Computed tomography (CT) of the adrenal glands is a modern, informative, gentle research method that allows timely detection of adrenal pathologies, and resolves the issue of surgical intervention.
The role of the adrenal glands
These are paired organs located above the upper ends of the kidneys. There are adrenal cortex (90%) immediately below the capsule and medulla. These structures are considered as two separate glands of internal secretion, since they are separated from each other by a connective tissue capsule and secrete hormones different in function and structure.
Three layers are distinguished in the cortical substance: glomerular - produces aldosterone, bundle - produces glucocorticoids (cortisone, cortisol, corticosterone), and net - sex hormones (male and female). Adrenaline and norepinephrine are produced in the medulla.
Pathology of the adrenal gland
The most common adrenal gland pathologies are:
- Hyperaldosteronism is a pathological condition of the body caused by excessive production of the adrenal cortex hormone aldosterone. Aldosterone regulates water-salt metabolism: it enhances the reverse absorption of sodium from primary urine and excretes potassium in the urine. Excess aldosterone causes sodium retention in the body. Since sodium attracts water to itself, this leads to the appearance of edema, an increase in the amount of blood and an increase in pressure. There are reasons: primary - are associated with damage to the adrenal glands themselves, secondary - are associated with the work of the hypothalamic-pituitary system of the brain or other factors not localized in the adrenal glands.
- Insufficiency of the cortex. In 98% of cases it has an autoimmune origin. The course of the pathology and signs are mainly due to the lack of cortisol and aldosterone. Treatment is hormone replacement therapy.
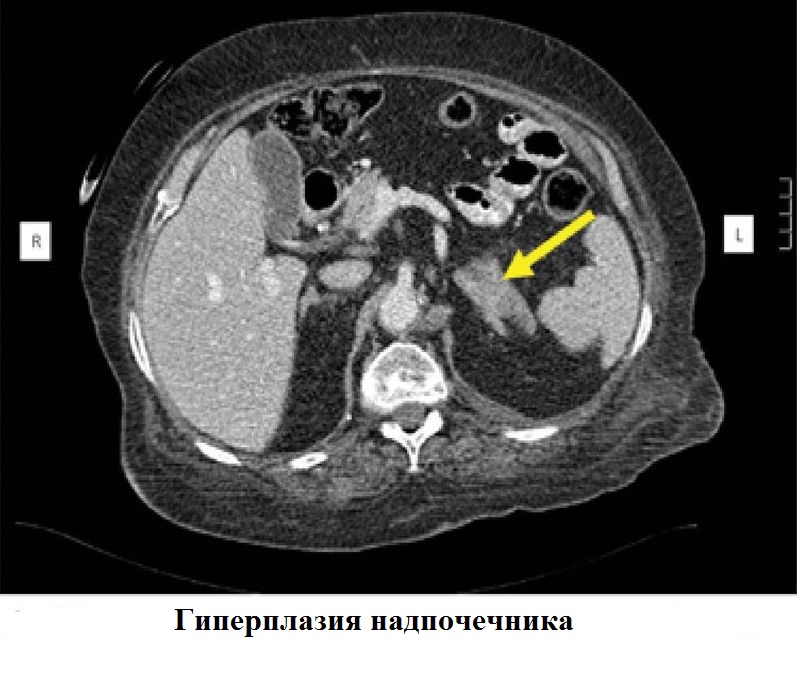
- Congenital adrenal cortical hyperplasia. It is characterized by insufficient production of corticosteroids and proliferation of the adrenal cortex. Treatment is hormone replacement therapy.
- Pheochromocytoma is a tumor secreting adrenaline and norepinephrine. In 10% of cases, malignant.
Indications for computed tomography of the adrenal glands
The doctor will send an adrenal CT scan in case of:
- benign or malignant adrenal gland tumors detected by ultrasound;
- the need for differential diagnosis of hyperplasia and adenoma;
- lowering or increasing blood pressure;
- coarsening of the voice in women, excessive hair growth on the body or face;
- breast enlargement in men;
- a sharp increase in body weight;
- muscle weakness, decreased muscle strength;
- lesions of the abdominal lymph nodes.
