Tubular human bones are bone formations of elongated cylindrical shape, less often trihedral. A strictly defined configuration does not exist. As a rule, the length of such a bone repeatedly prevails over the width. However, the proportions may be very different. The formation and growth of the tubular bone are accompanied by several factors, the main of which is the presence of calcium as a chemical element involved in the construction of bone tissue.
The process of formation of cellular structures is quite long. A lack of calcium often leads to bent bones. Excess of this important element can also negatively affect the formation of the skeleton in childhood. In order to prevent bone deformation in a growing body in time, it is necessary to maintain a balance of the chemical elements involved in the process.
Long and short tubular bones
The human skeleton is a logical construction endowed with a number of functional programs. Each part of the body performs its task, and the vital activity of the whole organism depends on the overall coherence of the individual areas. The human tubular bones are the most important part of the skeleton, and they have the musculoskeletal function. In this case, the activity of the body is possible only under the condition of interaction of all participants in the process. Some functions of bone complexes are programmed to move in a constant mode, such as walking or running. The cyclic repetition of the same actions takes on an automatic character, impulses no longer arise in the brain or even in the central nervous system, but in the muscle tissue involved in the process.
Tubular bones are connected to each other through tendons and muscles. The moving parts of the skeleton interact according to the principle of the articulated mechanism. Such devices in the human body are joints, each of which is covered with a special hyaline cartilage that prevents friction. At the point of mutual contact, the surfaces glide along a certain amplitude, their movement is rational and occurs in a strictly limited mode. The body of the tubular bone is vulnerable, any deviations from the given motion vector cause tension and pain. In the case of an extreme violation of the normal motor mode, the joint may lose its natural engagement, and thus a dislocation will occur.
The long tubular bones of the human skeleton are among the main supporting formations, quite strong and reliable. Nevertheless, they should be protected, not overloaded and often give rest. Long tubular bones are divided into separate types:
- tibia;
- tibia;
- femoral
- radiation;
- humeral;
- ulnar.
Short tubular bones:
- metatarsal;
- metacarpals;
- phalanges of the fingers.
Most often, short tubular bones are a continuation of long ones.
What tubular bones are levers, one way or another involved in the movement of the body? These are tibia and femur. Short tubular bones provide lever movement functions in a more limited range.
Structure
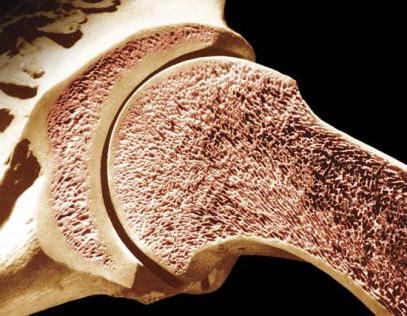
The tubular bones consist of the central part, the diaphysis, which is an elongated cavity ending at both ends with epiphyses. The yellow brain is located in the diaphysis, and the pineal glands have a firm, spongy consistency and are covered with cartilaginous layers.
The pineal gland is the widened end of the tubular bone, rounded, having a certain shape, designed to articulate with an adjacent joint. The combination of two or three parts forms a complete joint, functioning in a specific motor program of the body. The contacting fragments of the joints are in the form of an oncoming type, when the surface of one half is convex in shape and the other half is concave.
Periosteum
Outside, the tubular bones are covered with the periosteum, connective tissue layer. This is a living organic formation, the purpose of which is to protect functions.
Organics
The tubular substance of the bone is composed of organic and inorganic substances. The proportions of their content fluctuate throughout a person's life. Children's age is a period of dominance of organic substances in the body that give bones flexibility. With age, the composition of substances gradually changes; inorganic substances, which provide strength, take their rightful place. These are mainly calcium salts.
Physiological device
- The compact substance consists of many bone plates covering the bone with a continuous dense layer. Hard scales are combined into structural units, the so-called osteons. The formed fragments are cylindrical formations of an organic property, inside of which nerves and small blood vessels pass.
- The spongy substance is located under compact layers, differs from them in its porous structure. In the process of formation of a spongy substance, trabeculae are involved - a kind of bone septum. A lot depends on their strength.
- Bone marrow is the main blood-forming organ in the human body, which is located inside the tubular bones. It is divided into two types: yellow and red. The first is formed by fat cells and is located in the diaphysis - the main part of the tubular bone. Red bone marrow is located in the porous part of the pineal gland and is a reticular tissue densely penetrated by small blood vessels. Through these ducts, newly formed cells fall into the main channel. New blood cells are generated by stem cells living in the bone marrow. The process does not stop for a second. There are osteoclasts and osteoblasts, which renew bone structures, destroying obsolete.
Height
Tubular bones grow during the development of special epiphyseal plates. The cartilaginous layer between the pineal gland and the diaphysis can grow intensively in childhood and grow slowly during adolescence and then adulthood. The process is regulated hormonally and does not stop until its physiological completion.
The most active bone growth occurs during physiological traction. The first period lasts from 5 to 7, the second - from 11 to 15 years. Further, the growth of bone formations continues, but in slow motion. Finally, the skeleton formation phase ends by 20 years.
Fractures
A pathological violation of the integrity of individual structures of the skeleton as a result of excessive load can be qualified as fractures of the tubular bones.
The main causes of fractures:
- mechanical injuries;
- various diseases that cause a decrease in bone strength (osteomyelitis, osteoporosis).
Types of fractures:
- metaphysical;
- epiphyseal;
- diaphyseal.
Signs of a fracture:
- pain sharply increasing during exercise;
- swelling that occurs after some time at the site of damage;
- extensive hematoma, appearing 90 minutes after the injury;
- failure function of a damaged limb.
Signs of an absolute nature:
- unnatural limb position;
- chaotic mobility of individual parts;
- characteristic crunch (crepitus) at the site of damage;
- bone fractures in the wound detected by open fractures.
Recovery
Bone tissue regeneration and healing occurs due to the formation of new cells at the site of damage. The restoration of the tubular bone can take from several weeks to several months. The healing process requires absolute rest.
The cambial layer of the periosteum and the stem cells of the yellow brain participate in the regeneration.
The healing process is divided into four stages:
- Autolysis is the active concentration of leukocytes at the fracture site and the dissolution of dead tissue fragments.
- Proliferation - the reproduction of bone cells as a response to damage with the simultaneous production of cartilage, which is then mineralized.
- Restoring blood supply, impaired as a result of trauma, the formation of a compact substance.
- Complete restoration of the bone marrow canal, the return of functional abilities.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of fractures should be carried out in stationary conditions. To identify the complete picture of the damage, an X-ray examination is necessary to determine the absolute and relative signs of the fracture.
After the diagnosis, a course of treatment is carried out, which consists of manipulations on the application of a fixing gypsum tire. If necessary, traction drawing methods are used. This is followed by long-term monitoring of the patient's condition and drug treatment.