Our world is beautiful and fantastically diverse. Thousands of life forms delight with their beauty, strength, ability to survive and other unique features. But, unfortunately, there are beings in the world who are completely unattractive and differ only in that they live off other creatures. These are parasites. Medical parasitology deals with those that are dangerous to human health and life.
It is hard to imagine how many of them exist on Earth. These are viruses, and bacteria, and fungi, and helminths, and insects, and protozoa - just a few million species, and most of them can be harmful to one degree or another. To determine exactly what kind of parasites settled in a person and causes him trouble, there are special medical research institutions, for example, in Moscow this is the Institute of Parasitology, as well as Marcinowski Tropical Medicine. Here, studies are conducted to identify pests and prescribe effective treatment.
Similar institutions exist in many large cities of all developed countries of the world, because parasites attack people of all ages, races, nationalities and genders, and at any time of the year. How to recognize that you have become a victim of a small pest and killer? What to do and where to run for help? Let's get it right.
What is parasitology?
Let's get started with some terms. The most common of these is parasitology. This is a whole science that studies all biological parasites, their morphological characteristics, vital functions, principles of parasitism, etiology, pathogenesis, as well as the development of methods to combat them and the discovery of new drugs for the treatment of diseases that they cause. One of the major areas of this science specializing in human pests is medical parasitology. It can be defined as follows - this is a section in medicine that studies all forms of manifestation of the pathogenic activity of pests - how they infect humans, what diseases they cause, how they occur, what are dangerous, how to treat them and how to protect themselves from them.
There is also veterinary parasitology, which, in principle, is the same as medical, only for animals. In nature, there is a group of organisms that can affect both humans and animals. But in most cases, microorganisms through evolution have adapted for parasitic activity in any one kind of host, for example, only in birds or only in humans, or only in warm-blooded animals. Therefore, there are two sections of parasitology, one of which deals with microorganisms that cause human diseases, the other - animals.
Sections of Medical Parasitology
The army of parasites is not only numerous, but also multifaceted. Each of their species has its own peculiarities of life and causes completely different pathologies. To facilitate the task for scientists and somehow differentiate the research they are doing, in medical parasitology, several sections have been identified that are only interested in certain types of living forms:
- protozoology;
- arachnoenterology;
- helminthology.
Important: the symptoms of invasion caused by representatives of any of these sections are very often similar to the symptoms of diseases that are not associated with parasite infection, therefore, medications that do not lead to a positive result can be prescribed without appropriate tests. To exclude the likelihood of invasion, you need to contact the medical center of parasitology (if available in the village) or another medical institution involved in the diagnosis of parasitic diseases.
Medical protozoology
The compound word “protozoology” is composed of three simple words, which in Greek mean the following: “proto” - the first, “zoo” - the animal and “logic” - in free translation it is a speech about something, a doctrine. That is, the section of medical parasitology protozoology deals with the study of parasitic life forms that arose among the first on Earth. All of them are unicellular protozoa - amoeba, known from the school bench for ciliates and others. Most of them live in the environment without causing us trouble, but some members of the group have adapted to life in other organisms. Once in a person, they cause parasitic or, in other words, invasive diseases. These dangerous microorganisms include:
1. Amoeba. Their sizes are 0.5 mm or less, and the body is constantly changing shape, protruding one of the processes and pulling others. These tiny creatures, once in the human intestines, cause a formidable disease of amoebiasis, which occupies an "honorable" second place in the world in mortality from invasive pathologies. In humans, several types of amoeba parasitize. Dysenteric (Entamoeba histolytica) is the culprit of dysentery, the simplest genus Acanthamoeba provokes amoebic keratitis, and a number of amoebas cause amoebic encephalitis. You can get infected by drinking water or products containing amoebic cysts, as well as in close contact with their carrier. Once in the intestine and having invaded its walls, amoebas with blood are carried throughout the human body, settle in its other organs, often in the liver, and form additional foci of amoebiasis.
