As you know, almost all organisms on our planet have a cellular structure. Basically, all cells have a similar structure. This is the smallest structural and functional unit of a living organism. Cells can have different functions, and, consequently, variations in their structure. In many cases, they can act as independent organisms.
The cell structure is plants, animals, fungi, bacteria. However, there are some differences between their structurally functional units. And in this article we will consider the cellular structure. Grade 8 provides for the study of this topic. Therefore, the article will be interesting to students, as well as those who are simply interested in biology. This review will describe the
cellular structure, cells of various organisms, the similarities and differences between them.
History of the theory of cell structure
People did not always know what organisms consist of. The fact that all tissues are formed from cells has become known relatively recently. The science that studies this is biology. The cellular structure of the body was first described by scientists Matthias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann. It happened in 1838. Then the theory of cell structure consisted of the following provisions:
animals and plants of all kinds are formed from cells;
they grow through the formation of new cells;
the cell is the smallest unit of life;
an organism is a collection of cells.
Modern theory includes slightly different provisions, and there are a little more:
a cell can only come from a mother cell;
a multicellular organism does not consist of a simple collection of cells, but of organs integrated into tissues, organs and systems;
cells of all organisms have a similar structure;
a cell is a complex system consisting of smaller functional units;
a cell is the smallest structural unit capable of acting as an independent organism.
Cell structure
Since almost all living organisms have a cellular structure, it is worth considering the general characteristic of the structure of this element. Firstly, all cells are divided into prokaryotic and eukaryotic. In the latter there is a core that protects the hereditary information recorded on DNA. In prokaryotic cells, it is absent, and DNA floats freely. All eukaryotic cells are constructed according to the following scheme. They have a shell - a plasma membrane, additional protective formations are usually located around it. All that is beneath it, except the nucleus, is the cytoplasm. It consists of hyaloplasm, organelles and inclusions. Hyaloplasm is the main transparent substance that serves as the internal environment of the cell and fills its entire space. Organoids are permanent structures that perform certain functions, that is, they ensure the vital activity of a cell. Inclusions are inconsistent formations that also play a role, but do so temporarily.
The cell structure of living organisms
Now we will list the organelles that are the same for the cells of any living creature on the planet, except for bacteria. These are mitochondria, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, cytoskeleton. For bacteria, only one of these organoids is characteristic - ribosomes. Now consider the structure and functions of each organelle individually.
Mitochondria
They provide intracellular respiration. Mitochondria play the role of a kind of "power station", generating energy that is necessary for the life of the cell, for the passage of certain chemical reactions in it.
They belong to two-membrane organoids, that is, they have two protective shells - external and internal. Under them is a matrix - an analogue of hyaloplasm in the cell. Cristae form between the outer and inner membranes. These are the folds inside which the enzymes are located. These substances are needed in order to be able to carry out chemical reactions, due to which the energy necessary for the cell is released.
Ribosomes
They are responsible for protein metabolism, namely, for the synthesis of substances of this class. Ribosomes consist of two parts - subunits, large and small. The membrane of this organoid is absent. The subunits of the ribosomes are combined only immediately before the process of protein synthesis, the rest of the time they are separately. Substances here are produced based on information recorded on DNA. This information is delivered to the ribosomes using tRNA, since transporting DNA here every time would be very impractical and dangerous - the probability of its damage would be too high.
Golgi apparatus
This organoid consists of stacks of flat tanks. The functions of this organoid are that it accumulates and modifies various substances, and also participates in the formation of lysosomes.
Endoplasmic reticulum
It is divided into smooth and rough. The first is built of flat tubes. He is responsible for the production of steroids and lipids in the cell. Rough is called so because on the walls of the membranes of which it consists, there are numerous ribosomes. It performs a transport function. Namely, it transfers proteins from ribosomes synthesized there to the Golgi apparatus.
Lysosomes
They are single-membrane organoids, which contain enzymes necessary for the implementation of chemical reactions that occur during intracellular metabolism. The largest number of lysosomes is observed in leukocytes - cells that perform an immune function. This is explained by the fact that they carry out phagocytosis and are forced to digest a foreign protein, which requires a large amount of enzymes.
Cytoskeleton
This is the last organoid that is common to fungi, animals, and plants. One of its main functions is to maintain the shape of the cell. It is formed from microtubules and microfilaments. The first are hollow tubes of tubulin protein. Due to their presence in the cytoplasm, some organoids can move around the cell. In addition, cilia and flagella in unicellular organisms may also consist of microtubules. The second component of the cytoskeleton - microfilaments - consists of contractile proteins of actin and myosin. In bacteria, this organoid is usually absent. But some of them are characterized by the presence of the cytoskeleton, but more primitive, arranged not as difficult as in mushrooms, plants and animals.