What is contrast?
CT of the kidneys and adrenal glands is always performed using a contrast medium. It is necessary to enhance the image. CT adrenal glands without contrast will not differentiate individual parts of the adrenal glands from surrounding tissues, for example, from the vessels of the spleen.
As contrast agents, iodine preparations are used, which are administered intravenously or, when examining the intestines, inside. Non-ionic low-osmolar preparations with an iodine content of 320-370 mg / ml are used for adrenal CT scan with contrast. The drug is administered at a rate of 3-5 ml / s. A patient weighing 70-80 kg will be administered 70-120 ml of the drug. 99% of the drug is excreted through the kidneys.
Contraindications
CT is a gentle procedure. Nevertheless, certain risks exist:
- X-rays increase the likelihood of developing cancerous tumors;
- contrast agents can cause allergies;
- contrast medium negatively affects the kidneys.
The listed possible consequences determine the list of contraindications for CT adrenal glands:
1. Absolute:
- pregnancy, because x-ray radiation negatively affects the development of the fetus;
- overweight - if your body weight exceeds 120 kg, find out if the CT device has weight restrictions;
- metal prostheses or implants that cannot be removed.
2. Relative:
- age up to 12 years - up to three years, the child will not be able to lie still on the table of the device, but even for older children, x-ray exposure is dangerous;
- hyperkinesis or convulsive syndrome, which will not allow the patient to be stationary;
- claustrophobia, mental disorders;
- lactation.
To minimize radiation load on pregnant women and children, they reduce the duration of the study, reduce the current on the x-ray tube, reduce the number of phases of tomography, increase the time of rotation of the tube. For children, in some cases, it is possible to use sedatives. The mammary glands of lactating women are closed with bismuth screens.
3. With contrast:
- severe allergies to contrast agents (shock, cramps, respiratory arrest) - tell your doctor if you even have a slight allergy to iodine or seafood (nausea, urticaria, Quincke's edema), in which case you will need to enter antiallergic drugs (prednisone) and use solutions of non-ionic contrast medium;
- severe bronchial asthma or allergic diseases;
- severe renal failure - contrast agents, administered intravenously, are excreted through the kidneys and may interfere with their work;
- diabetes mellitus - tell your doctor if you are taking metformin, toxic to the kidneys, in which case you will need to stop taking it some time before the procedure;
- hyperthyroidism
- severe general condition.
Adrenal CT Preparation
If CT is only planned for the adrenal glands (not the intestines), then bowel cleansing or dieting is not required. If you plan to conduct adrenal CT scan with contrast, you must refrain from eating for 6 hours. This will reduce the likelihood of vomiting and nausea in response to the administration of a contrast agent.
Preparation for the procedure
An adrenal CT scan lasts no more than 10 minutes. Most of this time is spent on preparing the patient.
Preparation for the procedure includes:
- Dressing in a medical shirt. Dense elements of ordinary clothes, locks, buttons will leave shadows in the pictures and make diagnosis difficult.
- The introduction of contrast medium intravenously in the case of adrenal CT scan with contrast.
The patient may experience:
- a surge of heat throughout the body;
- metallic taste;
- nausea
- slight burning sensation.
These sensations will pass in a few seconds. Adverse reactions to intravenous administration of contrast are extremely rare: Quincke's edema, shortness of breath, bradycardia. To eliminate them, atropine, oxygen, beta-agonists, adrenaline will be administered. Severe reactions - shock, respiratory arrest, cramps, collapse - require resuscitation. All severe reactions develop within 15-45 minutes after administration of contrast. Therefore, you need to be under the supervision of a doctor this time.
Tell your doctor right away if you have:
- dizziness;
- swelling of the face;
- itchy skin, rash;
- sore throat;
- bronchospasm;
- unusual excitement
The location of the patient on the table of the tomograph - you will need to lie on your back with raised hands. Any movement will lead to fuzzy images, and pathology will be difficult to diagnose, so if necessary use pillows or straps to fix.
Procedure
The adrenal CT scan itself will go like this:
- Personnel will leave the room before turning on the device. At any time, the doctor can call or use the panic button.