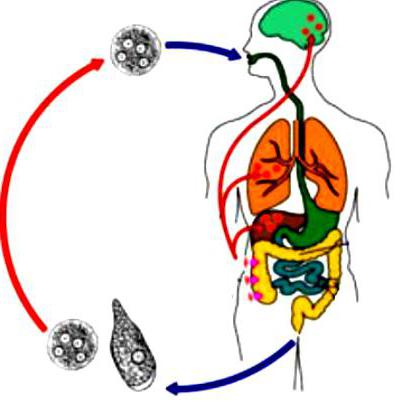
2. Flagellates. As the name implies, these protozoa move with the help of cilia, flagella and other similar formations. Medical parasitology and parasitic diseases are closely related, no matter what kind of organisms are considered. In particular, flagellated vaginal trichomonas causes urogenital trichomoniasis, which is fraught with infertility, and in cases when they become pregnant, trichomoniasis can cause miscarriage. Trichomonads, unlike many other parasites, live only in humans and are transmitted through close contact (sexual). Other prominent representatives of flagellates are members of the Leishmania clan, the Gambian trypanosome, which causes a deadly African trypanosomiasis. Trypanosomes carry tsetse flies. Once in a person, parasites move to the brain. Their activity disrupts the work of almost all body systems. There are still spore subjects, the most dangerous of which is Taxoplasma gandi, which causes toxoplasmosis.
3. Ciliates. Among them are not only shoes, but also Balantidium coli, the ingestion of which into the intestine leads to a severe ailment of balantidiasis. You can infect the intestinal balantidium from domestic animals, eating their meat that has not gone through sufficient cooking, as well as consuming water and products with parasite cysts.
Medical arachnoenterology
In Greek, arachnis is a spider. Accordingly, arachnoentomology is a medical parasitology dealing with arachnids and generally arthropod insects that parasitize humans. In total, more than one and a half million such parasites are discovered. They can be temporary (attacked, drank blood and left the victim) and permanent (live on the victim from their birth to death). This group of parasites is of great danger because they carry severe, and often even fatal, invasive diseases. So, ticks reward us with encephalitis, relapsing fever, borreliosis, scabies, fleas bring us plague, typhus, bugs - Chagas disease, mosquitoes - malaria, anthrax, yellow fever. There are other dangerous insect parasites - midges, tsetse flies, horseflies, wood lice. In addition, there is a huge detachment of insects, which by their nature are not parasites, but also carry dangerous diseases. These are flies, cockroaches, various bugs.
Medical helminthology
Among human parasites, there are not only microscopic ones, but also quite large ones, perfectly visible to the naked eye, and sometimes even huge individuals. These are worms and worms, but scientifically helminths. Every second, every second inhabitant of our planet is infected with them, and in Russia, according to research, 99% of residents suffer from helminthiasis. Therefore, it is difficult to overestimate the importance of the work that medical parasitology does, saving our citizens from this infection. Helminths can be picked up not only by those who do not observe hand hygiene or eat unwashed fruit and vegetables, but also those who eat unfinished dishes from meat of domestic animals, poultry, fish and drink untreated water.
You can get infected even by accident, for example, by swallowing with food an ant carrier of helminth larvae or cysts. There is a group of worms (they are called contact) that enter the victim’s body through intact skin. Medical parasitology, in particular helminthology, is engaged not only in differentiating worm species, but also in studying the cycles of their development, since for one group a person is the ultimate host, and for the other intermediate.
It is also important to study how and at what stage of its development a parasite can invade a person, which animal becomes an intermediate host, and how a person's vital activity is associated with this. This is especially true for flatworms. For example, for a bovine tapeworm that grows up to 10 meters long in a human body, this is cattle, for a pork tapeworm - pigs, for a wide ribbon - fish.