Plant Cell Organoids
The cellular structure of plants has some features. In addition to the above organelles, vacuoles and plastids are also present. The former are intended for the accumulation of substances in it, including unnecessary ones, since it is often impossible to remove them from the cell due to the presence of a dense wall around the membrane. The fluid that is inside the vacuole is called cell juice. In a young plant cell, there are initially several small vacuoles, which merge into one large cell as it ages. Plastids are divided into three types: chromoplasts, leukoplasts and chromoplasts. The former are characterized by the presence in them of red, yellow or orange pigment. In most cases, chromoplasts are needed to attract pollinating insects or animals that are involved in the distribution of fruits along with seeds. It is thanks to these organoids that the flowers and fruits have a diverse color. Chromoplasts can form from chloroplasts, which can be observed in autumn, when the leaves acquire yellow-red hues, as well as during ripening, when the green color gradually disappears completely. The next type of plastid - leukoplasts - are designed to store substances such as starch, some fats and proteins. Chloroplasts carry out the process of photosynthesis, due to which plants receive for themselves the necessary organic substances.
From six molecules of carbon dioxide and as much water, a cell can receive one glucose molecule and six oxygen, which is released into the atmosphere. Chloroplasts are double-membrane organoids. Their matrix contains thylakoids grouped into grains. These structures contain chlorophyll, and the photosynthesis reaction takes place here. In addition, the chloroplast matrix also has its own ribosomes, RNA, DNA, special enzymes, starch grains and lipid drops. The matrix of these organoids is also called the stroma.
Mushroom Features
These organisms also have a cellular structure. In antiquity, they were united in one kingdom with plants purely by their external characteristics, but with the advent of more developed science, it turned out that this could not be done.
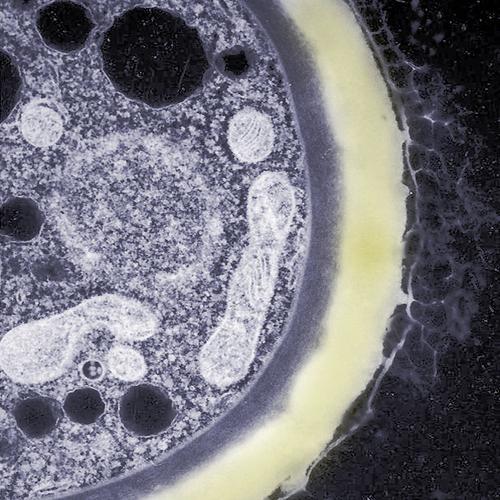
Firstly, mushrooms, unlike plants, are not autotrophs, they are not able to produce organic matter themselves, but only eat ready-made ones. Secondly, the cell of the fungus is more similar to the animal, although it has some features of the plant. The fungal cell, like the plants, is surrounded by a dense wall; however, it does not consist of cellulose, but of chitin. This substance is difficult to absorb by the body of animals, so mushrooms are considered heavy food. In addition to the organelles described above, which are characteristic of all eukaryotes, there is also a vacuole here - here is another similarity of mushrooms with plants. But plastid in the structure of the fungal cell is not observed. Between the wall and the cytoplasmic membrane there is a lomasoma, the functions of which are still not fully understood. The rest of the structure of the mushroom cell resembles an animal. In addition to organelles, inclusions such as fat droplets and glycogen also float in the cytoplasm.
Animal cells
They are characterized by all the organelles that were described at the beginning of the article. In addition, glycocalyx is located on top of the plasma membrane - a membrane composed of lipids, polysaccharides and glycoproteins. He is involved in the transport of substances between cells.
Nucleus
Of course, in addition to general organelles, animals, plant, fungal cells have a nucleus. It is protected by two shells in which there are pores. The matrix consists of karyoplasm (nuclear juice), in which chromosomes with hereditary information recorded on them float. There are also nucleoli that are responsible for the formation of ribosomes and RNA synthesis.
Prokaryotes
These include bacteria. The cellular structure of bacteria is more primitive. They have no core. The cytoplasm contains organelles such as ribosomes. Around the plasma membrane is a cell wall of murein. Most prokaryotes are equipped with motion organoids - mainly flagella. Around the cell wall can also be located an additional protective membrane - the mucous capsule. In addition to the basic DNA molecules, in the cytoplasm of bacteria are plasmids on which information is recorded that is responsible for increasing the body's resistance to adverse conditions.
Are all organisms built from cells?
Some believe that all living organisms have a cellular structure. But this is not true. There is such a kingdom of living organisms as viruses.
They are not made up of cells. This organism is represented by a capsid - a protein shell. Inside it is DNA or RNA, on which a small amount of genetic information is recorded. Around the protein coat can also be located lipoprotein, which is called supercapsid. Viruses can multiply only inside foreign cells. In addition, they are capable of crystallization. As you can see, the assertion that all living organisms have a cellular structure is incorrect.
comparison table
After we examined the structure of various organisms, to summarize. So, the cell structure, the table:
| Animals | Plants | Mushrooms | Bacteria |
| Nucleus | there is | there is | there is | No |
| Cell wall | No | Yes, from pulp | Yes, from chitin | Yes, from murein |
| Ribosomes | there is | there is | there is | there is |
| Lysosomes | there is | there is | there is | No |
| Mitochondria | there is | there is | there is | No |
| Golgi apparatus | there is | there is | there is | No |
| Cytoskeleton | there is | there is | there is | there is |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | there is | there is | there is | No |
| Cytoplasmic membrane | there is | there is | there is | there is |
| Additional shells | Glycocalyx | No | No | Mucous capsule |
That’s probably all. We examined the cellular structure of all organisms that exist on the planet.