The waters of the Atlantic stretch from the northernmost latitudes, pass through the equator and reach the coast of Antarctica. In each of these zones, its own course is formed, which largely affects the weather conditions and the temperature of the water. The climatic zones of the Atlantic Ocean are the Arctic, and the equatorial, and the tropics ... Of course, you cannot compare them with the terrestrial types of climate of the same name - the difference is too great. Therefore, in order to correctly identify them, we need a brief description of the Atlantic Ocean, its position and features.
Short description
So, the Atlantic Ocean is the second largest water reservoir on the planet. Its area is more than 91 million square kilometers, and the volume is 330 million cubic kilometers. The greatest depth of the ocean is 8742 meters, it is located in the area of the Puerto Rico trench. Salinity is 36 percent, making it the most saline body of water in the world. Another characteristic of the Atlantic Ocean is its rugged coastline. On the shores of all continents, which are washed by the waters of the Atlantic, there are seas, bays and straits that are part of it. In general, they make up about 16% of the total water volume.
Geographical position
The climatic zones of the Atlantic Ocean are determined by its geographical position. The reservoir stretches from the very north of the planet, that is, from the islands of Greenland and Iceland, to the very south - to Antarctica. In the west, it borders the shores of North and South America, and in the east - with Europe and Africa. In the Atlantic there are many islands of predominantly volcanic origin. Many of them are part of the seas that belong to the ocean. Among these can be called the Balearic, Malta (Mediterranean Sea), Antilles Large and Small (Caribbean Sea). On the expanses of the ocean itself are the Canary Islands, Cape Verde (Cape Verde Islands), Sandwich, Faroe Islands and many others. All of them are of volcanic origin, and the temperature in coastal waters depends on which climatic zones of the Atlantic Ocean surround them.
North hemisphere
The main features of the Atlantic Ocean are that the climatic zones that are located in its water area are identical both in the north and in the south, but the air temperature in both zones and humidity are very different from each other. As for the Northern Hemisphere, the climate here is relatively warm. The upper zones are Arctic glaciers, where the annual temperature fluctuations are about 25 degrees. In winter, the thermometer drops to 25-30 degrees below zero, in summer it rises to + 5-10. August is considered the hottest month in the north-west of the Atlantic, February is the coldest. A zone of low pressure is formed over the northern region - the Icelandic minimum. The amount of precipitation here is approximately 250 mm. In the temperate latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere, temperature fluctuations are already 10 degrees. The amount of precipitation is increasing up to 1000 mm per year. The tropics are called the Azores maximum due to high pressure. Precipitation here occurs mainly in winter, and in the summer, eastern trade winds blow dry air. In general, the temperature in the Northern Hemisphere of the Atlantic is much higher than in the Southern Hemisphere.
Southern Hemisphere
The polar climatic zones of the Atlantic Ocean are arctic in the north and Antarctic in the south, and we are now considering the latter. Here the maximum annual temperature fluctuations are observed - up to 30 degrees. In winter there are terrible frosts - up to -40 Celsius or more, and in summer the air barely warms up to +1. August is considered to be the coldest month, and February is the hottest. In the temperate zone, temperature fluctuations are 15 degrees. In summer it is quite warm here - up to +20, and in winter the thermometer column drops to -10. The average rainfall reaches 1,500 mm per year. A big difference can be seen between the northern and southern tropics. If the climate is mostly arid above the equator, then in the south, due to the fact that the ocean is expanding, a large cloudiness is forming. The amount of precipitation here is 1500-2000 mm per year. Temperature fluctuations are more significant than one degree. In some areas, they are 3-4 degrees.
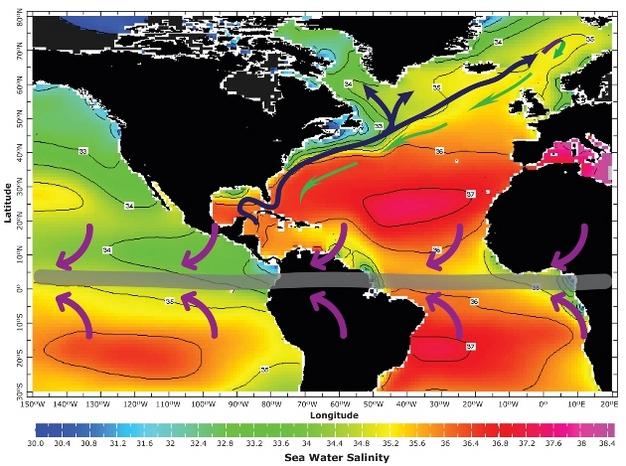
Equatorial zone
Atlantic waters cross the equatorial zone - such is their geography. The Atlantic Ocean in this area heats up to the maximum, and, most importantly, it is the zone of the most abundant precipitation and fog. Throughout the year, the temperature of the air and water surface does not change here. Precipitation occurs mainly in winter, but in general it rains evenly in every season. Their number is 3000 mm per year. Above the equator, fogs form in the Atlantic waters mainly in summer. Most of them go to the southern hemisphere, to the elevation of La Plata in Argentina. Those that form closer to the northeast are called sand fogs. They are formed due to strong winds that blow from the Sahara.