posterior surface of the vertebral body and the base of the spinous process is less than 12 mm. Such measurements are characterized by narrowing, in which there is a decrease in the cross section of the central channel. There is another type of stenosis - lateral. It is characterized by a narrowing of the holes between the vertebrae. Such a diagnosis is established if the holes are reduced to four millimeters.