- During the procedure, a slight noise or crackling of the device will be heard, pain and discomfort should not be.
- When the patient is inside the device, a scanning beam begins to rotate around him. Layered images — slices 0.5–0.6 mm thick — will be visible on a computer monitor. When superimposed on each other, a three-dimensional model of the adrenal gland region is obtained. The patient will be asked to hold his breath several times.
- First, take some general shots.
- Then contrast is introduced through the catheter, images are taken in the arterial and venous phase, delayed images.
- After the procedure, a catheter is removed from the vein, the patient changes into his clothes.
A radiologist will need 30-60 minutes to analyze the images and draw up a conclusion with a seal and signature.
Identified diseases
Detect using CT:
- adrenal adenoma - a benign neoplasm;
- malignant neoplasms;
- lipomas, hematomas, cysts;
- adrenal tuberculosis;
- involvement of adjacent tissues in the pathological process (e.g., lymph nodes).
Can be differentiated by CT adrenal education:
1. Crust:
- hyperplasia - excessive proliferation;
- adenoma - a benign tumor;
- cortical carcinoma - cancer of the epithelium of the adrenal cortex;
- mesenchymal tumors (fibromas, angiomas) - benign or malignant tumors from the connective, vascular, adipose, muscle, and other soft tissues;
- neuroectodermal tumors - benign or malignant tumors that develop from the beginnings of nervous tissue;
- hematomas - hemorrhages;
- cysts are pathological cavities in the organ.
2. Cerebral substance:
- chromaffin tissue tumors;
- tumors of nonchromaffin tissue.
3. Mixed formations:
- corticomedular adenoma;
- corticomedicular carcinoma.
How are adrenal gland pathologies detected?
Pathology of the adrenal gland is detected in two cases.
1. The appearance of clinical signs of excessive synthesis of hormones.
Excess of each hormone manifests itself in its own way. For example, in the case of hyperaldosteronism (excess of aldosterone), the patient complains of high blood pressure, periodic cramps, muscle weakness. Then the doctor directs the patient to take blood and urine tests and make an ultrasound of the adrenal glands. The reason for the high content of aldosterone can be: cirrhosis of the liver with ascites, chronic nephritis, heart failure, a diet poor in sodium, excess potassium in food, toxicosis of pregnant women. All these conditions enhance the activity of renin, which stimulates the production of aldosterone. The diagnosis will be made, treatment prescribed. CT scan is not necessary.
If the cause remains undetected, or any adrenal gland lesions are detected by ultrasound, the patient can be referred for CT of the kidneys and adrenal glands with contrast. The contrast agent stains cells of benign and malignant formations in different ways, which makes it possible to distinguish them from each other. CT will give an answer, a benign tumor or a malignant one. For example, a common cause of excess aldosterone is an adenoma of the glomerular zone of the adrenal cortex - a benign tumor.
2. Accidental detection of an adrenal tumor during an ultrasound or CT scan without contrast enhancement of the abdominal organs. The patient will be referred for adrenal CT scan with intravenous contrast enhancement. CT will give the answer: benign tumor or malignant. If the tumor was detected by chance, as a rule, it is hormonally inactive.
Treatment of adenoma and other benign formations
Small benign tumors that do not secrete hormones do not treat. They are observed, conducting repeated CT procedures once a year without contrast, analyze the level of cortisol and some other indicators in the blood. For example, 20-40% of the detected tumors, accompanied by an increased level of aldosterone, are not removed. Large benign tumors (more than 4 cm) or hormone producing tumors are surgically removed.
The operation to remove a benign adrenal tumor can be performed in three ways: open, laparoscopic and retroperitoneoscopic (lumbar). Most often carried out in an open way, although it is the most traumatic of all.
Cancer treatment
The most successful treatment for a cancer of the adrenal gland is complete surgical removal. It is advisable to remove the nearest to the tumor and enlarged lymph nodes, which will increase the patient's lifespan. With a tumor growing in the kidney, the kidney is also removed. More often, the adrenal gland is removed in an open way. Laparoscopy is not recommended for tumors greater than 5 cm or the presence of metastases in the lymph nodes.