Nematodes
So called roundworms, of which 24 thousand species were found and described in nature. Fortunately, not all of them are parasitic in humans, but those that chose people for themselves during the evolution cause us quite unpleasant diseases - nematodes. Pinworms, most known to the general public, are pinworms, which are the most common helminths in children around the world and cause enterobiosis. Pinworms live only in a person (in the intestines), infection occurs through dirty hands, unwashed fruits and vegetables, underwear and household items that the patient uses.
A parasitologist can easily determine pinworm infestation by the only characteristic symptom - severe itching in the anus, since helminths lay eggs there. To cause itching, they secrete special acid. The patient begins to comb these places, and the eggs in this process fall on his hands, and then in his mouth, on clothes, toys - anywhere. In the external environment they live long, so the next victim, if she does not wash her hands, can easily settle pinworms in her body. Another well-known representative of nematodes are roundworms, causing ascariasis. They also live only in humans, but at various stages of their development they settle in the lungs or intestines. The source of infection in this case is also only a sick person, and the cause of infection lies in insufficient personal hygiene.
Diagnostics
As can be seen from the foregoing, there are hundreds of human parasites, and each has its own characteristics. To establish an accurate diagnosis, a parasitologist must collect an anamnesis:
- ascertains the conditions under which infection could occur (the patient’s life, his work or being on vacation, for example, in the forest or in countries where epidemics of parasitic diseases are frequent);
- the presence or absence of the patient's contacts with animals of various groups and so on);
- symptoms of the disease (whether itching, rash, signs of intoxication, weakness, anemia).
A decisive role in the diagnosis is performed by laboratory tests. They are direct and indirect. Direct are the detection of eggs, larvae or other living forms of parasites in human secretions (feces, sputum, urine). This work is performed by the parasitology laboratory, where the patient must pass only fresh materials for research. So, some types of helminths can be found in the feces no later than 20 minutes after defecation.
If it is difficult or impossible to collect fresh material (for example, if parasites are in the liver, in the brain), indirect tests are performed. They consist in detecting in the patient’s blood special antibodies produced by the body to protect against invasion.
Treatment
Parasitology medical preparations for the destruction of parasites in the human body offers the most diverse. A single remedy that saves from all forms and types of invasion does not exist. Therefore, only doctors should prescribe treatment, and only after an accurate diagnosis. To date, drugs have been developed that include mebendazole, diethylcarbamazine, levamisole, piperazine adipate and other substances. Each of them can destroy only a certain type of parasite. In some cases, for example, when infected with bovine tapeworm, treatment is carried out surgically.
Veterinary parasitology
This section is important not only for people who have pets, but for each of us, since even those who have absolutely no contact with animals anywhere can become infected by eating meat, fish, or they may become victims of insect bites. Veterinary parasitology solves a very wide range of tasks:
- examines domestic animals for any known parasites present in them;
- makes treatment;
- makes sure that contaminated meat, milk, other livestock products, as well as fish and seafood are not on the shelves, inspects live and fallen animals, and establishes quarantine zones in case of detection of an invasion.
Prevention
In order not to suffer from many types of parasites, excellent vaccines have been developed to date. They must be used necessarily when traveling on vacation or work to the countries of Latin America, Africa, and other regions where specific insects live (kiss bugs, tsetse flies and others), which can cause dangerous diseases. For vaccination, you must contact the Institute of Parasitology or the medical institution of your locality engaged in this activity. For residents of regions where outbreaks of diseases caused by parasitic insects are frequent (for example, tick-borne encephalitis is the Urals, Siberia, the Far East), and for those who have gathered in these regions for permanent or temporary residence, vaccination is also mandatory.
An important point in the prevention of invasive diseases is the use of only products tested by the Sanitary and Epidemiological Service. In addition, you should not use water from ponds without prior boiling.
But the main means available to all segments of the population to prevent invasion is hygiene, that is, washing hands, fruits, vegetables, as well as sufficient culinary processing of meat, fish, milk.