It is impossible to say unequivocally what the climate of the Atlantic Ocean is, since this reservoir is located in almost all zones of our planet. It stretches from North to South, touching the shores of the polar islands and continents. Its width is equal to the difference between Europe and North America, between Africa and South America. Of course, this situation will cause various weather conditions in certain areas of this geographical object. Therefore, we now consider the climate of the Atlantic Ocean briefly, characterizing its main zones and their features.
Belts in which the pond lies
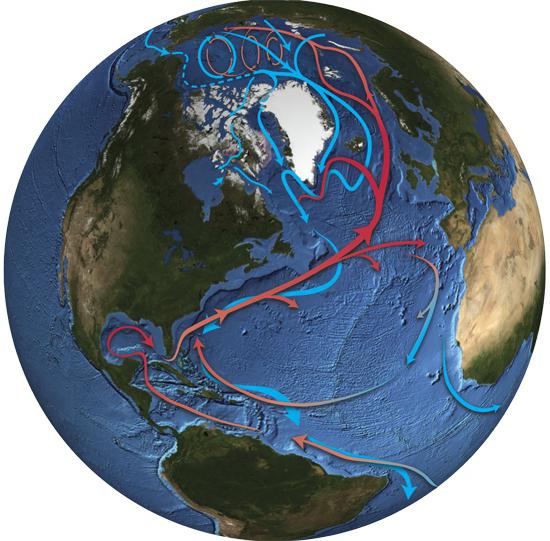
To begin with, we note that in terms of size, the waters of the Atlantic are considered the second in the world. The ocean itself plays a crucial role in shaping the climate on the continents that are adjacent to it. For example, its northern part is warmer than the southern part due to the Gulf Stream. Therefore, in Western Europe and North Africa, the climate is mild, without sudden changes in temperature. But the land adjacent to it in the south is characterized by more windy weather and a sharper change in temperature. Thus, the climate of the Atlantic Ocean forms the weather on the lands that it washes, which greatly affects the seismic state of the entire planet. The waters of the Atlantic themselves are located immediately in all climatic zones. We will count from the equator in both directions, since their location is identical. This is the equatorial belt, subequatorial, tropical, subtropical and temperate. Further, in the North, the waters pass into the Arctic zone, and in the south into the Antarctic.
Air temperature and water surface
Here it must be emphasized that it depends on which hemisphere we are talking about - the North or the South, how warm or cold this or that climate zone will be. Equatorial latitude is characterized by, you guessed it, the highest temperature indicators. Here, during the year, the thermometer does not fall below +25 (on average, it is 30-32). About the same way surface water heats up . In the northern tropics dry trade winds blow, which carry sand from the Sahara. Because in the summer it is very dry and hot here - more than 23 degrees; in winter, the temperature drops to 21. The southern tropics are cooler and wetter, since the water area is expanding here. Temperate latitudes are a zone of sharp annual temperature drops (in both hemispheres). In summer it is hot here as in the tropics, and in winter the thermometer drops to +5 and below. The Arctic zone is characterized by temperature differences of 20 degrees. In winter, the ocean freezes here, in summer the temperature rises to 3-5 above zero. The coldest region is the Antarctic zone. Here the climate of the Atlantic Ocean becomes polar, because the annual difference is more than 30 degrees.

Humidity and latitudinal zoning
Each strip of the Atlantic has its own special pressure. Thanks to it, zones of maxima and minima are distinguished, which form clouds and nebula above the waters. These indicators affect what climate in the Atlantic Ocean will form over one or another part of it. The equator is a zone of reduced pressure, that is, a minimum. There is a maximum of precipitation - from 3000 mm per year, most of which falls in the summer. In winter, fogs often form. Northern tropics and temperate latitudes form a zone of the Azores maximum. Precipitation here is very small - an average of 750 mm, but often trade winds and stronger winds that form tornadoes and storms. Below the equator is the area of the South Atlantic maximum. Here the pressure is also high, but rains happen much more often (up to 1000 mm), due to the smaller number of winds. Antarctica and the Arctic are two minimum zones. The average rainfall is 2000 mm, the regions are stable against winds.
Features of the climate of the Atlantic Ocean
In addition to the fact that the northern part, due to the Gulf Stream, is much warmer than the southern one, differences in temperature are also observed in some areas between the West and the East. Between 30 degrees north latitude and 30 degrees south latitude, ocean water is much warmer off the coast of America than near Africa. This is caused by the same trade winds that occur in the tropical and subtropical bands. They blow from the shores of Africa, bringing with them not only the sand of the Sahara, but also the sharp daily temperature fluctuations that can be traced in the desert. Because of this, the water cools, and waves often rise in it. Also, such winds do not allow clouds to gather to balance the humidity in the air. The closer to the West, the more calm the trade winds become. Storms sometimes occur here, but in general the water is warmer and the air temperature is much higher than in the East.
Summarizing
The climate of the Atlantic Ocean is a mix, which includes both icy expanses that freeze for six months and hot equatorial territories, where it is always very warm and humid.